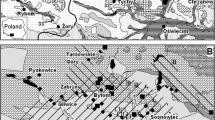
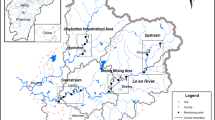
Abstract
The total concentrations of Cd in bulk sediments and those of the BCR sequential extraction fractions of sediments from inlets of the Four Rivers that feed Dongting Lake were determined using ICP-MS techniques. The results suggested that Cd was heterogeneously distributed in the inlet sediments of the rivers, with the highest degree of enrichment in sediments from the Xiangjiang River. The Cd anomaly was defined as Cd enrichment in sediments with an EF (enrichment factor) > 10.0, and it was identified in the inlet sediments of the Xiangjiang River. Cd in the sediments was dominated by acid-soluble Cd at a proportion of 23.9–69.8 (%) compared to its total concentrations in the sediments. The inlet sediments of the Four Rivers were contaminated with Cd, with the highest degree of contamination in the inlet sediments of the Xiangjiang River. The Cd contamination as well as the Cd anomaly in the sediments were closely related to the industrial activities (e.g. smelting and refining for ore minerals) in the areas, and Cd contamination at high levels may represent an ecological risk for the lake watershed. Cd contamination of the inlet sediments may also impact the lake basin sediments and is harmful to the lake ecological system, particularly for sediments of the Xiangjiang River. Therefore, it is essential to control and treat Cd contamination in the inlet sediments for ecological environmental protection of lake watersheds.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Bábek O, Grygar TM, Faměra M, Hron K, Nováková T, Sedláček J (2015) Geochemical background in polluted river sediments: how to separate the effects of sediment provenance and grain size with statistical rigour? CATENA 135:240–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.07.003
Bi B, Liu XH, Guo XC, Lu SY (2018) Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34076–34090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3329-8
Botsou F, Karageorgis AP, Dassenakis E, Scoullos M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and mineral magnetic characterization of the Asopos River sediments (Central Greece). Mar Pollut Bull 62:547–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.11.029
Cappuyns V, Swennen R, Verhulst J (2004) Assessment of acid neutralizing capacity and potential mobilisation of trace metals from land-disposed dredged sediments. Sci Total Environ 333:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.05.007
Chai LY, Li H, Yang ZH, Min XB, Liao Q, Liu Y, Men SH, Yan YN, Xu JX (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7872-x
Chen X, McGowan S, Xu L, Zeng LH, Yang XD (2016) Effects of hydrological regulation and anthropogenic pollutants on Dongting Lake in the Yangtze floodplain. Ecohydrology 9:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1637
Cheng HX, Yang ZF, Xi XH (2005) A research framework for source tracking and quantitative assessment of the Cd anomalies along the Yangtze River Basin. Earth Sci Front 12:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00184.x (in Chinese)
Degryse F, Smolders E, Merckx R (2006) Labile Cd complexes increase Cd availability to plants. Environ Sci Technol 40:830–836. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050894t
Din ZB (1992) Use of aluminium to normalize heavy-metal data from estuarine and coastal sediments of Straits of Melaka. Mar Pollut Bull 24:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(92)90472-I
Du Y, Cai SM, Zhang XY, Zhao Y (2001) Interpretation of the environmental change of Dongting Lake, middle reach of Yangtze River, China, by 210Pb measurement and satellite image analysis. Geomorphology 41:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00114-3
Fang XH, Peng B, Zhang K, Zeng DZ, Kuang XL, Wu BJ, Tan CY, Wang X (2016) Heavy metal contamination of bed sediments in inlet area of the lowermost Yuanjiang River, Hunan Province of China. Geogr Res 35:1887–1898. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj201610008 (in Chinese)
Fang XH, Peng B, Zhang K, Yang ZX, Xiao Y, Xie WC, Yan CY, Xie YT, Tan CY, Wan DJ, Wang X (2018) Geochemical study on evolution of heavy-metal contamination developed in bed sediments from the Yuanjiang River inlet to Dongting Lake, China. Acta Sci Circumst 38:2586–2598. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0075 (in Chinese)
Fang XH, Peng B, Wang X, Song ZL, Zhou DX, Wang Q, Qin ZL, Tan CY (2019) Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 689:557–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.330
Fang XH, Peng B, Song Z, Wu SC, Chen DT, Zhao YF, Liu J, Dai YN, Tu XL (2021) Geochemistry of heavy metal-contaminated sediments from the Four River inlets of Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(22):27593–27613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12635-0
Fuge WR, Pearce FM, Pearce NJG, Perkins WT (1993) Geochemistry of Cd in the secondary environment near abandoned metalliferous mines, Wales. Appl Geochem 8:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(09)80006-1
Gao L, Wang ZW, Li SH, Chen JY (2018) Bioavailability and toxicity of trace metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn) in sediment cores from the Shima River, South China. Chemosphere 192:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.110
Grygar TM, Popelka J (2016) Revisiting geochemical methods of distinguishing natural concentrations and pollution by risk elements in fluvial sediments. J Geochem Explor 170:39–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.003
Guo J, Wang CM, Huang DZ, Li LQ, Lian H (2019) Pollution characterization and water quality assessment of Dongting Lake. Environ Chem 38:152–160. https://doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018013104 (in Chinese)
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hansen DJ, Berry WJ, Boothman WS, Pesch CE, Mahony JD, Di Toro DM, Robson DL, Ankley GT, Ma D, Yan Q (1996) Predicting the toxicity of metal-contaminated field sediments using interstitial concentration of metals and acid-volatile sulfide normalizations. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2080–2094. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620151204
He ZF, Li FL, Dominech S, Wen XH, Yang SY (2019) Heavy metals of surface sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary: distribution, speciation and environmental risks. J Geochem Explor 198:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.12.015
Hu NJ, Huang P, Zhang H, Wang XJ, Zhu AM, Liu JH, Shi XF (2017) Geochemical source, deposition, and environmental risk assessment of cadmium in surface and core sediments from the Bohai Sea, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:827–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7800-0
Huang Z, Liu C, Zhao X, Dong J, Zheng B (2018) Risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment at the drinking water source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ Sci Eur 32:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-00305-w
Jain CK (2004) Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Res 38:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.042
Kong M, Dong ZL, Chao JY, Zhang YM, Yin HB (2015) Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu. China Environ Sci 35:1223–1229 (in Chinese)
Li F, Huang JH, Zeng GM, Yuan XZ, Li XD, Liang J, Wang XY, Tang XJ, Bai B (2013) Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J Geochem Explor 132:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.05.007
Li FF, Li LQ, Fu Z, Yin YY, Liu Y (2017) Pollution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the inlets of Dongting Lake, China. Geochimica 46:580–589. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.06.008 (in Chinese)
Liu XH, Gao YT, Khan S, Duan G, Chen AK, Ling L, Zhao L, Liu ZH, Wu XC (2008) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on contaminated sites and their potential accumulation capacity in Heqing, Yunnan. J Environ Sci 20:1469–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62551-6
Liu JY, Liang J, Yuan XZ, Zeng G, Yuan Y, Wu HP, Huang XL, Liu JF, Hua SS, Li F, Li XD (2015) An integrated model for assessing heavy metal exposure risk to migratory birds in wetland ecosystem: a case study in Dongting Lake Wetland, China. Chemosphere 135:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.053
Liu JJ, Xu YZ, Cheng YX, Zhao YY, Pan YN, Fu GY, Dai YZ (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2711–2723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8044-8
Luo SW, Zhang SZ (1992) Occurrence and formation of ore minerals in Hunan Province. Press of Central-South University, Changsha, pp 186–274
Morillo J, Usero J, Gracia I (2002) Partitioning of metals in sediments from the Odiel River (Spain). Environ Int 28:263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00033-8
Müller G (1986) Schadstoffe in sedimenten-sedimente als schadstoffe. Mitt Österreichische Geologische Gesellschaft 79:107–126
Peng B, Frei R (2004) Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic constraints on metal and fluid sources in W-Sb-Au mineralization at Woxi and Liaojiaping (Western Hunan, China). Mineral Deposita 39:313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-004-0409-0
Peng B, Song ZL, Tu XL, Xiao ML, Wu FC, Lv HZ (2004) Release of heavy metals during weathering of the Lower Cambrian black shales in western Hunan, China. Environ Geol 45:1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-0974-7
Peng B, Tang XY, Yu CX, Tan CY, Tu XL, Liu Q, Yang KS, Xiao M, Xu JZ (2011) Heavy metal contamination of inlet sediments of the Xiangjiang River and Pb isotopic geochemical implication. Acta Geol Sin 85:282–299. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00181 (in Chinese)
Peng B, Wu FC, Xiao ML., Xie SR, Lv HZ, Dai YN (2005) The resource functions and environmental effects of black shales. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 24(2):153–188. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Qiao YM, Yang Y, Gu JG, Zhao JG (2013) Distribution and geochemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments from coastal area suffered rapid urbanization, a case study of Shantou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 68:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.12.003
Qiu ML, Yuan CC, Yin GY (2020) Effect of terrain gradient on cadmium accumulation in soils. Geoderma 375:114501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114501
Quevauviller P, Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Rubio R, Ure A, Muntau H (1997) Certification of trace metal extractable contents in a sediment reference material (CRM 601) following a three-step sequential extraction procedure. Sci Total Environ 205:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00205-2
Ruiz F (2001) Trace Metals in Estuarine Sediments from the Southwestern Spanish Coast. Mar Pollut Bull 42:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00192-2
Sahoo PK, Guimarães JTF, Souza-Filho PWM, Powell MA, da Silva MS, Moraes AM, Alves R, Leite AS, Júnior WN, Rodrigues TM, Costa VE, Dall’Agnol R (2019) Statistical analysis of lake sediment geochemical data for understanding surface geological factors and processes: an example from Amazonian upland lakes, Brazil. CATENA 175:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.003
Sasmaz M, Öbek E, Sasmaz A (2019) Bioaccumulation of cadmium and thallium in Pb-Zn tailing waste water by Lemna minor and Lemna gibba. Appl Geochem 100:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.011
Singh P (2009) Major, trace and REE geochemistry of the Ganga River sediments: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Chem Geol 266:242–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.06.013
Solomon A, Rasheed K, Olanipekun E (2016) Spatial distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediment of River Ilaje, Nigeria. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.9734/IRJPAC/2016/22031
Steinmann P, Shotyk W (1997) Geochemistry, mineralogy, and geochemical mass balance on major elements in two peat bog profiles (Jura Mountains, Switzerland). Chem Geol 138:25–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00171-4
Sun WL, Sang LX, Jiang BF (2012) Trace metals in sediments and aquatic plants from the Xiangjiang River, China. J Soils Sediments 12:1649–1657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0596-8
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39:611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Thomas RP, Ure AM, Davidson CM, Littlejohn D, Rauret G, Rubio R, López-Sánchez JF (1994) Three-stage sequential extraction procedure for the determination of metals in river sediments. Anal Chim Acta 286:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(94)85088-7
Tu C, Guan F, Sun YH, Guo PP, Liu Y, Li LZ, Scheckel KG, Luo YM (2018) Stabilizing effects on a Cd polluted coastal wetland soil using calcium polysulphide. Geoderma 332:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.013
Tyszka R, Pietranik A, Kierczak J, Zieliński G, Darling J (2018) Cadmium distribution in Pb-Zn slags from Upper Silesia, Poland: implications for cadmium mobility from slag phases to the environment. J Geochem Explor 186:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.12.001
Wang YQ, Yang LY, Kong LH, Liu EF, Wang LF, Zhu JR (2015) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. CATENA 125:200–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.023
Wang Q, Peng B, Fang XH, Zhou DX, Qin ZL, Wu SC, Zhao YF, Liu J, Chen DT, Wang X, Tan CY, Wan DJ (2020) Mineralogical compositions of heavy-metal contaminated bed sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province of China. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 39:558–575. https://doi.org/10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2020.39.038 (in Chinese)
Weltje GJ, Brommer MB (2011) Sediment-budget modelling of multi-sourced basin fills: application to recent deposits of the western Adriatic mud wedge (Italy). Basin Res 23:291–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.2010.00484.x
Wen HJ, Zhang YX, Cloquet C, Zhu CW, Fan HF, Luo CG (2015) Tracing sources of pollution in soils from the Jinding Pb–Zn mining district in China using cadmium and lead isotopes. Appl Geochem 52:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.025
Wester RC, Maibach HI, Sedik L, Melendres J, Dizio S, Wade M (1992) In vitro percutaneous absorption of cadmium from water and soil into human skin. Toxicol Sci 19:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/19.1.1
Williams PN, Lei M, Sun GX, Huang Q, Lu Y, Deacon C, Meharg AA, Zhu YG (2009) Occurrence and partitioning of cadmium, arsenic and lead in mine impacted paddy rice: Hunan, China. Environ Sci Technol 43:637–642. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802412r
Xia XQ, Mao YQ, Ji JF, Ma HR, Chen J, Liao QL (2007) Reflectance spectroscopy study of Cd contamination in the sediments of the Changjiang River, China. Environ Sci Technol 41:3449–3454. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0624422
Xiao Y, Peng B, Yang ZX, Xie WC, Fang XH, Zeng DZ (2017) Speciation of heavy metals in riverbed sediments of heavy pollution section of the lowermost of the Xiangjiang River. Environ Chem 36:1977–1986. https://doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017011802 (in Chinese)
Xie WC, Peng B, Kuang XL, Xiao Y, Yang ZX, Fang XH, Zeng DZ, Wu BJ, Tu XL, Wang X, Tan CY (2017) Lead isotopic tracing for heavy metal contamination sources developed in riverbed sediments of the Changsha, Xiangtan and Zhuzhou sections of the Xiangjiang River, China. Geochimica 46:380–394 (in Chinese)
Yan Y, Han L, Yu RL, Hu G, Zhang WF, Cui JY, Yan Y, Huang HB (2020) Background determination, pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in estuarine sediments from Quanzhou Bay, southeast China. CATENA 187:104322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104322
Ye L, Li CY, Liu TG, Li XB, Pi DH (2004) The environmental impact of cadmium-rich Pb-Zn deposit for the example of Niujiaotang Cd rich deposit, Duyun, Guizhou, China. Adv Earth Science 19:456–460 (in Chinese)
Yu XJ, Huo SL, Zan FY, Zhao GC, Xi BD, Su J (2013) Distribution characteristics and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake, China. Chin J Environ Eng 7:439–450 (in Chinese)
Yuan CG, Shi JB, He B, Liu JF, Liang LN, Jiang GB (2004) Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environ Int 30:769–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.01.001
Yuan ZW, Luo T, Liu XW, Hua H, Zhuang YJ, Zhang XH, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Xu WW, Ren JH (2019) Tracing anthropogenic cadmium emissions: from sources to pollution. Sci Total Environ 676:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.250
Zachmann DW, van der Veen A, Friese K (2013) Floodplain lakes as an archive for the metal pollution in the River Elbe (Germany) during the 20th century. Appl Geochem 35:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.05.009
Zhang LC, Zhao GJ (1996) The species and geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in the sediments of Kangjiaxi River in the Shuikoushan Mine Area, China. Appl Geochem 11:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(95)00096-8
Zhang YX, Tian Y, Shen MC, Zeng GM (2018a) Heavy metals in soils and sediments from Dongting Lake in China: occurrence, sources, and spatial distribution by multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13687–13696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1590-5
Zhang ZX, Lu Y, Li HP, Tu Y, Liu BY, Yang ZG (2018b) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 645:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026
Zeng DZ, Peng B, Zhang K, Fang XH, Tan CY, Kuang XL, Wu BJ, Tu XL (2017) Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal contamination in bed sediments from inlet areas of the Lishui River to Dongting Lake. Acta Sci Circum 37(9):3480–3488 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhong LY, Liu LM, Yang JW (2012) Characterization of heavy metal pollution in the paddy soils of Xiangyin County, Dongting lake drainage basin, central south China. Environ Earth Sci 67(8): 2261–2268
Acknowledgements
Mr. Tu Xianglin at the Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is thanked for his help with the ICP-MS analysis.
Funding
The work was financially supported by the Construction Program for First-Class Disciplines (Geography) of Hunan Province and the Aid Program for Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province (2014), China. Part of the work was also supported by the National Scientific Foundation Committee of China (Grant No. 41073095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bo Peng, Sicheng Wu: Ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims.
Sicheng Wu, Bo Peng, Xiaohong Fang, Shurong Xie, Xiaomin Li, Chunxia Jiang, Yanan Dai: Management activities to annotate (produce metadata), scrub data, and maintain research data (including software code, where it is necessary for interpreting the data itself) for initial use and later re-use. Application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyse or synthesize study data. Provision of study materials, reagents, materials, patients, laboratory samples, animals, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools. Programming, software development; designing computer programs; implementation of the computer code and supporting algorithms; testing of existing code components. Verification, whether as a part of the activity or separate, of the overall replication/reproducibility of results/experiments and other research outputs. Preparation, creation, and/or presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/data presentation.
Bo Peng: Acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication. Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. Management and coordination responsibility for the research activity planning and execution. Oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution, including mentorship external to the core team.
Sicheng Wu: Development or design of methodology; creation of models.
Bo Peng, Sicheng Wu: Preparation, creation, and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation). Preparation, creation, and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary, or revision—including pre- or post-publication stages.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Severine Le Faucheur
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ., Peng, B., Fang, X. et al. Distribution and assessment of cadmium contamination in sediments from the Four River inlets to Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 66072–66085 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15636-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15636-1