Abstract
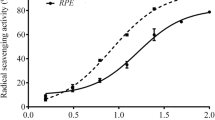
Narcissus tazetta (Amaryllidaceae) is a medicinal plant widely used for cut flowers and potted ornamental plant in Tunisia flora. The current study evaluated the phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of its flower extracts and investigated its potential protective activity against cadmium chloride (CdCl2)–induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Mice were divided into six groups of six each: group 1, serving as negative controls, received by intraperitoneal way only distilled water; group 2 received by intraperitoneal way CdCl2 (0.16 mg/kg bw); groups 3 and 4 received CdCl2 at the same dose of group 2 and 100 or 200 mg/kg bw of Narcissus tazetta flower extracts via oral route; groups 5 and 6, serving as positive controls, received only Narcissus tazetta flower extracts. Polyphenolic compounds of the extract were analyzed by colorimetric and high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) methods. Total antioxidant activity and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging potential of the extract were estimated using colorimetric method. Results indicated that ethanolic flower extract contained high levels of total phenolic and flavonoid along with a strong total antioxidant and DPPH free radical scavenging activities. HPLC-MS analysis identified eight phenolic compounds, including rutin, kaempferol glycosides, and chlorogenic acids. The extract also exhibited marked hepatoprotective effects against CdCl2 toxicity by reducing hepatic levels of malondialdehyde, advanced oxidation protein products, hydrogen peroxide, metallothioneins, and DNA degradation. Additionally, co-administration of Narcissus tazetta flower extracts lowered the plasma activities of transaminases, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, and lactate dehydrogenase and increased hepatic levels of reduced glutathione, nonprotein thiols, vitamin C, and catalase activity. The hepatoprotective effects of the extract were demonstrated by histopathological improvement of liver disorders. The current study provided ethnopharmacological application of Narcissus tazetta flower extracts against CdCl2-induced oxidative stress, suggesting its chemoprevention role of its phenolic compounds as a natural antioxidant.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- AOPP:
-
Advanced oxidation protein products
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- CdCl2 :
-
Cadmium chloride
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DPPH:
-
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- γGT:
-
Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatograph
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- MTs:
-
Metallothioneins
- NPSH:
-
Nonprotein thiols
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- Vit C:
-
Vitamin C
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Bati Ay E, Gül M, Açikgöz AM, Yarilgaç T, Kara ŞM (2018) Assessment of antioxidant activity of giant snowdrop (Galanthus elwesii Hook) extracts with their total phenol and flavonoid contents. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 52(4):128–132. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.52.4s.88
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gel. Anal Biochem 44(1):276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Benedec D, Oniga I, Hanganu D, Gheldiu AM, Pușcaș C, Silaghi-Dumitrescu R, Duma M, Tiperciuc B, Vârban R, Vlase L (2018) Sources for developing new medicinal products: biochemical investigations on alcoholic extracts obtained from aerial parts of some Romanian Amaryllidaceae species. BMC Complement Altern Med 18(226):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2292-8
Chater S, Douki T, Garrel C, Favier A, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2008) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in kidney of pregnant female rats. C R Biol 331(6):426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2008.03.009
Chun Chen H, Shan Chi H, Yun Lin L (2013) Headspace solid-phase microextraction analysis of volatile components in Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis Roem. Molecules 18:13723–13734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113723
Clark SJ, Melki J (2002) DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer: which is the guilty party? Oncogene 21(35):5380–5387. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205598
Dewanto V, Wu X, Adom KK, Liu RH (2002) Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem 50:3010–3014. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011558
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-I
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Emmanuel Oyinloye B, Adenowo AF, Osunsanmil FO, Ogunyinka BI, Nwozo SO, Paul Kappol A (2016) Aqueous extract of Monodora myristica ameliorates cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in male rats. Springer Plus 5:641. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2228-z
Erkan N, Akgonen S, Ovat S, Goksel G, Ayranci E (2011) Phenolic compounds profile and antioxidant activity of Dorystoechas hastata L. Boiss et Heldr. Food Res Int 44:3013–3020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.015
Erlejman AG, Verstraeten SV, Fraga CG, Oteiza PI (2004) The interaction of flavonoids with membranes: potential determinant of flavonoid antioxidant effects. Free Radic Res 38(12):1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760400016105
Flohe L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05015-1
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(11):3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113782
Girja SS, Chandrat SV (1998) Cadmium toxicity and bioantioxidants: status of vitamin E and ascorbic acid of selected organs in rat. J Appl Toxicol 9(2):119–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2550090209
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1(22):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
Gong G, Qin Y, Huang W, Zhou S, Yang X, Li D (2010) Rutin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis through regulating reactive oxygen species mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 628(1-3):27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.11.028
Grey-Wilson C, Mathew B (1981) The bulbous plants of Europe and their allies. Collins, London
Hamdi A, Jaramillo-Carmona S, Srairi Beji R, Tej R, Zaoui S, Rodríguez-Arcos R, Jiménez-Araujo A, Kasria M, Lachaal M, Karray Bouraoui N, Guillén-Bejarano R (2017) The phytochemical and bioactivity profiles of wild Asparagus albus L. plant. Food Res Int 99(Pt 1):720–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.06.027
Hatano T, Kagawa H, Yasuhara T, Okuda T (1988) Two new flavonoids and other constituents in licorice root their relative astringency and radical scavenging effect. Chem Pharm Bull 36:1090–1097. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.36.2090
He Q, Luo Y, Zhang P, An C, Zhang A, Li X, You L, Liu C (2019) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant potential of radish seed aqueous extract on cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in mice. Phcog Mag 15:283–289. https://doi.org/10.4103/pm.pm_365_18
Homeira Soleimani S, Bernard F, Amini M, Khavari-nezhad RA (2019) Cadmium accumulation and alkaloid production of Narcissus tazetta plants grown under in vitro condition with cadmium stress. Plant Physiol Rep 25:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-019-00476-6
Igarashi K, Mikami T, Takahashi Y, Sato H (2008) Comparison of the preventive activity of isorhamnetin glycosides from Atsumi-kabu (red turnip, Brassica, campestris L.) leaves on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72(3):856–860. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70558
Jacques-Silva MC, Nogueira CW, Broch LC (2001) Diphenyldiselenide and ascorbic acid changes deposition of selenium and ascorbic acid in liver and brain of mice. Pharmacol Toxicol 88(33):119–125. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0773.2001.d01-92.x
Jadoon S, Malik A (2017) DNA Damage by heavy metals in animals and human beings: an overview. Biochem Pharmacol 6(3):1000235. https://doi.org/10.4172/2167-0501.1000235
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11(3):151–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136485
Jurczuk M, Brzóska MM, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J, Gäazyn-Sidorczuk M, Kulikowska-Karpinska E (2004) Antioxidant enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to cadmium and ethanol. Food Chem Toxicol 42(3):429–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2003.10.005
Jurczuk M, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J, Brzoska MM (2006) Involvement of some low-molecular thiols in the peroxidative mechanisms of lead and ethanol action on rat liver and kidney. Toxicology 219(1-3):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.10.022
Li X, Lu M, Tang D, Shi Y (2015) Composition of carotenoids and flavonoids in Narcissus cultivars and their relationship with flower Color. PLoS One 10(11):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142074
Li FK, Li X, Ye J, Lu L, Ke Xu X, Liang Li H, Dong Zhang W, Heng Shen Y (2016) Chemical constituents of Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis and their antioxidant activities. Fitoterapia 113:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2016.07.013
Li S, Yue Tan H, Wang N, Cheung F, Hong M, Feng Y (2018) The potential and action mechanism of polyphenols in the treatment of liver diseases. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8394818
Liu Q, Pana R, Dinga L, Zhanga F, Hua L, Dinga B, Zhue L, Xiad Y, Doua X (2017) Rutin exhibits hepatoprotective effects in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by reducing hepatic lipid levels and mitigating lipid induced oxidative injuries. Int Immunopharmacol 49:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.05.026
López S, Jaume Francesc B, Carles VC (2002) Acetylcholinesterase activity of some Amaryllidaceae alkaloids and Narcissus extracts. Life Sci 71(21):2521–2529. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(02)02034-9
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madejczyk MS, Baer CE, Dennis WE, Minarchick VC, Leonard SS, Jackson DA, Stallings JD, Lewis JA (2015) Temporal changes in rat liver gene expression after acute cadmium and chromium exposure. PLoS One 10:e0127327. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127327
Matovic V, Buha A, Dukic-Cosic D, Bulat Z (2015) Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem Toxicol 78:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.02.011
Mężyńska M, Brzóska MM (2018) Review of polyphenol-rich products as potential protective and therapeutic factors against cadmium hepatotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol 39(1):117–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3709
Mirani N, Ashraf J, Siddique J, Rub A (2012) Protective effect of rutin against cadmium induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. J Pharmacol Toxicol 7(3):150–157. https://doi.org/10.3923/jpt.2012.150.157
Ou P, Wolff SP (1996) A discontinuous method for catalase determination at near physiological concentrations of H2O2 and its application to the study of H2O2 fluxes within cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods 31:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-022X(95)00039-T
Paul A, Das J, Das S, Samadder A, Khuda-Bukhsh Poly AR (2013) Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nano-encapsulation of chelidonine, an active bioingredient of greater celandine (Chelidonium majus), enhances its ameliorative potential against cadmium induced oxidative stress and hepatic injury in mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):937–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.08.008
Petrovic S, Ozretic B, Krajnovic-Ozretic M, Bobinac D (2001) Lysosomal membranestability and metallothioneins in digestive gland of mussels (Mytilusgallo provincialis Lam.) as biomarkers in a field study. Mar Pollut Bull 42(12):1373–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00167-9
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1999.40199
Rameshk M, Sharififar F, Mehrabani M, Pardakhty A, Farsinejad A, Mehrabani M (2018) Proliferation and in vitro wound healing effects of the microniosomes containing Narcissus tazetta L. Bulb Extract on Primary Human Fibroblasts (HDFs). DARU J Pharm Sci 26:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-018-0211-7
Ravi GS, Narayana Charyulu R, Dubey A, Prabhu P, Hebbar S, Candida Mathias A (2018) Nano-lipid complex of rutin: development, characterisation and in vivo investigation of hepatoprotective, antioxidant activity and bioavailability study in rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 19(8):3631–3649. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1195-9
Ruíz-Ramón F, Águila DJ, Egea-Cortines M, Weiss J (2014) Optimization of fragrance extraction: daytime and flower age affect scent emission in simple and double narcissi. Ind Crop Prod 52:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.034
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. CSHL Press, New York, pp 577–581
Satarug S (2019) Cadmium sources and toxicity. Toxics 7(2):25. https://doi.org/. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7020025
Sener B, Orhan I, Satayavivad J (2003) Antimalarial activity screening of some alkaloids and the plant extracts from Amaryllidaceae. Phytother Res 17(10):1220–1223. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1346
Shehab NG, Abu-Gharbieh E, Bayoumi FA (2015) Impact of phenolic composition on hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of four desert medicinal plants. BMC Complement Altern Med 15(401):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0919-6
Shi H, Shi A, Dong L, Lu X, Wang Y, Zhao J, Dai F, Guo X (2016) Chlorogenic acid protects against liver fibrosis in vivo and in vitro through inhibition of oxidative stress. Clin Nutr 35(6):1366–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2016.03.002
Shibata H, Sakamoto Y, Oka M, Kono Y (1999) Natural antioxidant, chlorogenic acid, protects against DNA breakage caused by monochloramine. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63(7):1295–1297. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.63.1295
Singleton VL, Rosi JA (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16:144–158
Smalinskiene A, Lesauskaite V, Savickiene N, Zitkevicius V, Savickas A, Ryselis S, Kregzdyte R, Abdrakhmanov O, Sadauskiene I, Ivanov L (2008) The relationship of Echinacea purpurea to the toxicity of cadmium. Pharm Biol 43(9):797–802. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200500408590
Suvarna SK, Layton C, Bancroft JD (2013) Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques, 7th edn. Churchill Livingston, NewYork, p 637
Viarengo A, Ponzano E, Dondero F, Fabbri R (1997) A simple spectrophotometric methodfor metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: an application to Mediterranean and Antarctic mollusks. Mar Environ Res 44:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(96)00103-1
Wanga H, Chena L, Zhanga X, Xua L, Xiea B, Shia H, Duana Z, Zhangc H, Rena F (2018) Kaempferol protects mice from D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver failure by regulating the ER stress-Grp78-CHOP signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 111:468–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.105
Willems J, Khamis MM, Mohammed Saeid W, Purves RW, Katselis G, Low N, El-Aneed A (2016) Analysis of a series of chlorogenic acid isomers using differential ion mobility and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 933:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.05.041
Witko V, Nguyen AT, Descamps-Latscha B (1992) Microtiter plate assay for phagocyte-derived taurine chloramines. J Clin Lab Anal 6(1):47–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.1860060110
Xu T, Huang S, Huang Q, Ming Z, Wang M, Li R, Zhao Y (2019) Kaempferol attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting activin receptor–like kinase 5. J Cell Mol Med 23:6403–6410. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14528
Zang Y, Zhang D, Yu C, Jin C, Igarashi K (2017) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of kaempferol 3-O-b-D- (2,6-di-O-a-L-rhamnopyranosyl) galactopyronoside against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 26(4):1071–1076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0170-7
Zhao J, Zhang S, You S, Liu T, Xu F, Ji T, Gu Z (2017) Hepatoprotective Effects of nicotiflorin from Nymphaea candida against concanavalin A-induced and D-galactosamine-induced liver injury in mice. Int J Mol Sci 18(3):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030587
Zhishen J, Tang M, Wu J (1999) The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem 64(4):555–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00102-2
Acknowledgements
The current work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Laboratory of Plant Productivity and Environmental Constraints (LR18ES04). The authors are grateful to Dr. Abdelali Hannoufa, research scientist-adjunct professor at Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, for critical reading of the manuscript and Mr. Mejri Hssan for his skillful technical assistance.
Funding
This work received financial assistance from the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SBA and MS were responsible for most of the work; NS contributed to data analysis, AH contributed to the biochemical assays and data analysis; SB contributed to the molecular assays; SBA wrote the manuscript draft; MEL and NKB edited and revised the manuscript and supervised the research project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animals received humane care in accordance with the International Guidelines for Animal Care and with strict adherence to the Ethical Committee of Faculty of Sciences, Sfax, Tunisia, under the ethical approval no. 1204.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Abdallah, ., Sefi, M., Soudani, N. et al. Potential antioxidant effects of Narcissus tazetta phenolic compounds against cadmium chloride–induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 66193–66205 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15497-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15497-8