Abstract
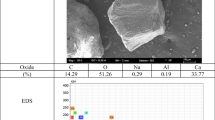
This paper uses a new integrated method, namely PHDVPSS, which utilizes vacuum pressure (VP) coupled with prefabricated horizontal drain along with solidification/stabilization (SS) for the effective treatment of high-water content dredged contaminated sediment (DCS). This study sought to evaluate the physico-mechanical and microstructural behaviour of high-water content DCS treated with MgO-GGBS (MG) and Portland cement (PC) as PHDVPSS binders and compared to the traditional Portland cement solidification/stabilization (SS-PC) method. Physico-mechanical and microstructural characteristics of the DCS treated with the PHDVPSS method were evaluated by performing a number of tests such as unconfined compressive strength (UCS), toxicity characteristics of the leaching process (TCLP), pH, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) combined with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Treatment results showed that the DCS treated with the MG binder in the PHDVPSS method showed superior performance in terms of a significant reduction in the water content and leachability of zinc (Zn) along with higher mechanical strength and dry density of the samples compared to the traditional SS-PC method. After 56-day curing time, VP-MG cases showed 17.6 % and 50 % higher dry density values, resulting in 2.5 and 17.3 times higher UCS values than VP-PC and SS-PC cases, respectively. In contrast, VP-MG cases showed lower pH values than those of VP-PC and SS-PC cases. Moreover, VP-MG cases exhibited 37.5 % and 44.3 % lower leached Zn concentration during a TCLP test than VP-PC cases and SS-PC cases, respectively. XRD and SEM-EDS tests showed that more voluminous hydration products were produced in the VP-MG cases, which in turn produced a dense stabilized matrix and significantly reduced the leachability of zinc.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
ASTM D4219 (2008) Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength index of chemical-grouted soils. ASTM Int 162:705–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(82)90398-9
ASTM D4972-01, 2001. Standard test method for pH of soils. Annu. B. ASTM Intl.
Audry S, Schäfer J, Blanc G, Jouanneau J-M (2004) Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ Pollut 132:413–426
Cai Y, Qiao H, Wang J, Geng X, Wang P, Cai Y (2017) Experimental tests on effect of deformed prefabricated vertical drains in dredged soil on consolidation via vacuum preloading. Eng Geol 222:10–19
Chen CF, Ju YR, Chen CW, Di Dong C (2019) Changes in the total content and speciation patterns of metals in the dredged sediments after ocean dumping: Taiwan continental slope. Ocean Coast Manag 181:104893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.104893
Du YJ, Jiang NJ, Liu SY, Jin F, Singh DN, Puppala AJ (2014) Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of cement-stabilized zinc-contaminated kaolin. Can Geotech J 51:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2013-0177
Du YJ, Bo YL, Jin F, Liu CY (2016) Durability of reactive magnesia-activated slag-stabilized low plasticity clay subjected to drying-wetting cycle. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 20:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2015.1030088
Feng YS, Du YJ, Reddy KR, Xia WY (2018) Performance of two novel binders to stabilize field soil with zinc and chloride: mechanical properties, leachability and mechanisms assessment. Constr Build Mater 189:1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.072
Gang Y, Won EJ, Ra K, Choi JY, Lee KW, Kim K (2018) Environmental assessment of contaminated marine sediments treated with solidification agents: directions for improving environmental assessment guidelines. Mar Environ Res 139:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.05.011
Goodarzi AR, Movahedrad M (2017) Stabilization/solidification of zinc-contaminated kaolin clay using ground granulated blast-furnace slag and different types of activators. Appl Geochem 81:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.04.014
Goodarzi AR, Zandi MH (2016) Assessing geo-mechanical and leaching behavior of cement–silica-fume-stabilized heavy metal-contaminated clayey soil. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5730-2
Griffin H, O’kelly BC (2014) Ground improvement by vacuum consolidation-a review. Proc Inst Civ Eng Gr Improv 167:274–290. https://doi.org/10.1680/grim.13.00012
Gu K, Jin F, Al-Tabbaa A, Shi B, Liu J (2014) Mechanical and hydration properties of ground granulated blastfurnace slag pastes activated with MgO-CaO mixtures. Constr Build Mater 69:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.07.032
Haha MB, Lothenbach B, Le Saout GL, Winnefeld F (2011) Influence of slag chemistry on the hydration of alkali-activated blast-furnace slag—Part I: Effect of MgO. Cem Concr Res 41:955–963
Ho LS, Nakarai K, Ogawa Y, Sasaki T, Morioka M (2017) Strength development of cement-treated soils: Effects of water content, carbonation, and pozzolanic reaction under drying curing condition. Constr Build Mater 134:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.065
Indraratna B, Rujikiatkamjorn C, Ameratunga J, Boyle P (2011) Performance and prediction of vacuum combined surcharge consolidation at port of brisbane. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 137:1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000519
Jin F, Al-Tabbaa A (2014) Evaluation of novel reactive MgO activated slag binder for the immobilisation of lead and zinc. Chemosphere 117:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.027
Jin F, Gu K, Al-Tabbaa A (2015) Strength and hydration properties of reactive MgO-activated ground granulated blastfurnace slag paste. Cem Concr Compos 57:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.10.007
Jin F, Wang F, Al-Tabbaa A (2016) Three-year performance of in-situ solidified/stabilised soil using novel MgO-bearing binders. Chemosphere 144:681–688
Khalid U, Liao CC, Ye G l, Yadav SK (2018) Sustainable improvement of soft marine clay using low cement content: a multi-scale experimental investigation. Constr Build Mater 191:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.034
Kogbara RB, Al-Tabbaa A, Yi Y, Stegemann JA (2013) Cement–fly ash stabilisation/solidification of contaminated soil: performance properties and initiation of operating envelopes. Appl Geochem 33:64–75
Li XD, Zhang YM, Poon CS, Lo IMC (2001) Study of zinc in cementitious material stabilised/solidified wastes by sequential chemical extraction and microstructural analysis. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 13:1–7
Liang X, Zang Y, Xu Y, Tan X, Hou W, Wang L, Sun Y (2013) Sorption of metal cations on layered double hydroxides. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 433:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.05.006
Lo IMC, Tang CI, Li XD, Poon CS (2000) Leaching and microstructural analysis of cement-based solidified wastes. Environ Sci Technol 34:5038–5042. https://doi.org/10.1021/es991224o
Makusa GP, Mácsik J, Holm G, Knutsson S (2016) Process stabilization-solidification and the physicochemical factors influencing the strength development of treated dredged sediments. Geotechnical Special Publication:532–545. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784480168.053
Malviya R, Chaudhary R (2006) Factors affecting hazardous waste solidification/stabilization: a review. J Hazard Mater 137:267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.065
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2:108–118
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. J Hazard Mater 85:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00226-6
Nagahara H, Fujiyama T, Ishiguro T, Ohta H (2004) FEM analysis of high airport embankment with horizontal drains. Geotext Geomembr 22(1-2):49–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-1144(03)00051-7
Pu H, Mastoi AK, Chen X et al (2021) An integrated method for the rapid dewatering and solidification/stabilization of dredged contaminated sediment with a high water content. Front Environ Sci Eng 15:1–12
Scrivener KL, Kirkpatrick RJ (2008) Innovation in use and research on cementitious material. Cem Concr Res 38:128–136
Shinsha H, Kumagai T (2014) Bulk compression of dredged soils by vacuum consolidation method using horizontal drains. Geotech Eng 45(3):78–85
Usepa U (1992) EPA method 1311-toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. United States Environ. Prot, Agency, Washington, DC
Wang DX, Abriak NE, Zentar R, Xu W (2012) Solidification/stabilization of dredged marine sediments for road construction. Environ Technol 33:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.551840
Wang D, Abriak NE, Zentar R (2013) Strength and deformation properties of Dunkirk marine sediments solidified with cement, lime and fly ash. Eng Geol 166:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.09.007
Wang F, Wang H, Jin F, Al-Tabbaa A (2015) The performance of blended conventional and novel binders in the in-situ stabilisation/solidification of a contaminated site soil. J Hazard Mater 285:46–52
Wang F, Jin F, Shen Z, Al-Tabbaa A (2016) Three-year performance of in-situ mass stabilised contaminated site soils using MgO-bearing binders. J Hazard Mater 318:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.018
Wang P, Han Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Cai Y, Xu F, Pu H (2020) Apparent clogging effect in vacuum-induced consolidation of dredged soil with prefabricated vertical drains. Geotext Geomembr 48:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.02.010
Wu DQ, Xu WY, Zhu DP (2013) The chemical-physical combined method for improving clay slurry in land reclamation. Geotech Spec Publ 308–315. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784413128.037
Xia WY, Feng YS, Du YJ, Reddy KR, Wei ML (2018) Solidification and stabilization of heavy metal-contaminated industrial site soil using KMP binder. J Mater Civ Eng 30:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002264
Xiao H, Wang W, Goh SH (2017) Effectiveness study for fly ash cement improved marine clay. Constr Build Mater 157:1053–1064
Yi Y, Al-Tabbaa A, Liska M (2014a) Properties and microstructure of GGBS-magnesia pastes. Adv Cem Res 26:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1680/adcr.13.00005
Yi Y, Liska M, Al-Tabbaa A (2014b) Properties of two model soils stabilized with different blends and contents of GGBS, MgO, lime, and PC. J Mater Civ Eng 26:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000806
Yi Y, Liska M, Jin F, Al-Tabbaa A (2016) Mechanism of reactive magnesia – ground granulated blastfurnace slag (GGBS) soil stabilization. Can Geotech J 53:773–782. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2015-0183
Zak R, Deja J (2015) Spectroscopy study of Zn, Cd, Pb and Cr ions immobilization on C-S-H phase. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 134:614–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.069
Zhang R, Dong C, Lu Z, Pu H (2019) Strength characteristics of hydraulically dredged mud slurry treated by flocculation-solidification combined method. Constr Build Mater 228:116742
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge and appreciate the support received from the Institute of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and the Department of Civil Engineering, Quaid-e-Awam University of Engineering Science and Technology, Nawabshah, Pakistan.
Funding
This investigation was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under the Grant No. 2016YFC0800200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aamir Khan Mastoi: Conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, data analysis, writing-original draft and writing-review and editing
Hefu Pu: Conceptualization, supervision, writing-original draft and funding acquisition
Xunlong Chen: Methodology, investigation, data analysis, writing-original draft and writing-review and editing
Alidekyi Sharif Nyanzi: Investigation, methodology and writing-review and editing
Ashfaque Ahmed Jhatial: Data analysis, writing original draft and writing-review and editing
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consented for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mastoi, A.K., Pu, H., Chen, X. et al. Physico-mechanical and microstructural behaviour of high-water content zinc-contaminated dredged sediment treated with integrated approach PHDVPSS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 58331–58341 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14770-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14770-0