Abstract
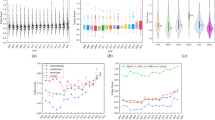
Whether financial agglomeration is conducive to improving the green efficiency of water resources is of great significance for China to realize water saving and consumption reduction, and green sustainable development. Based on the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2017, this paper uses the SBM model with undesirable output to measure the green efficiency of water resources in China and empirically examines the impact of financial agglomeration on the green efficiency of water resources. The results show that the green efficiency of water resources in China presents the “N” type fluctuation characteristic, and the overall trend is increasing. The mean value of green efficiency of water resources in China fluctuates around 0.6, which is at a medium level, and there is still a large room for improvement. Secondly, there are obvious spatial differences in China’s green efficiency of water resources, showing a gradient of “Eastern>Central>Western.” Thirdly, at the national level, financial agglomeration has a significant positive impact on the green efficiency of water resources, and there is an inverted “U”-shaped relationship between financial agglomeration and green efficiency of water resources. Fourthly, at the regional level, the impact of financial agglomeration on green efficiency of water resources has significant regional differences. Finally, based on the above conclusions, specific proposals for financial agglomeration to improve the green efficiency of water resources are put forward.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Notes
The eastern region includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan. The central region includes Shanxi, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Anhui, and Jiangxi. The western region includes Inner Mongolia, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, and Ningxia.
References
An W (2008) A probe into the connotation, mechanism and practice of green finance. Econ Survey 05:156–158. https://doi.org/10.15931/j.cnki.1006-1096.2008.05.039
Ang JB (2011) Financial development, liberalization and technological deepening. Eur Econ Rev 55:688–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroecorev.2010.09.004
Azad MAS, Ancev T (2014) Measuring environmental efficiency of agricultural water use: a Luenberger environmental indicator. J Environ Manag 145:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.05.037
Benfratello L, Schiantarelli F, Sembenelli A (2008) Banks and innovation: micro econometric evidence on Italian Firms. J Financ Econ 90:197–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2008.01.001
Buera FJ, Kaboski JP, Shin Y (2011) Finance and development: a tale of two sectors. Am Econ Rev 101(5):1964–2002. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.101.5.1964
China’s National Bureau of Statistics, 2020. China Statistical Yearbook 2019. http://www.stats.gov.cn/
Deng XR, Liu WQ (2013) The empirical research of financial agglomeration on industrial structure upgrade: based on ESDA model. Nanjing J Soc Sci (10):5-12+20. https://doi.org/10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2013.10.015
Deng GY, Li L, Song YN (2016) Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol Indic 69:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.03.052
Guo YR, Hu Y, Shi k, Bilan Y (2020) Valuation of water resource green efficiency based on SBM-TOBIT panel model: case study from Henan Province, China. Sustainability 12:6944 https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176944
He YQ, Chen LX, Jiao JX, Wang Y (2017) Study on the relationship between space-time discrepancy of regional financial agglomeration and the provincial eco-efficiency in China. J Appl Stat Manag 36:162–174. https://doi.org/10.13860/j.cnki.sltj.20160418-005
King RG, Levine R (1993) Finance and growth: Schumpeter might be right. Q J Econ 108:717–737. https://doi.org/10.2307/2118406
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35:688–726. https://doi.org/10.2307/2729790
Li XX, Xia G, Cai N (2015) Green finance and sustainable development. Finance Forum 20:30–40. https://doi.org/10.16529/j.cnki.11-4613/f.2015.10.009
Liu J, Huang JY, Cao LY (2007) The mechanism of financial agglomeration’s effect on the real economy. Manag Word 4:152–153. https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2007.04.019
Ma HL, Huang JC, Zhang JG (2012) Water resource utility efficiency and its influencing factors considering undesirable goods. China Population Res Environ 22:35–42. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2012.10.006
Ma HL, Ding YQ, Wang L (2017) Measurement and convergence analysis of green water utilization efficiency. J Nat Res 32:406–417. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.20160381
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, 2020. China Water Resources Bulletin 2019 http://www.mwr.gov.cn/.
Pandit NR, Cook GAS, Swann GMP (2001) The dynamic of industrial clustering in British financial services. Serv Ind J 21:33–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/714005045
Park YS (1982) The economics of offshore financial centers. Columbia J World Bus 4:31–35
Qu CY, Shao J, Shi ZK (2020) Does financial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? Energy Policy 146:111810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111810
Salazar J (1998) Environmental finance: linking two world. In: A workshop on financial innovations for biodiversity, vol 1. Bratislava, pp 2–18
Shan HJ (2008) Re-estimating the capital stock of China: 1952~2006. J Quant Tech Econ 25:17–31
Shi BZ, Xu N, Liu M, Deng M (2018) Impacts and channels of financial agglomeration on green economic efficiency of city: empirical analysis on 249 cities at level of municipality or above. Technol Econ 37:87–95
Sun JL, Li HS (2012) Financial agglomeration and industrial structure upgrading-empirical analysis based on inter-provincial economic data from 2003 to 2007. Economist 03:80–86. https://doi.org/10.16158/j.cnki.51-1312/f.2012.03.006
Sun CZ, Ma QF (2020) Spatial correlation network of water resources green efficiency between provinces of China. Geogr Res 39:53–63. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj020180926
Sun CZ, Jiang K, Zhao LS (2017) Measurement of green efficiency of water utilization and its spatial pattern in China. J Nat Res 32:1999–2011. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.20161076
Tadesse S (2012) Financial architecture and economic performance: international evidence. J Financ Intermed 11(4):429–454. https://doi.org/10.1006/jfin.2002.0352
Tobin J (1958) Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 26:24–36. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907382
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2010) Dynamic DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Omega 38:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2009.07.003
Wu JF (2016) A spatial econometric study on financial agglomeration and regional ecological efficiency. Stat Decision 03:149–153. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2016.03.040
Xu CH, Pan ZW (2019) Threshold effect of regional green water resource efficiency improvement: in the perspective of heterogeneous environmental regulation. Jilin Univ J Soc Sci Ed 59:83-94+220-221. https://doi.org/10.15939/j.jujsse.2019.06.jj1
Yang Q, Liu HJ (2015) Regional disparity and influencing factors of agricultural water resources efficiency with the constraint of pollution. J Quant Tech Econ 32: 114-128+158. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2015.01.008
Yang GS, Xie QH (2019) Study on spatial and temporal differentiation of green water resources efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Res Environ Yangtze Basin 28:349–358
Yao X, Feng W, Zhang X, Wang W, Zhang C, You S (2018) Measurement and decomposition of industrial green total factor water efficiency in China. J Clean Prod 198:1144–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.138
Yin G (2013) Reserve financing and government infrastructure investment: an application to China. J Policy Model 35(6):992–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2013.07.001
Yuan HX, Zhang TS, Feng YD, Liu YB, Ye XY (2019) Does financial agglomeration promote the green development in China? A spatial spillover perspective. J Clean Prod 237:117808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117808
Zhang H, Ding D, Ke L (2019) The effect of R&D input and financial agglomeration on the growth private enterprises: evidence from Chinese manufacturing industry. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 55:2298–2313. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496X.2018.1526668
Zhang CB, Wang XH, Gu ZL (2021) Empirical test of the impact of financial agglomeration on high quality economic development-based on provincial panel data from 2005 to 2019. J Ind Technol Econ 40:99–109. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-910X.2021.02.013
Zhao LS, Sun CZ, Liu FC (2017) Interprovincial two-stage water resource utilization efficiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. J Clean Prod 164:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.252
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. What is more, the data and materials used in this paper are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This research was supported by the General Projects of the National Social Science Fund of China (Grant No. 20BGL189).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Zhang: Conceptualization, validation, and writing-review and editing. Die Wang: Methodology, visualization, formal analysis, and writing-original draft. Xuemeng Liu: Software, data curation, and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Wang, D. & Liu, X. Does financial agglomeration promote the green efficiency of water resources in China?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 56628–56641 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14679-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14679-8