Abstract
Novel copper-nickel ferrite nanocatalyst loaded on multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNTs-CuNiFe2O4) was synthesized and applied to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) in the degradation of the reactive black 5 (RB5). The structure of the catalyst was well characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The MWCNTs-CuNiFe2O4/PMS system showed a high performance in the degradation of RB5 with a kinetic rate of 1.5–2.5 times higher than homogeneous and heterogeneous systems. Maximum degradation efficiency (99.60%) was obtained at an initial pH of 7, catalyst dosage of 250 mg/L, PMS dosage of 4 mM, the temperature of 25 °C, and reaction time of 15 min. Anion experiments emphasized that the presence of nitrate, carbonate, and phosphate in the solution reduced the degradation efficiency by producing reactive species with low oxidation potential. The RB5 degradation rate evolved with temperature, and the activation energy was obtained to be 44.48 kJ/mol. The mechanism of PMS activation and production of free radicals was proposed based on tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), ethanol (EtOH), and potassium iodide (KI) scavengers. Trapping experiments showed that both sulfate (SO4•-) and hydroxyl (•OH) radicals are involved in the catalytic degradation of RB5. The effective treatment of real wastewater and tap water by the MWCNTs-CuNiFe2O4/PMS system requires a long reaction time. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis indicated that RB5 can be degraded via methylation, decarboxylation, hydroxylation, and ring/chain cleavage pathways. The stable catalytic activity after three consecutive cycles suggested that MWCNTs-CuFe2O4 is a novel reusability catalyst in PMS activation.
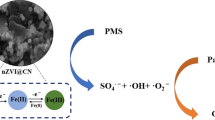
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Ahamad HS, Meshram NS, Bankar SB, Dhoble SJ, Rewatkar KG (2017) Structural properties of CuxNi1-xFe2O4 nano ferrites prepared by urea-gel microwave auto combustion method. Ferroelectrics 516(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2017.1362285
Al Hakim S, Jaber S, Zein Eddine N, Baalbaki A, Ghauch A (2020) Degradation of theophylline in a UV254/PS system: matrix effect and application to a factory effluent. Chem Eng J 380:122478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122478
Ashrafi S, Mengelizadeh N, Dadban Shahamat Y, Zare MR, Jalil M, Berizi Z, Shooshtarian MR, Parvizimehr A, Zolghadr R (2020) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as a reusable novel peroxymonosulfate activator for degradation of Reactive Black 5. Water Environ Res 92(7):969–974. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1291
Ballav N, Debnath S, Pillay K, Maity A (2015) Efficient removal of Reactive Black from aqueous solution using polyaniline coated ligno-cellulose composite as a potential adsorbent. J Mol Liq 209:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.05.051
Camilli L, Passacantando M (2018) Advances on sensors based on carbon nanotubes. Chemosensors 6(4):62
Chen J, Zhang L, Huang T, Li W, Wang Y, Wang Z (2016) Decolorization of azo dye by peroxymonosulfate activated by carbon nanotube: radical versus non-radical mechanism. J Hazard Mater 320:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.038
Chen Z, Wang L, Xu H, Wen Q (2020) Efficient heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by modified CuFe2O4 for degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Chem Eng J 389:124345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124345
Dong X, Ren B, Sun Z, Li C, Zhang X, Kong M, Zheng S, Dionysiou DD (2019) Monodispersed CuFe2O4 nanoparticles anchored on natural kaolinite as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for bisphenol A degradation. Appl Catal B Environ 253:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.052
Du Y, Ma W, Liu P, Zou B, Ma J (2016) Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 308:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.035
Ensafi AA, Saeid F, Rezaei B, Allafchian AR (2014) NiFe2O4 nanoparticles decorated with MWCNTs as a selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor for the determination of epinephrine using differential pulse voltammetry. Anal Methods 6(17):6885–6892. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY01232A
Felista MM, Wanyonyi WC, Ongera G (2020) Adsorption of anionic dye (Reactive black 5) using macadamia seed husks: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Sci Afr 7:e00283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00283
Gayathri Manju B, Raji P (2019) Green synthesis of nickel–copper mixed ferrite nanoparticles: structural, optical, magnetic, electrochemical and antibacterial studies. J Electron Mater 48(12):7710–7720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07603-x
Ghadari R, Namazi H, Aghazadeh M (2018) Synthesis of graphene oxide supported copper–cobalt ferrite material functionalized by arginine amino acid as a new high–performance catalyst. Appl Organomet Chem 32(1):e3965. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3965
Gupta NK, Ghaffari Y, Kim S, Bae J, Kim KS, Saifuddin M (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants over MFe2 O4 (M= Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) nanoparticles at neutral pH. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61930-2
Hamzeh Y, Ashori A, Azadeh E, Abdulkhani A (2012) Removal of Acid Orange 7 and Remazol Black 5 reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel biosorbent. Mater Sci Eng C 32(6):1394–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.04.015
Han W, Li D, Zhang M, Ximin H, Duan X, Liu S, Wang S (2020) Photocatalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by surface-tailored carbon quantum dots. J Hazard Mater 395:122695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122695
He D, Li Y, Lyu C, Song L, Feng W, Zhang S (2020) New insights into MnOOH/peroxymonosulfate system for catalytic oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol: morphology dependence and mechanisms. Chemosphere 255:126961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126961
Iranpour F, Pourzamani H, Mengelizadeh N, Bahrami P, Mohammadi H (2018) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of reactive black 5 removal by three dimensional electro-Fenton process. J Environ Chem Eng 6(2):3418–3435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.05.023
Karimi H, Rajabi HR, Kavoshi L (2020) Application of decorated magnetic nanophotocatalysts for efficient photodegradation of organic dye: a comparison study on photocatalytic activity of magnetic zinc sulfide and graphene quantum dots. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 397:112534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112534
Kermani M, Farzadkia M, Morovati M, Taghavi M, Fallahizadeh S, Khaksefidi R, Norzaee S (2020) Degradation of furfural in aqueous solution using activated persulfate and peroxymonosulfate by ultrasound irradiation. J Environ Manag 266:110616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110616
Kesavan G, Nataraj N, Chen S-M, Lin L-H (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for the electrochemical detection of bisphenol A. New J Chem 44(19):7698–7707. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ00608D
Kharisov BI, Dias HVR, Kharissova OV (2019) Mini-review: ferrite nanoparticles in the catalysis. Arab J Chem 12(7):1234–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.10.049
Kim T-Y, Park S-S, Cho S-Y (2012) Adsorption characteristics of Reactive Black 5 onto chitosan beads cross-linked with epichlorohydrin. J Ind Eng Chem 18(4):1458–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.02.006
La DD, Nguyen TA, Jones LA, Bhosale SV (2017) Graphene-supported spinel CuFe2O4 composites: novel adsorbents for arsenic removal in aqueous media. Sensors 17(6):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061292
Laohaprapanon S, Matahum J, Tayo L, You S-J (2015) Photodegradation of Reactive Black 5 in a ZnO/UV slurry membrane reactor. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 49:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.11.017
Lee H, Lee H-J, Jeong J, Lee J, Park N-B, Lee C (2015) Activation of persulfates by carbon nanotubes: Oxidation of organic compounds by nonradical mechanism. Chem Eng J 266:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.065
Masotti A, Caporali A (2013) Preparation of magnetic carbon nanotubes (Mag-CNTs) for biomedical and biotechnological applications. Int J Mol Sci 14(12):24619–24642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224619
Meriç S, Kaptan D, Ölmez T (2004) Color and COD removal from wastewater containing Reactive Black 5 using Fenton’s oxidation process. Chemosphere 54(3):435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.08.010
Mohammadi Amini M, Mengelizadeh N (2020) Catalytic degradation of mefenamic acid by peroxymonosulfate activated with MWCNTs-CoFe2O4: influencing factors, degradation pathway, and comparison of activation processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45324–45335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10427-6
Nabil GM, El-Mallah NM, Mahmoud ME (2014) Enhanced decolorization of reactive black 5 dye by active carbon sorbent-immobilized-cationic surfactant (AC-CS). J Ind Eng Chem 20(3):994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.06.034
Obasi PN, Akudinobi BB (2020) Potential health risk and levels of heavy metals in water resources of lead–zinc mining communities of Abakaliki, southeast Nigeria. Appl Water Sci 10(7):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01233-z
Othman I, Abu Haija M, Ismail I, Zain JH, Banat F (2019) Preparation and catalytic performance of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide (CuFe2O4/rGO) for phenol degradation. Mater Chem Phys 238:121931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121931
Palas B, Ersöz G, Atalay S (2018) Catalytic wet air oxidation of Reactive Black 5 in the presence of LaNiO3 perovskite catalyst as a green process for azo dye removal. Chemosphere 209:823–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.151
Peng J, Zhou H, Liu W, Ao Z, Ji H, Liu Y, Su S, Yao G, Lai B (2020) Insights into heterogeneous catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by natural chalcopyrite: pH-dependent radical generation, degradation pathway and mechanism. Chem Eng J 397:125387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125387
Rajabi HR, Sajadiasl F, Karimi H, Alvand ZM (2020) Green synthesis of zinc sulfide nanophotocatalysts using aqueous extract of Ficus Johannis plant for efficient photodegradation of some pollutants. J Mater Res Technol 9(6):15638–15647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.11.017
Rajabzadeh M, Khalifeh R, Eshghi H, Bakavoli M (2018) A facile hydrothermal synthesis of novel hollow triple-shell CuNiFe2O4 nanospheres with robust catalytic performance in the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. J Catal 360:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2018.01.028
Rao P, Godbole RV, Bhagwat S (2016) Copper doped nickel ferrite nano-crystalline thin films: A potential gas sensor towards reducing gases. Mater Chem Phys 171:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.01.016
Rigo C, Severo EC, Mazutti MA et al (2017) Preparation of nickel ferrite/carbon nanotubes composite by microwave irradiation technique for use as catalyst in photo-fenton reaction. Mater Res 20:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0672
Roushani M, Mavaei M, Daneshfar A, Rajabi HR (2017) Application of graphene quantum dots as green homogenous nanophotocatalyst in the visible-light-driven photolytic process. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(7):5135–5143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6169-7
Shahamat YD, Zazouli MA, Zare MR, Mengelizadeh N (2019) Catalytic degradation of diclofenac from aqueous solutions using peroxymonosulfate activated by magnetic MWCNTs-CoFe3 O4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 9(29):16496–16508. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02757B
Suwattanamala A, Bandis N, Tedsree K, Issro C (2017) Synthesis, characterization and adsorption properties of Fe3O4 /MWCNT magnetic nanocomposites. Mater Today: Proc 4(5, Part 2):6567–6575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.06.169
Tan C, Lu X, Cui X, Jian X, Hu Z, Dong Y, Liu X, Huang J, Deng L (2019) Novel activation of peroxymonosulfate by an easily recyclable VC@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhanced degradation of sulfadiazine. Chem Eng J 363:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.145
Tian R, Dong H, Chen J, Li R, Xie Q (2020) Amorphous Co3O4 nanoparticles-decorated biochar as an efficient activator of peroxymonosulfate for the removal of sulfamethazine in aqueous solution. Sep Purif Technol 250:117246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117246
Tuan Nguyen HD, Nguyen HT, Nguyen TT, le Thi AK, Nguyen TD, Phuong Bui QT, Bach LG (2019) The preparation and characterization of MnFe2O4-decorated expanded graphite for removal of heavy oils from water. Materials 12(12):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121913
Velinov N, Petrova T, Ivanova R, Tsoncheva T, Kovacheva D, Mitov I (2020) Synthesis and characterization of copper-nickel ferrite catalysts for ethyl acetate oxidation. Hyperfine Interact 241(1):31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-019-1654-z
Wang Z, Du Y, Liu Y, Zou B, Xiao J, Ma J (2016) Degradation of organic pollutants by NiFe2O4/peroxymonosulfate: efficiency, influential factors and catalytic mechanism. RSC Adv 6(13):11040–11048. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA21117D
Wang Y, Tian D, Chu W, Li M, Lu X (2019) Nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as an activator of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of antibiotics norfloxacin. Sep Purif Technol 212:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.051
Wang Y, Li X, Hu X-L, Su Z-M (2020) A novel 3D cobalt(II) metal–organic framework to activate peroxymonosulfate for degradation of organic dyes in water. J Solid State Chem 289:121443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121443
Wu L-K, Wu H, Zhang H-B, Cao HZ, Hou GY, Tang YP, Zheng GQ (2018) Graphene oxide/CuFe2O4 foam as an efficient absorbent for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J 334:1808–1819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.096
Xi T, Li X, Zhang Q et al (2021) Enhanced catalytic oxidation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol via singlet oxygen dominated peroxymonosulfate activation on CoOOH@ Bi 2 O 3 composite. Front Environ Sci Eng 15(4):1–11
Yao Y, Xu F, Chen M, Xu Z, Zhu Z (2010) Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on carbon nanotubes. Bioresour Technol 101(9):3040–3046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.042
Zhao Z, Zhao J, Yang C (2017) Efficient removal of ciprofloxacin by peroxymonosulfate/Mn3O4-MnO2 catalytic oxidation system. Chem Eng J 327:481–489
Zhou X, Kong L, Jing Z, Wang S, Lai Y, Xie M, Ma L, Feng Z, Zhan J (2020) Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic β-CD-MnFe2O4 as a peroxymonosulfate activator for efficient removal of 2,4- dichlorophenol: structure, performance, and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 394:122528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122528
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Islamic Azad University of Bushehr for the technical support of the research.
Funding
This research was supported by the Islamic Azad University of Bushehr.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tayebeh Tabatabaie conceived of the presented idea. The first draft was written by Mehdi Alhamd. Iman Parseh and Fazel Amiri developed the theory, performed the computations, and verified the analytical methods. Nezamaddin Mengelizadeh performed the experiments. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors certify that this manuscript is the original work of the authors, all data collected during the study are presented in this manuscript, and no data from the study has been or will be published elsewhere separately.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1755 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhamd, M., Tabatabaie, T., Parseh, I. et al. Magnetic CuNiFe2O4 nanoparticles loaded on multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a novel catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of reactive black 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57099–57114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14590-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14590-2