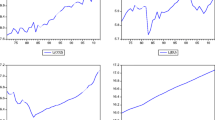
Abstract
Greenhouse gases are the major issues globally leading to climate change and increased pollution of the atmosphere. CO2 emissions have divergent effect to the environment that also causes the economic performance of any country. The main motive of this analysis was to expose the influence of CO2 emission on population growth, fossil fuel energy consumption, economic progress, and energy usage in Nepal by using time series data ranging from 1971 to 2019, and data stationarity was checked with the help of unit root tests. An autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) method with cointegration test was employed to adjudicate the variable dynamics with short- and long-run evidence. Furthermore, variable causality was tested through the Granger causality test. Study findings show that during long-run analysis that fossil fuel energy consumption and energy utilization has constructive affinity with carbon dioxide emission that exposed the p-values (0.0000) and (0.1065) correspondingly, while population growth and economic progress uncovered an inimical relation to CO2 emission. Similarly, the outcomes via short-run analysis also show that fossil fuel energy consumption and energy utilization have productive relation with CO2 emission which shows the p-values (0.0000) and (0.1317), while population growth and economic progress demonstrate an adverse influence to CO2 emission. The causality test results also validate a unidirectional linkage among variables. In attempt to participate in the global fight to clean up the atmosphere, the Nepali government and officials must take new measures to reduce CO2 emissions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CO2e:
-
Carbon dioxide emission
- ARDL:
-
Autoregressive distributed lag
- WDI:
-
World Development Indicators
- POPUG:
-
Population growth
- FOFUEC:
-
Fossil fuel energy consumption
- ECOGRO:
-
Economic growth
- ENGU:
-
Energy use
- UECM:
-
Unrestricted Error Correction Model
- P-P:
-
Phillips-Perron
- ADF:
-
Augmented Dickey-Fuller
- ECM:
-
Error Correction Model
References
Adom PK, Bekoe W, Amuakwa-Mensah F, Mensah JT, Botchway E (2012) Carbon dioxide emissions, economic growth, industrial structure, and technical efficiency: empirical evidence from Ghana, Senegal, and Morocco on the causal dynamics. Energy 47(1):314–325
Ahmad M, Akram W, Ikram M, Shah AA, Rehman A, Chandio AA, Jabeen G (2021a) Estimating dynamic interactive linkages among urban agglomeration, economic performance, carbon emissions, and health expenditures across developmental disparities. Sustainable Production and Consumption 26:239–255
Ahmad M, Chandio AA, Solangi YA, Shah SAA, Shahzad F, Rehman A, Jabeen G (2021b) Dynamic interactive links among sustainable energy investment, air pollution, and sustainable development in regional China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(2):1502–1518
Ahmad M, Rehman A, Shah SAA, Solangi YA, Chandio AA, Jabeen G (2021c) Stylized heterogeneous dynamic links among healthcare expenditures, land urbanization, and CO2 emissions across economic development levels. Sci Total Environ 753:142228
Aïssa MSB, Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2014) Output, renewable energy consumption and trade in Africa. Energy Policy 66:11–18
Alam MJ, Begum IA, Buysse J, Rahman S, Van Huylenbroeck G (2011) Dynamic modeling of causal relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in India. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15(6):3243–3251
Alam MJ, Begum IA, Buysse J, Van Huylenbroeck G (2012) Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth nexus in Bangladesh: cointegration and dynamic causality analysis. Energy Policy 45:217–225
Alimi M, Rhif A, Rebai A (2017) Nonlinear dynamic of the renewable energy cycle transition in Tunisia: evidence from smooth transition autoregressive models. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(13):8670–8679
Alvarado R, Ortiz C, Jiménez N, Ochoa-Jiménez D, Tillaguango B (2021a) Ecological footprint, air quality and research and development: the role of agriculture and international trade. J Clean Prod 288:125589
Alvarado R, Tillaguango B, López-Sánchez M, Ponce P, Işık C (2021b) Heterogeneous impact of natural resources on income inequality: the role of the shadow economy and human capital index. Econ Analysis and Policy 69:690–704
Antonakakis N, Chatziantoniou I, Filis G (2017) Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: an ethical dilemma. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:808–824
Apergis N, Payne JE (2010) Renewable energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from a panel of OECD countries. Energy Policy 38(1):656–660
Arouri MEH, Youssef AB, M’henni H, Rault C (2012) Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 45:342–349
Aye GC, Edoja PE (2017) Effect of economic growth on CO2 emission in developing countries: evidence from a dynamic panel threshold model. Cogent Economics & Finance 5(1):1379239
Azam M, Khan AQ, Ozturk I (2019) The effects of energy on investment, human health, environment and economic growth: empirical evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(11):10816–10825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04497-4
Bekhet HA, Matar A, Yasmin T (2017) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development in GCC countries: dynamic simultaneous equation models. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:117–132
Bento JPC, Moutinho V (2016) CO2 emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and international trade in Italy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:142–155
Bhattacharya M, Churchill SA, Paramati SR (2017) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renew Energy 111:157–167
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü (2016) The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: a revisited Environmental Kuznets Curve approach. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:838–845
Carvalho TS, Santiago FS, Perobelli FS (2013) International trade and emissions: the case of the Minas Gerais state—2005. Energy Econ 40:383–395
Chaudhary R, Bisai S (2018) Factors influencing green purchase behavior of millennials in India. Management Environ Quality: An Intern J 29:798–812
Chaudhry A (2010) A panel data analysis of electricity demand in Pakistan. Lahore Journal of Economics, 15(Special Edition), 75-106
Chishti MZ, Ahmad M, Rehman A, Khan MK (2021) Mitigations pathways towards sustainable development: assessing the influence of fiscal and monetary policies on carbon emissions in BRICS economies. J Clean Prod 292:126035
Chiu YB (2017) Carbon dioxide, income and energy: evidence from a non-linear model. Energy Econ 61:279–288
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74(366a):427–431
Dinda S (2008) Climate change and human insecurity. International Journal of Global Environmental Issues 9(1-2):103–109
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew Energy 94:429–439
Dong K, Sun R, Dong X (2018) CO2 emissions, natural gas and renewables, economic growth: assessing the evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 640:293–302
Ehigiamusoe KU, Lean HH (2019) Effects of energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development on carbon emissions: evidence from heterogeneous income groups. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):22611–22624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05309-5
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156
Ghezloun A, Oucher N, Chergui S (2012) Energy policy in the context of sustainable development: case of Algeria and Tunisia. Energy Procedia 18:53–60
Goh T, Ang BW (2018) Quantifying CO2 emission reductions from renewables and nuclear energy–some paradoxes. Energy Policy 113:651–662
Han J, Du T, Zhang C, Qian X (2018) Correlation analysis of CO2 emissions, material stocks and economic growth nexus: evidence from Chinese provinces. J Clean Prod 180:395–406
Hasnisah A, Azlina AA, Che CMI (2019) The impact of renewable energy consumption on carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from developing countries in Asia. Int J Energy Econ Policy 9(3):135. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.7535
Hu JL, Lin CH (2008) Disaggregated energy consumption and GDP in Taiwan: a threshold co-integration analysis. Energy Econ 30(5):2342–2358
Hussain I, Rehman A (2021) Exploring the dynamic interaction of CO2 emission on population growth, foreign investment, and renewable energy by employing ARDL bounds testing approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13502-8
Irfan M, Zhao ZY, Panjwani MK, Mangi FH, Li H, Jan A, Ahmad M, Rehman A (2020) Assessing the energy dynamics of Pakistan: prospects of biomass energy. Energy Rep 6:80–93
Jardón A, Kuik O, Tol RS (2017) Economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions: an analysis of Latin America and the Caribbean. Atmósfera 30(2):87–100
Javid M, Sharif F (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve and financial development in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:406–414
Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2017) The role of renewable energy and agriculture in reducing CO2 emissions: evidence for North Africa countries. Ecol Indic 74:295–301
Johansen S, Juselius K (1990) Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—with applications to the demand for money. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 52(2):169–210
Joo YJ, Kim CS, Yoo SH (2015) Energy consumption, Co2 emission, and economic growth: evidence from Chile. Internat j green ener 12(5):543–550
Khan MK, Teng JZ, Khan MI (2019) Effect of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan with dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23480–23490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05640-x
Knox P, Agnew JA, McCarthy L (2014) The geography of the world economy. Routledge, sixth edition
Koçak E, Şarkgüneşi A (2017) The renewable energy and economic growth nexus in Black Sea and Balkan countries. Energy Policy 100:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.007
Kwakwa PA, Alhassan H, Adu G (2020) Effect of natural resources extraction on energy consumption and carbon dioxide emission in Ghana. Intern J Ener Sector Management 14(1):20–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-09-2018-0003
Lee JW (2013) The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 55:483–489
Li R, Su M (2017) The role of natural gas and renewable energy in curbing carbon emission: case study of the United States. Sustainability 9(4):600
Loizides J, Vamvoukas G (2005) Government expenditure and economic growth: evidence from trivariate causality testing. J Appl Econ 8(1):125–152
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16478–16494
Lv Z (2017) The effect of democracy on CO2 emissions in emerging countries: does the level of income matter? Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:900–906
Magazzino C (2016) The relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Italy. Intern J Sustain Ener 35(9):844–857
Maji IK, Sulaiman C, Abdul-Rahim AS (2019) Renewable energy consumption and economic growth nexus: a fresh evidence from West Africa. Energy Rep 5:384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.03.005
Martinho VJPD (2016) Energy consumption across European Union farms: efficiency in terms of farming output and utilized agricultural area. Energy 103:543–556
Nasrollahi Z, Hashemi MS, Bameri S, Taghvaee VM (2020) Environmental pollution, economic growth, population, industrialization, and technology in weak and strong sustainability: using STIRPAT model. Environ Dev Sustain 22(2):1105–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0237-5
Ohler A, Fetters I (2014) The causal relationship between renewable electricity generation and GDP growth: a study of energy sources. Energy Econ 43:125–139
Olale E, Ochuodho TO, Lantz V, El Armali J (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve model for greenhouse gas emissions in Canada. J Clean Prod 184:859–868
Pao HT, Yu HC, Yang YH (2011) Modeling the CO2 emissions, energy use, and economic growth in Russia. Energy 36(8):5094–5100
Paramati SR, Mo D, Gupta R (2017) The effects of stock market growth and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Energy Econ 66:360–371
Perera F (2018) Pollution from fossil-fuel combustion is the leading environmental threat to global pediatric health and equity: solutions exist. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(1):16
Pesaran HH, Shin Y (1998) Generalized impulse response analysis in linear multivariate models. Econ Lett 58(1):17–29
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Phillips PC, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 75:335–346
Rehman A, Rauf A, Ahmad M, Chandio AA, Deyuan Z (2019) The effect of carbon dioxide emission and the consumption of electrical energy, fossil fuel energy, and renewable energy, on economic performance: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(21):21760–21773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05550-y
Rehman A, Zhang D, Chandio AA, Irfan M (2020a) Does electricity production from different sources in Pakistan have dominant contribution to economic growth? Empirical evidence from long-run and short-run analysis. Electr J 33(3):106717
Rehman A, Ma H, Ozturk I, Ahmad M, Rauf A, Irfan M (2020b) Another outlook to sector-level energy consumption in Pakistan from dominant energy sources and correlation with economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09245-7
Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021a) Towards environmental sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
Rehman A, Ma H, Chishti MZ, Ozturk I, Irfan M, Ahmad M (2021b) Asymmetric investigation to track the effect of urbanization, energy utilization, fossil fuel energy and CO 2 emission on economic efficiency in China: another outlook. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(14):17319–17330
Rehman A, Ma H, Ozturk I, Murshed M, Dagar V (2021c) The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: a roadmap to sustainable development. In: The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: a roadmap to sustainable development. Environment, Development and Sustainability, pp 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01418-9
Riti JS, Song D, Shu Y, Kamah M (2017) Decoupling CO2 emission and economic growth in China: is there consistency in estimation results in analyzing environmental Kuznets curve? J Clean Prod 166:1448–1461
Saidi K, Hammami S (2015) The impact of CO2 emissions and economic growth on energy consumption in 58 countries. Energy Rep 1:62–70
Salim RA, Hassan K, Shafiei S (2014) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic activities: further evidence from OECD countries. Energy Econ 44:350–360
Sanglimsuwan K (2011) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: an econometric analysis. Int Res J Financ Econ 67(1):97–102
Sebri M, Ben-Salha O (2014) On the causal dynamics between economic growth, renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and trade openness: fresh evidence from BRICS countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 39:14–23
Shabbir MS, Shahbaz M, Zeshan M (2014) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, real GDP and CO2 emissions nexus: a structural VAR approach in Pakistan. Bulletin of Energy Economics 2(3):91–105
Shah SAA, Longsheng C (2020) New environmental performance index for measuring sector-wise environmental performance: a case study of major economic sectors in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(33):41787–41802
Song J, Yang W, Wang S, Wang XE, Higano Y, Fang K (2018) Exploring potential pathways towards fossil energy-related GHG emission peak prior to 2030 for China: an integrated input-output simulation model. J Clean Prod 178:688–702
Spetan AA (2016) Renewable energy consumption, CO2 Emissions and Economic growth: a case of Jordan. International Journal of Business and Economics Research 5(6):217–226
Ulucak R, Khan SUD (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain Cities Soc 54:101996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101996
Wang S, Fang C, Guan X, Pang B, Ma H (2014) Urbanisation, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: a panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl Energy 136:738–749
Wang Z, Zhang B, Wang B (2018) Renewable energy consumption, economic growth and human development index in Pakistan: evidence form simultaneous equation model. J Clean Prod 184:1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.260
Younis I, Naz A, Shah SAA, Nadeem M, Longsheng C (2021) Impact of stock market, renewable energy consumption and urbanization on environmental degradation: new evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12731-1
Zhao X, Zhang X, Li N, Shao S, Geng Y (2017) Decoupling economic growth from carbon dioxide emissions in China: a sectoral factor decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 142:3500–3516
Ziabakhsh-Ganji Z, Kooi H (2012) An Equation of State for thermodynamic equilibrium of gas mixtures and brines to allow simulation of the effects of impurities in subsurface CO2 storage. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 11:S21–S34
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kalpana Regmi: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, visualization, writing the original draft; Abdul Rehman: investigation, visualization, formal analysis, review, editing, and made suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Regmi, K., Rehman, A. Do carbon emissions impact Nepal’s population growth, energy utilization, and economic progress? Evidence from long- and short-run analyses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 55465–55475 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14546-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14546-6