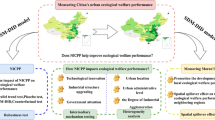
Abstract
The advancement of technological innovations may facilitate the coordinated development of the economy and ecological environment (EGE); however, few studies have noted the role of innovation efficiency (INEF) as a bridge between economic development and EGE. To fill in this gap, this paper adopts DMSP/OLS nighttime light data to measure the level of economic development and the improved data envelopment analysis model to measure INEF, establishing an index system to quantify EGE. Then we propose the panel threshold-mediating (PTM) model that combines the panel threshold model and the mediating effect model. On these bases, considering INEF as a mediator, we use this novel PTM model to empirically test the nonlinear relationship between economic development and EGE in 283 Chinese cities from 2003 to 2018. The results indicate that (1) while economic development can improve EGE, its positive impact on EGE differs with different INEF thresholds. A higher INEF threshold indicates a stronger positive effect of economic development on EGE. (2) For the entire sample, the mediating effect of INEF between economic development and EGE is not significant. However, after applying the PTM model, we found that the mediating effect of INEF was concealed by the sample population. (3) When INEF is lower than 0.2381, its complete mediating effect is verified. When INEF is higher than 0.2381, its mediating effect is not significant. On the contrary, economic development directly improves EGE. (4) Industrial agglomeration, the scale of government expenditure, residents’ education level, degree of opening up, and transport infrastructure are all conducive to EGE. These findings can help cities at different INEF levels to achieve coordinated development of economy and EGE.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials used to support the findings of this study are shared by the requesting author.
References
Abid M (2017) Does economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental quality? A comparative analysis of EU and MEA countries. J Environ Manag 188:183–194
Acaravci A, Ozturk I (2010) On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 35(12):5412–5420
Amara DB, Chen H (2020) A mediation-moderation model of environmental and eco-innovation orientation for sustainable business growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Antonakakis N, Chatziantoniou I, Filis G (2017) Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: an ethical dilemma. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:808–824
Apergis N (2016) Environmental Kuznets curves: new evidence on both panel and country-level CO2 emissions. Energy Econ 54:263–271
Armeanu D, Vintilă G, Andrei JV, Gherghina ŞC, Drăgoi MC, Teodor C (2018) Exploring the link between environmental pollution and economic growth in EU-28 countries: is there an environmental Kuznets curve? PLoS One 13(5):e0195708
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113:356–367
Barnes SJ (2019) Understanding plastics pollution: the role of economic development and technological research. Environ Pollut 249:812–821
Bennett MM, Smith LC (2017) Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens Environ 192:176–197
Cagno E, Ramirez-Portilla A, Trianni A (2015) Linking energy efficiency and innovation practices: empirical evidence from the foundry sector. Energy Policy 83:240–256
Cao X, Deng M, Song F, Zhong S, Zhu J (2019) Direct and moderating effects of environmental regulation intensity on enterprise technological innovation: the case of China. PLoS One 14(10):e0223175
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Chen X, Nordhaus WD (2011) Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(21):8589–8594
Chen W, Si W, Chen ZM (2020) How technological innovations affect urban eco-efficiency in China: a prefecture-level panel data analysis. J Clean Prod 122479
Cheng Y, Awan U, Ahmad S, Tan Z (2021) How do technological innovation and fiscal decentralization affect the environment? A story of the fourth industrial revolution and sustainable growth. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 162:120398
Chin AT (1996) Containing air pollution and traffic congestion: transport policy and the environment in Singapore. Atmos Environ 30(5):787–801
Cruz-Cázares C, Bayona-Sáez C, García-Marco T (2013) You can’t manage right what you can’t measure well: technological innovation efficiency. Res Policy 42(6–7):1239–1250
Dauda L, Long X, Mensah CN, Salman M (2019) The effects of economic growth and innovation on CO 2 emissions in different regions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(15):15028–15038
Dauda L, Xingle L, Mensah CN, Salman M, Boamah KB, Ampon-Wireko S, Dogbe CSK (2020) Innovation, trade openness and CO2 emissions in selected countries in Africa. J Clean Prod:125143
de Leeuw FA, Moussiopoulos N, Sahm P, Bartonova A (2001) Urban air quality in larger conurbations in the European Union. Environ Model Softw 16(4):399–414
Destek MA, Manga M (2021) Technological innovation, financialization, and ecological footprint: evidence from BEM economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Destek MA, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2018) Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: the role of ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29387–29396
Dong F, Zhang Y, Zhang X (2020) Applying a data envelopment analysis game cross-efficiency model to examining regional ecological efficiency: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 122031
Erdoğan S, Yıldırım S, Yıldırım DÇ, Gedikli A (2020) The effects of innovation on sectoral carbon emissions: evidence from G20 countries. J Environ Manag 267:110637
Fan Y, Fang C, Zhang Q (2019) Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J Clean Prod 229:289–298
Fan F, Cao D, Ma N (2020a) Is improvement of innovation efficiency conducive to haze governance? Empirical evidence from 283 Chinese cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(17):6095
Fan F, Lian H, Wang S (2020b) Can regional collaborative innovation improve innovation efficiency? An empirical study of Chinese cities. Growth Chang 51(1):440–463
Feleki E, Vlachokostas C, Moussiopoulos N (2018) Characterisation of sustainability in urban areas: an analysis of assessment tools with emphasis on European cities. Sustain Cities Soc 43:563–577
Fernández YF, López MF, Blanco BO (2018) Innovation for sustainability: the impact of R&D spending on CO2 emissions. J Clean Prod 172:3459–3467
Fethi S, Rahuma A (2019) The role of eco-innovation on CO 2 emission reduction in an extended version of the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from the top 20 refined oil exporting countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(29):30145–30153
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156
Gan X, Fernandez IC, Guo J, Wilson M, Zhao Y, Zhou B, Wu J (2017) When to use what: methods for weighting and aggregating sustainability indicators. Ecol Indic 81:491–502
Gan T, Yang H, Liang W (2020) How do urban haze pollution and economic development affect each other? Empirical evidence from 287 Chinese cities during 2000–2016. Sustain Cities Soc 102642
Ghisetti C, Quatraro F (2017) Green technologies and environmental productivity: a cross-sectoral analysis of direct and indirect effects in Italian regions. Ecol Econ 132:1–13
Gill AR, Viswanathan KK, Hassan S (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) and the environmental problem of the day. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:1636–1642
Gormus S, Aydin M (2020) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis using innovation: new evidence from the top 10 innovative economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27904–27913
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1992) Environmental impacts of a north American free trade agreement (no. w3914). National Bureau of Economic Research
Guo Y, Tong L, Mei L (2020a) The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J Clean Prod 258:120584
Guo Y, Zhang Q, Lai KK, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhang W (2020b) The impact of urban transportation infrastructure on air quality. Sustainability 12(14):5626
Hansen BE (1999) Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: estimation, testing, and inference. J Econ 93(2):345–368
Hao W, Rasul F, Bhatti Z, Hassan MS, Ahmed I, Asghar N (2021) A technological innovation and economic progress enhancement: an assessment of sustainable economic and environmental management. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Henderson JV, Storeygard A, Weil DN (2012) Measuring economic growth from outer space. Am Econ Rev 102(2):994–1028
Hodler R, Raschky PA (2014) Regional favoritism. Q J Econ 129(2):995–1033
Hodson EL, Brown M, Cohen S, Showalter S, Wise M, Wood F, Caron J, Feijoo F, Iyer G, Cleary K (2018) US energy sector impacts of technology innovation, fuel price, and electric sector CO2 policy: results from the EMF 32 model intercomparison study. Energy Econ 73:352–370
Hojnik J, Ruzzier M, Manolova TS (2018) Internationalization and economic performance: the mediating role of eco-innovation. J Clean Prod 171:1312–1323
Holz CA (2014) The quality of China's GDP statistics. China Econ Rev 30:309–338
Hu W, Guo Y, Tian J, Chen L (2019) Eco-efficiency of centralized wastewater treatment plants in industrial parks: a slack-based data envelopment analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 141:176–186
Huang Y, Niu Z, Yang C (2020) Testing firm-level data quality in China against Benford’s law. Econ Lett 109182
Iacovidou E, Hahladakis JN, Purnell P (2020) A systems thinking approach to understanding the challenges of achieving the circular economy. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–22
Ibrahiem DM (2020) Do technological innovations and financial development improve environmental quality in Egypt? Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(10):10869–10881
Jain D, Tiwari G (2016) How the present would have looked like? Impact of non-motorized transport and public transport infrastructure on travel behavior, energy consumption and CO2 emissions–Delhi, Pune and Patna. Sustain Cities Soc 22:1–10
Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2015) The environmental Kuznets curve, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy, and trade in Tunisia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:173–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.049
Jevons WS (1865) The coal question: can Britain survive? In: Flux AW (ed) The coal question: an inquiry concerning the progress of the nation, and the probable exhaustion of our coal-mines. Augustus M. Kelley, New York
Jin X, Li X, Feng Z, Wu J, Wu K (2020) Linking ecological efficiency and the economic agglomeration of China based on the ecological footprint and nighttime light data. Ecol Indic 111:106035
Kaika D, Zervas E (2013) The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) theory. Part B: critical issues. Energy Policy 62:1403–1411
Kais S, Sami H (2016) An econometric study of the impact of economic growth and energy use on carbon emissions: panel data evidence from fifty eight countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 59:1101–1110
Kumar S, Managi S (2009) Energy price-induced and exogenous technological change: assessing the economic and environmental outcomes. Resour Energy Econ 31(4):334–353
Levin N, Kyba CC, Zhang Q, de Miguel AS, Román MO, Li X et al (2020) Remote sensing of night lights: a review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens Environ 237:111443
Li Q, Lu L, Weng Q, Xie Y, Guo H (2016) Monitoring urban dynamics in the Southeast USA using time-series DMSP/OLS nightlight imagery. Remote Sens 8(7):578
Li W, Yi P, Zhang D, Zhou Y (2020a) Assessment of coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment: case study of resource-based cities in Northeastern China. Sustainable Cities and Society:102208
Li X, Cai G, Luo D (2020b) GDP distortion and tax avoidance in local SOEs: evidence from China. Int Rev Econ Financ 69:582–598
Liu Z, He C, Zhang Q, Huang Q, Yang Y (2012) Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc Urban Plan 106(1):62–72
Liu S, Hou P, Gao Y, Tan Y (2020) Innovation and green total factor productivity in China: a linear and nonlinear investigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–22
Low BS, Selvaraja KG, Ong TH, Ong KK, Koshy S (2020) Education background and monthly household income are factors affecting the knowledge, awareness and practice on haze pollution among Malaysians. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:30419–30425
Lu C, Xue B, Lu C, Wang T, Jiang L, Zhang Z, Ren W (2016) Sustainability investigation of resource-based cities in northeastern China. Sustainability 8(10):1058
McCormick K, Anderberg S, Coenen L, Neij L (2013) Advancing sustainable urban transformation. J Clean Prod 50:1–11
Mensah CN, Long X, Boamah KB, Bediako IA, Dauda L, Salman M (2018) The effect of innovation on CO 2 emissions of OCED countries from 1990 to 2014. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29678–29698
Mensah CN, Long X, Dauda L, Boamah KB, Salman M (2019) Innovation and CO 2 emissions: the complimentary role of eco-patent and trademark in the OECD economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):22878–22891
Miao C, Fang D, Sun L, Luo Q (2017) Natural resources utilization efficiency under the influence of green technological innovation. Resour Conserv Recycl 126:153–161
Musgrave RA (1986) Public finance in a democratic society: fiscal doctrine, growth, and institutions, vol 2. New York University Press, New York
Nelson RR (1982) The role of knowledge in R&D efficiency. Q J Econ 97(3):453–470. https://doi.org/10.2307/1885872
Nguyen TT, Pham TAT, Tram HTX (2020) Role of information and communication technologies and innovation in driving carbon emissions and economic growth in selected G-20 countries. J Environ Manag 261:110162
Nosheen M, Iqbal J, Abbasi MA (2021) Do technological innovations promote green growth in the European Union? Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:639–647
Pablo-Romero MDP, De Jesús J (2016) Economic growth and energy consumption: the energy-environmental Kuznets curve for Latin America and the Caribbean. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:1343–1350
Pao HT, Yu HC, Yang YH (2011) Modeling the CO2 emissions, energy use, and economic growth in Russia. Energy 36(8):5094–5100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.06.004
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779
Rajé F, Tight M, Pope FD (2018) Traffic pollution: a search for solutions for a city like Nairobi. Cities 82:100–107
Rawski TG (2001) What is happening to China's GDP statistics? China Econ Rev 12(4):347–354
Ruzzenenti F, Galvin R, Sorrell SR, Font Vivanco D, Wagner A, Walnum HJ (2019) The rebound effect and the Jevon's paradox: beyond the conventional wisdom. Frontiers in Energy Research 7:90
Samargandi N (2017) Sector value addition, technology and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 78:868–877
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019a) Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 646:862–871
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019b) A review on environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis using bibliometric and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 649:128–145
Seman NAA, Govindan K, Mardani A, Zakuan N, Saman MZM, Hooker RE, Ozkul S (2019) The mediating effect of green innovation on the relationship between green supply chain management and environmental performance. J Clean Prod 229:115–127
Shao Q (2020) Nonlinear effects of marine economic growth and technological innovation on marine pollution: panel threshold analysis for China's 11 coastal regions. Mar Policy 121:104110
Shen Y, Yue S, Pu Z, Lai X, Guo M (2020) Sustainable total-factor ecology efficiency of regions in China. Sci Total Environ 734:139241
Sheng Y, Zhao J, Zhang X, Song J, Miao Y (2019) Innovation efficiency and spatial spillover in urban agglomerations: a case of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Pearl River Delta. Growth Chang 50(4):1280–1310
Shi X, Wu Y, Fu D (2020) Does University-industry collaboration improve innovation efficiency? Evidence from Chinese firms⋄. Econ Model 86:39–53
Sinclair TM (2019) Characteristics and implications of Chinese macroeconomic data revisions. Int J Forecast 35(3):1108–1117
Song X, Zhou Y, Jia W (2019) How do economic openness and R&D investment affect green economic growth?—evidence from China. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:405–415
Sorrell S (2009) Jevons’ paradox revisited: the evidence for backfire from improved energy efficiency. Energy Policy 37(4):1456–1469
Su X, Mahadevan S, Xu P, Deng Y (2015) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis using evidence theory and AHP. Risk Anal 35(7):1296–1316
Sun B (2018) Heterogeneous direct rebound effect: theory and evidence from the energy star program. Energy Econ 69:335–349
Tang Y, Chen S, Huang J (2020) Green research and development activities and SO 2 intensity: an analysis for China. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–16
Tombe T, Zhu X (2019) Trade, migration, and productivity: a quantitative analysis of China. Am Econ Rev 109(5):1843–1872
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509
Tone K (2002) A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 143:32–41
Tran TH, Mao Y, Nathanail P, Siebers PO, Robinson D (2019) Integrating slacks-based measure of efficiency and super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Omega 85:156–165
Twum FA, Long X, Salman M, Mensah CN, Kankam WA, Tachie AK (2021) The influence of technological innovation and human capital on environmental efficiency among different regions in Asia-Pacific. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Wang S, Li Q, Fang C, Zhou C (2016) The relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 542:360–371
Wang SJ, Su YX, Zhao YB (2018) Regional inequality, spatial spillover effects and influencing factors of China’s city-level energy-related carbon emissions. Acta Geograph Sin 73(3):414–428
Wang S, Jia M, Zhou Y, Fan F (2019a) Impacts of changing urban form on ecological efficiency in China: a comparison between urban agglomerations and administrative areas. J Environ Plan Manag:1–23
Wang S, Zhang J, Fan F, Lu F, Yang L (2019b) The symbiosis of scientific and technological innovation efficiency and economic efficiency in China—an analysis based on data envelopment analysis and logistic model. Tech Anal Strat Manag 31(1):67–80
Wang H, Yang G, Qin J (2020) City centrality, migrants and green Inovation efficiency: evidence from 106 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(2):652
Wendling Z, Esty D, Emerson J, Levy M, de Sherbinin A et al (2018) The 2018 environmental performance index report. Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy, New Haven, CT https://epi.envirocenter.yale.edu/node/36476
Xi J (2017) Report of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China. People’s Press:35–36
Xiao W, Lv X, Zhao Y, Sun H, Li J (2020) Ecological resilience assessment of an arid coal mining area using index of entropy and linear weighted analysis: a case study of Shendong coalfield, China. Ecol Indic 109:105843
Yang N, Zhang Z, Xue B, Ma J, Chen X, Lu C (2018) Economic growth and pollution emission in China: structural path analysis. Sustainability 10(7):2569
Yang B, Jahanger A, Ali M (2021) Remittance inflows affect the ecological footprint in BICS countries: do technological innovation and financial development matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–19
Yii KJ, Geetha C (2017) The nexus between technology innovation and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: evidence from granger causality test. Energy Procedia 105:3118–3124
Yu Y, Du Y (2019) Impact of technological innovation on CO2 emissions and emissions trend prediction on ‘new Normal’economy in China. Atmospheric Pollution Research 10(1):152–161
Yu J, Zhou K, Yang S (2019) Regional heterogeneity of China's energy efficiency in “new normal”: a meta-frontier super-SBM analysis. Energy Policy 134:110941
Yuan H, Feng Y, Lee CC, Cen Y (2020) How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ 92:104944
Zaman K, Abd-el Moemen M (2017) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and economic development: evaluating alternative and plausible environmental hypothesis for sustainable growth. Renew Sust Energ Rev 74:1119–1130
Zhang J, Lawell CYCL (2017) The macroeconomic rebound effect in China. Energy Econ 67:202–212
Zhang Q, Zhang S, Ding Z, Hao Y (2017) Does government expenditure affect environmental quality? Empirical evidence using Chinese city-level data. J Clean Prod 161:143–152
Zhang L, Yang J, Li D, Liu H, Xie Y, Song T, Luo S (2019a) Evaluation of the ecological civilization index of China based on the double benchmark progressive method. J Clean Prod 222:511–519
Zhang P, Shi X, Sun Y, Cui J, Shao S (2019b) Have China's provinces achieved their targets of energy intensity reduction? Reassessment based on nighttime lighting data. Energy Policy 128:276–283
Zhou K, Zhou B, Yu M (2020) The impacts of fiscal decentralization on environmental innovation in China. Growth Chang 51(4):1690–1710
Zhu Y, Wang Z, Yang J, Zhu L (2020) Does renewable energy technological innovation control China’s air pollution? A spatial analysis. J Clean Prod 250:119515
Zugravu-Soilita N (2017) How does foreign direct investment affect pollution? Toward a better understanding of the direct and conditional effects. Environ Resour Econ 66(2):293–338
Acknowledgements
This article has been corrected by Editage (http://www.editage.cn/) in English.
Funding
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2124002-02); the 68th batch of general funding of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2020 M680960); youth project of Liaoning social science planning fund (Grant No. L20CJL001); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42071154); Major Program of the Chinese National Social Science Foundation (Grant No. 18ZDA040); and Ministry of Education Humanities and Social Sciences Research Program Fund (Grant No. 20YJA790010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Song Wang provided ideas; Jiexin Wang completed the model derivation and thesis writing; and Fei Fan did the translation and checking.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to publish
The authors carefully revised and improved the article. All authors consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Innovation efficiency (INEF) bridges economic development (ECON) and ecological environment (EGE).
• Panel threshold-mediating (PTM) model is built to test the ECON-EGE nexus in China.
• INEF is a complete mediator for ECON to improve EGE when INEF is less than 0.2381.
• ECON directly improves EGE when INEF is higher than 0.2381.
• Policy advice is proposed for Chinese cities with various INEF levels to improve EGE.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, J. & Fan, F. The hidden mediating role of innovation efficiency in coordinating development of economy and ecological environment: evidence from 283 Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 47668–47684 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13808-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13808-7