Abstract
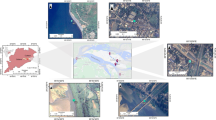
Urban river runoff carrying various anthropogenic sources of heavy metals (HMs) is the most important input pathways for HM pollutions in the coastal region, apportioning sources of environmental pollutants is key to controlling coastal HM pollution. In the study, surface sediments were collected from seven urban rivers flowing through Lianyungang City and discharging into Haizhou Bay, Eastern China. The concentrations of HMs of the river sediments were, in mg/kg (mean value ± standard deviation): Mn (550 ± 227) > Zn (67 ± 61) > Cr (33 ± 12) > Ni (21 ± 8.5) > Cu (16 ± 7.6) > Pb (15 ± 5.6) > Cd (0.11 ± 0.06), which were slightly to moderately polluted. As important outlets for municipal and industrial sewages, the Shawang River and Linhong River were the most polluted. Based on the multivariate statistical analysis, HMs were attributed to anthropogenic source (industrial, domestic, and agricultural discharges) and natural source (soil parent materials and atmospheric deposition). Based on isotope source apportionment, Pb was mainly from natural source, exhausts of leaded gasoline vehicles, and coal combustion, with the mean contributions of 39.3%, 23.7%, and 37.0%, respectively, and Sr originated from natural source and anthropogenic source, with mean contributions of 31.8% and 68.2%, respectively. Pb-Sr isotopes illustrated that anthropogenic inputs were the dominant source for HMs in urban river sediments flowing into Haizhou Bay, and the isotope tracing results make up the discriminating deficiency of the multivariate statistical analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez-Iglesias P, Rubio B, Millos J (2012) Isotopic identification of natural vs. anthropogenic lead sources in marine sediments from the inner Ría de Vigo (NW Spain). Sci Total Environ 437:22–35
Binh Thanh N, Dung Doan D, Tong Xuan N, Vinh Ngoc N, Duong Thuy Phuc N, My Hoang N, Huong Thu Thi T, Hao Phu D, Anh Hung L, Quang-Vu B (2020) Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River, Vietnam. Environ Pollut 256
Birch GF, Apostolatos C (2013) Use of sedimentary metals to predict metal concentrations in black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) tissue and risk to human health (Sydney estuary, Australia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5481–5491
Callaway JC, Delaune RD, Patrick WH (1998) Heavy metal chronologies in selected coastal wetlands from Northern Europe. Mar Pollut Bull 36:82–96
Cheema AI, Liu G, Yousaf B, Abbas Q, Zhou H (2020) A comprehensive review of biogeochemical distribution and fractionation of lead isotopes for source tracing in distinct interactive environmental compartments. Sci Total Environ 719:135658
Chen BB, Hu RQ, Chen MD (1985) The natural background values of environmental elements in the beach soils of Jiangsu province. (in Chinese). J Nanjing Agric Univ 8:54–60
Chen B, Liu J, Hu L, Liu M, Wang L, Zhang X, Fan D (2017) Spatio-temporal distribution and sources of Pb identified by stable isotopic ratios in sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent areas. Sci Total Environ 580:936–945
Cheng H, Hu Y (2010) Lead (Pb) isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China: a review. Environ Pollut 158:1134–1146
Cheng YX, Zhang R, Li TG, Zhang F, Russell J, Guan ML, Han Q, Zhou YR, Xiao X, Wang XQ (2019) Spatial distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent coastal areas based on mercury, lead and strontium isotopic compositions. Catena 174:154–163
Compiled by Lianyungang local chronicle Office (2016). Lianyungang Yearbook. http://www.book-wind.com.
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37:4311–4330
Duan X, Li Y (2017) Distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24753–24764
Fang X, Peng B, Wang X, Song Z, Zhou D, Wang Q, Qin Z, Tan C (2019) Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan province, China. Sci Total Environ 689:557–570
Feng ZH, Zhang T, Li Y, He XR, Wang R, Xu JT, Gao G (2019) The accumulation of microplastics in fish from an important fish farm and mariculture area, Haizhou Bay, China. Sci Total Environ 696:133948
Gan H, Lin J, Liang K, Xia Z (2013) Selected trace metals (As, Cd and Hg) distribution and contamination in the coastal wetland sediment of the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 66:252–258
Gao XL, Zhou FX, Chen CTA (2014) Pollution status of the Bohai Sea: an overview of the environmental quality assessment related trace metals. Environ Int 62:12–30
Han D, Cheng J, Hu X, Jiang Z, Mo L, Xu H, Ma Y, Chen X, Wang H (2017) Spatial distribution, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 115:141–148
Han B, Lin FX, Ding Y, Zheng L (2018) Distribution characteristics, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Haizhou Bay, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24:847–858
Hu X, Sun Y, Ding Z, Zhang Y, Wu J, Lian H, Wang T (2014) Lead contamination and transfer in urban environmental compartments analyzed by lead levels and isotopic compositions. Environ Pollut 187:42–48
Jeong Y-J, Cheong C-S, Shin D, Lee K-S, Jo HJ, Gautam MK, Lee I (2012) Regional variations in the lead isotopic composition of galena from southern Korea with implications for the discrimination of lead provenance. J Asian Earth Sci 61:116–127
Jiang Y-H, Jiang S-Y, Ling H-F, Dai B-Z (2006) Low-degree melting of a metasomatized lithospheric mantle for the origin of Cenozoic Yulong monzogranite-porphyry, east Tibet: Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotopic constraints. Earth Planet Sci Lett 241:617–633
JMFB (Jiangsu Marine and Fisheries Bureau), 2016. Marine environmental Quality Bulletin of Jiangsu Province(http://hyyyyj.jiangsu.gov.cn/module/download/downfile.jsp?classid=0&filename=b213c4652256440298e8c6b73c5bf2e1.pdf).
Komárek M, Ettler V, Chrastný V, Mihaljevič M (2008) Lead isotopes in environmental sciences: A review. Environ Int 34:562–577
Kong J, Guo QJ, Wei RF, Strauss H, Zhu GX, Li SL, Song ZL, Chen TB, Song B, Zhou T, Zheng GD (2018) Contamination of heavy metals and isotopic tracing of Pb in surface and profile soils in a polluted farmland from a typical karst area in southern China. Sci Total Environ 637:1035–1045
Li Y, Li HG (2017) Historical records of trace metals in core sediments from the Lianyungang coastal sea, Jiangsu, China. Mar Pollut Bull 116:56–63
Li Y, Liu FC (2015) Heavy metal concentrations and enzymatic activities in the functional zone sediments of Haizhou Bay, Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China. Environ Monit Assess 187:660
Li Y, Li HG, Liu FC (2017) Pollution in the urban soils of Lianyungang, China, evaluated using a pollution index, mobility of heavy metals, and enzymatic activities. Environ Monit Assess 189:34
Li Y, Zhang H, Shao LM, Zhou XL, He PJ (2019) Impact of municipal solid waste incineration on heavy metals in the surrounding soils by multivariate analysis and lead isotope analysis. J Environ Sci 82:47–56
Lin CQ, Yu RL, Hu GR, Yang QL, Wang XM (2016) Contamination and isotopic composition of Pb and Sr in offshore surface sediments from Jiulong River, Southeast China. Environ Pollut 218:644–650
Linkov I, von Stackelberg KE, Burmistrov D, Bridges TS (2001) Uncertainty and variability in risk from trophic transfer of contaminants in dredged sediments. Sci Total Environ 274:255–269
Liu Z, Pan S, Yin Y, Huang J, Wang A, Pang R (2010) Depositional environment and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in Linhong estuary. Geochimica 39:456–468
Liu B, Wang J, Xu M, Zhao L, Wang Z (2019a) Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Haizhou Bay national ocean park, China. Mar Pollut Bull 149:110651
Liu QX, Jia ZZ, Li SY, Hu JT (2019b) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and quantitative source apportionment in surface sediments along a partially mixed estuary (Modaomen, China). Chemosphere 225:829–838
Luo LL, Mei K, Qua LY, Zhang C, Chen H, Wang SY, Di D, Huang H, Wang ZF, Xia F, Dahlgren RA, Zhang MH (2019) Assessment of the Geographical Detector Method for investigating heavy metal source apportionment in an urban watershed of Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 653:714–722
Martin J-M, Meybeck M (1979) Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar Chem 7:173–206
Monikh FA, Safahieh A, Savari A, Doraghi A (2013) Heavy metal concentration in sediment, benthic, benthopelagic, and pelagic fish species from Musa Estuary (Persian Gulf). Environ Monit Assess 185:215–222
Naser HA (2013) Assessment and management of heavy metal pollution in the marine environment of the Arabian Gulf: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 72:6–13
N'Guessan YM, Probst JL, Bur T, Probst A (2009) Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, S-W France): where do they come from? Sci Total Environ 407:2939–2952
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Ramesh R, Chen Z, Cummins V, Day J, D’Elia C, Dennison B, Forbes DL, Glaeser B, Glaser M, Glavovic B, Kremer H, Lange M, Larsen JN, Le Tissier M, Newton A, Pelling M, Purvaja R, Wolanski E (2015) Land–ocean interactions in the coastal zone: past, present & future. Anthropocene 12:85–98
Ranjbar Jafarabadi A, Riyahi Bakhtiyari A, Shadmehri Toosi A, Jadot C (2017) Spatial distribution, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in marine surface sediments and coastal seawaters of fringing coral reefs of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Chemosphere 185:1090–1111
Reese A, Zimmermann T, Pröfrock D, Irrgeher J (2019) Extreme spatial variation of Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic signatures and 48 element mass fractions in surface sediment of the Elbe River Estuary - Suitable tracers for processes in dynamic environments? Sci Total Environ 668:512–523
Sherman LS, Blum JD, Dvonch JT, Gratz LE, Landis MS (2015) The use of Pb, Sr, and Hg isotopes in Great Lakes precipitation as a tool for pollution source attribution. Sci Total Environ 502:362–374
Sun X, He J, Shi Y, Zhu X, Li Y (2012) Spatiotemporal change in land use patterns of coupled human–environment system with an integrated monitoring approach: a case study of Lianyungang, China. Ecol Complex 12:23–33
Sun X, Fan D, Liu M, Tian Y, Pang Y, Liao H (2018) Source identification, geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ Pollut 241:938–949
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang SL, Xu XR, Sun YX, Liu JL, Li HB (2013) Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 76:7–15
Wang PC, Li ZG, Liu JL, Bi XY, Ning YQ, Yang SC, Yang XJ (2019a) Apportionment of sources of heavy metals to agricultural soils using isotope fingerprints and multivariate statistical analyses. Environ Pollut 249:208–216
Wang SS, Hu GR, Yan Y, Wang S, Yu RL, Cui JY (2019b) Source apportionment of metal elements in PM2.5 in a coastal city in Southeast China: combined Pb-Sr-Nd isotopes with PMF method. Atmos Environ 198:302–312
Wang X, Fu R, Li H, Zhang Y, Lu M, Xiao K, Zhang X, Zheng C, Xiong Y (2020a) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments: a comprehensive, large-scale evaluation for the Bohai Sea, China. Environ Pollut 260:113986
Wang X, Liu B, Zhang W (2020b) Distribution and risk analysis of heavy metals in sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:10802–10810
Wang Y, Duan X, Wang L (2020c) Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci Total Environ 710:134953
Wiederhold JG (2015) Metal stable isotope signatures as tracers in environmental geochemistry-critical review. Environ Sci Technol 49:2606–2624
Ye Z, Chen J, Gao L, Liang Z, Li S, Li R, Jin G, Shimizu Y, Onodera S-I, Saito M, Gopalakrishnan G (2020) 210Pb dating to investigate the historical variations and identification of different sources of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 150:110670
Yu R, Zhang W, Hu G, Lin C, Yang Q (2016) Heavy metal pollution and Pb isotopic tracing in the intertidal surface sediments of Quanzhou Bay, southeast coast of China. Mar Pollut Bull 105:416–421
Zhang R, Zhang F, Ding Y, Gao J, Chen J, Zhou L (2013a) Historical trends in the anthropogenic heavy metal levels in the tidal flat sediments of Lianyungang, China. J Environ Sci 25:1458–1468
Zhang R, Zhang F, Zhang TC (2013b) Sedimentary records of PAHs in a sediment core from tidal flat of Haizhou Bay, China. Sci Total Environ 450:280–288
Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhang F, Ding Y, Gao J, Chen J, Yan H, Shao W (2013c) Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 74:403–412
Zhang R, Zhang F, Zhang TC, Yan HQ, Shao W, Zhou L, Tong HB (2014) Historical sediment record and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from tidal flats of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 89:487–493
Zhang R, Guan ML, Shu YJ, Shen LY, Chen XX, Zhang F, Li TG (2016) Historical record of lead accumulation and source in the tidal flat of Haizhou Bay, Yellow Sea: insights from lead isotopes. Mar Pollut Bull 106:383–387
Zhang R, Zhang F, Guan M, Shu Y, Li T (2017) Sources and chronology of combustion-derived pollution to Shilianghe Reservoir, eastern China: evidences from PAHs profiles, As, Hg, Pb and Pb isotopes. Catena 149:232–240
Zhang Z, Lu Y, Li H, Tu Y, Liu B, Yang Z (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 645:235–243
Zhang YM, Wang J, Meng K, Qiu YF (2019) Changes of heavy metal content in sediments at Haizhou bay and risk assessment. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17:11327–11339
Zhang M, Sun X, Xu J (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the East China Sea: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111473
Zhao G, Ye S, Yuan H, Ding X, Wang J (2017) Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2966–2979
Zhao LS, Hu GR, Yan Y, Yu RL, Cui JY, Wang XM, Yan Y (2019) Source apportionment of heavy metals in urban road dust in a continental city of eastern China: Using Pb and Sr isotopes combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Atmos Environ 201:201–211
Zhou L, Lu XL, Jiang MY, Wang J (2006) Analysis and evaluation of Lianyungang coastal eco-environment based on remote sensing image. J Huaihai Instit Technol (Natural Sciences Edition) 15:63–67
Zhu A, Liu J, Qiao S, Zhang H (2020) Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea of China. Mar Pollut Bull 153:110901
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the Marine Special Program of Jiangsu Province in China (No. JSZRHYKJ202007), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1901215, 41771218, and 41271228), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST (No. 2020r047).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Funding
Marine Special Program of Jiangsu Province in China (No.): JSZRHYKJ202007.
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.): U1901215, 41771218, and 41271228.
Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST (No.): 2020r047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Longjiang Mao, Yuling Wu;
Methodology: Zhihai Tan, Wanzhu Feng;
Formal analysis and investigation: Xiaoqian Deng, Longjiang Mao;
Writing-original draft preparation: Xiaoqian Deng;
Writing-review and editing: Yuling Wu, Ye Liang;
Funding acquisition: Longjiang Mao, Yuling Wu;
Resources: Longjiang Mao, Yuanzhi Zhang;
Supervision: Yuling Wu, Longjiang Mao, Yuanzhi Zhang.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Stuart Simpson
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 223 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, X., Wu, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of the urban rivers flowing into Haizhou Bay, Eastern China: using multivariate statistical analyses and Pb-Sr isotope fingerprints. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 36354–36366 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13287-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13287-w