Abstract
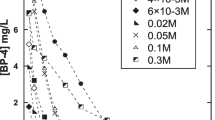
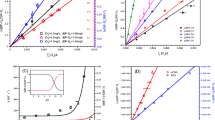
Benzophenone-3 (BP-3) is used in a wide range of personal care products and plastics to resist ultraviolet light, which has aroused considerable public concern due to its endocrine-disrupting effects. In this work, we systematically investigated the chemical oxidation process of BP-3 by KMnO4. The influences of several factors, such as pH, oxidant dose, temperature, coexisting water constituents, and water matrices, on BP-3 degradation efficiency were evaluated. The removal rate of 10 μM BP-3 could reach 91.3% in 2 h under the conditions of pH = 8.0, [BP-3]0:[KMnO4]0 = 1:20, and T = 25 °C, with the observed rate constant (kobs) value of 0.0202 min−1. The presence of typical anions (Cl−, NO3−, SO42−) and HA could slightly increase BP-3 removal, while HCO3− caused a relatively significant promotion of BP-3 degradation. On the basis of mass spectrometry and theoretical calculations, hydroxylation, direct oxidation, and carbon–carbon bridge bond cleavage were mainly involved in the oxidation process. Toxicity assessment revealed that the acute and chronic toxicities were reduced significantly, which suggested KMnO4 is a promising technique for BP-3 removal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelraheem WHM, He X, Duan X, Dionysiou DD (2015) Degradation and mineralization of organic UV absorber compound 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid (PBSA) using UV-254 nm/H2O2. J Hazard Mater 282:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.041
Balmer ME, Buser HR, Müller MD, Poiger T (2005) Occurrence of some organic UV filters in wastewater, in surface waters, and in fish from Swiss lakes. Environ Sci Technol 39:953–962. https://doi.org/10.1021/es040055r
Blair RM, Fang H, Branham WS, Hass BS, Dial SL, Moland CL, Tong W, Shi L, Perkins R, Sheehan DM (2000) The estrogen receptor relative binding affinities of 188 natural and xenochemicals: structural diversity of ligands. Toxicol Sci 54:138–153. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/54.1.138
Bu L, Shi Z, Zhou S (2017) Enhanced degradation of Orange G by permanganate with the employment of iron anode. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7777-8
Calafat AM, Wong LY, Ye X, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Concentrations of the sunscreen agent benzophenone-3 in residents of the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116:893–897. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11269
Cao W, Yu Y, Wei J, Al-Basher G, Pan X, Li B, Xu X, Alsultan N, Chen J, Qu R, Wang Z (2020) KMnO4-mediated reactions for hexachlorophene in aqueous solutions: direct oxidation, self-coupling, and cross-coupling. Chemosphere 259:127422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127422
Careghini A, Mastorgio AF, Saponaro S, Sezenna E (2015) Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5711–5741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3974-5
Chen J, Qu R, Pan X, Wang Z (2016) Oxidative degradation of triclosan by potassium permanganate: kinetics, degradation products, reaction mechanism, and toxicity evaluation. Water Res 103:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.041
Coronado M, De Haro H, Deng X, Rempel MA, Lavado R, Schlenk D (2008) Estrogenic activity and reproductive effects of the UV-filter oxybenzone (2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl-methanone) in fish. Aquat Toxicol 90:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.08.018
Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2009) Chemical analysis and ecotoxicological effects of organic UV-absorbing compounds in aquatic ecosystems. Trends Anal Chem 28:708–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2009.03.010
Díaz-Cruz MS, Gago-Ferrero P, Llorca M, Barceló D (2012) Analysis of UV filters in tap water and other clean waters in Spain. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:2325–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5560-8
Du J, Sun B, Zhang J, Guan X (2012) Parabola-like shaped pH-rate profile for phenols oxidation by aqueous permanganate. Environ Sci Technol 46:8860–8867. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302076s
Fent K, Zenker A, Rapp M (2010) Widespread occurrence of estrogenic UV-filters in aquatic ecosystems in Switzerland. Environ Pollut 158:1817–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.11.005
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery JA Jr, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam MJ, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas OV, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ (2009) Gaussian 09 (Revision A.02). Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford
Gago-Ferrero P, Badia-Fabregat M, Olivares A, Piña B, Blánquez P, Vicent T, Caminal G, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2012) Evaluation of fungal-and photo-degradation as potential treatments for the removal of sunscreens BP3 and BP1. Sci Total Environ 427:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.089
Gago-Ferrero P, Demeestere K, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2013a) Ozonation and peroxone oxidation of benzophenone-3 in water: effect of operational parameters and identification of intermediate products. Sci Total Environ 443:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.006
Gago-Ferrero P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2011) Fast pressurized liquid extraction with in-cell purification and analysis by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of UV filters and their degradation products in sediments. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:2195–2204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4951-1
Gago-Ferrero P, Mastroianni N, Silvia Diaz-Cruz MS, Barcelo D (2013b) Fully automated determination of nine ultraviolet filters and transformation products in natural waters and wastewaters by on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1294:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.04.037
Giokas DL, Salvador A, Chisvert A (2007) UV filters: from sunscreens to human body and the environment. Trends Anal Chem 26:360–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.02.012
Gong P, Yuan H, Zhai P, Xue Y, Li H, Dong W, Mailhot G (2015) Investigation on the degradation of benzophenone-3 by UV/H2O2 in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 277:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.078
Guo Y, Lin Q, Xu B, Qi F (2016) Degradation of benzophenone-3 by the ozonation in aqueous solution: kinetics, intermediates and toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7962–7974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5941-1
Jiang J, Pang S, Ma J (2009) Oxidation of triclosan by permanganate (Mn (VII)): importance of ligands and in situ formed manganese oxides. Environ Sci Technol 43:8326–8331. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901663d
Jiang J, Pang S, Ma J (2010) Role of ligands in permanganate oxidation of organics. Environ Sci Technol 44:4270–4275. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100038d
Jiang J, Pang S, Ma J, Liu H (2012) Oxidation of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals by potassium permanganate in synthetic and real waters. Environ Sci Technol 46:1774–1781. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2035587
Kunisue T, Chen Z, Louis GMB, Sundaram R, Hediger ML, Sun L, Kannan K (2012) Urinary concentrations of benzophenone-type UV filters in U.S. women and their association with endometriosis. Environ Sci Technol 46:4624–4632. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204415a
Liao C, Kannan K (2014) Widespread occurrence of benzophenone-type UV light filters in personal care products from China and the United States: an assessment of human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 48:4103–4109. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405450n
Liu H, Yao J, Wang L, Wang X, Qu R, Wang Z (2019) Effective degradation of fenitrothion by zero-valent iron powder (Fe0) activated persulfate in aqueous solution: kinetic study and product identification. Chem Eng J 358:1479–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.153
Liu Y, Ying G, Shareef A, Kookana RS (2011) Photostability of the UV filter benzophenone-3 and its effect on the photodegradation of benzotriazole in water. Environ Chem 8:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1071/en11068
Liu Y, Ying G, Shareef A, Kookana RS (2012) Biodegradation of the ultraviolet filter benzophenone-3 under different redox conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.749
Luo S, Gao L, Wei Z, Spinney R, Dionysiou DD, Hu WP, Chai L, Xiao R (2018) Kinetic and mechanistic aspects of hydroxyl radical-mediated degradation of naproxen and reaction intermediates. Water Res 137:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.002
Manasfi T, Storck V, Ravier S, Demelas C, Coulomb B, Boudenne JL (2015) Degradation products of benzophenone-3 in chlorinated seawater swimming pools. Environ Sci Technol 49:9308–9316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00841
Morohoshi K, Yamamoto H, Kamata R, Shiraishi F, Koda T, Morita M (2005) Estrogenic activity of 37 components of commercial sunscreen lotions evaluated by in vitro assays. Toxicol in Vitro 19:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2005.01.004
Negreira N, Canosa P, Rodriguez I, Ramil M, Rubi E, Cela R (2008) Study of some UV filters stability in chlorinated water and identification of halogenated by-products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1178:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.057
Pan X, Chen J, Wu N, Qi Y, Xu X, Ge J, Wang X, Li C, Qu R, Sharma VK, Wang Z (2018a) Degradation of aqueous 2,4,4'-Trihydroxybenzophenone by persulfate activated with nitrogen doped carbonaceous materials and the formation of dimer products. Water Res 143:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.038
Pan X, Yan L, Li C, Qu R, Wang Z (2017) Degradation of UV-filter benzophenone-3 in aqueous solution using persulfate catalyzed by cobalt ferrite. Chem Eng J 326:1197–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.068
Pan X, Yan L, Qu R, Wang Z (2018b) Degradation of the UV-filter benzophenone-3 in aqueous solution using persulfate activated by heat, metal ions and light. Chemosphere 196:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.152
Pang S, Jiang J, Gao Y, Zhou Y, Huangfu X, Liu Y, Ma J (2014) Oxidation of flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A by aqueous permanganate: reaction kinetics, brominated products, and pathways. Environ Sci Technol 48:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4041094
Qu R, Li C, Liu J, Xiao R, Pan X, Zeng X, Wang Z, Wu J (2018) Hydroxyl radical based photocatalytic degradation of halogenated organic contaminants and paraffin on silica gel. Environ Sci Technol 120:7220–7229. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00499
Rodil R, Moeder M, Altenburger R, Schmittjansen M (2009) Photostability and phytotoxicity of selected sunscreen agents and their degradation mixtures in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1513–1524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3113-1
Rodil R, Quintana JB, Concha-Graña E, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2012) Emerging pollutants in sewage, surface and drinking water in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 86:1040–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.053
Sanderson H, Johnson DJ, Wilson CJ, Brain RA, Solomon KR (2003) Probabilistic hazard assessment of environmentally occurring pharmaceuticals toxicity to fish, daphnids and algae by ECOSAR screening. Toxicol Lett 144:383–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00257-1
Santos AJM, Miranda MS, Esteves da Silva JCG (2012) The degradation products of UV filters in aqueous and chlorinated aqueous solutions. Water Res 46:3167–3176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.057
Schlumpf M, Cotton B, Conscience M, Haller V, Steinmann B, Lichtensteiger W (2001) In vitro and in vivo estrogenicity of UV screens. Environ Health Perspect 109:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.01109239
Schlumpf M, Kypke K, Wittassek M, Angerer J, Mascher H, Mascher D, Vökt C, Birchler M, Lichtensteiger W (2010) Exposure patterns of UV filters, fragrances, parabens, phthalates, organochlor pesticides, PBDEs, and PCBs in human milk: correlation of UV filters with use of cosmetics. Chemosphere 81:1171–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.079
Schreurs RH, Sonneveld E, Jansen JH, Seinen W, van der Burg B (2005) Interaction of polycyclic musks and UV filters with the estrogen receptor (ER), androgen receptor (AR), and progesterone receptor (PR) in reporter gene bioassays. Toxicol Sci 83:264–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi035
Suzuki T, Kitamura S, Khota R, Sugihara K, Fujimoto N, Ohta S (2005) Estrogenic and antiandrogenic activities of 17 benzophenone derivatives used as UV stabilizers and sunscreens. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.07.005
Tang R, Chen M, Ding G, Chen X, Han X, Zhou K, Chen L, Xia Y, Tian Y, Wang X (2013) Associations of prenatal exposure to phenols with birth outcomes. Environ Pollut 178:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.03.023
Vione D, Caringella R, De Laurentiis E, Pazzi M, Minero C (2013) Phototransformation of the sunlight filter benzophenone-3 (2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone) under conditions relevant to surface waters. Sci Total Environ 463:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.090
Waldemer R, Tratnyek PG (2006) Kinetics of contaminant degradation by permanganate. Environ Sci Technol 40:1055–1061. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051330s
Xiao R, Gao L, Wei Z, Spinney R, Luo S, Wang D, Dionysiou DD, Tang C-J, Yang W (2017) Mechanistic insight into degradation of endocrine disrupting chemical by hydroxyl radical: an experimental and theoretical approach. Environ Pollut 231:1446–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.006
Xu X, Chen J, Wang S, Ge J, Qu R, Feng M, Sharma VK, Wang Z (2018) Degradation kinetics and transformation products of chlorophene by aqueous permanganate. Water Res 138:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.057
Yan YE, Schwartz FW (1999) Oxidative degradation and kinetics of chlorinated ethylenes by potassium permanganate. J Contam Hydrol 37:343–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(98)00166-1
Yang B, Ying G (2013) Oxidation of benzophenone-3 during water treatment with ferrate (VI). Water Res 47:2458–2466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.018
Ye X, Zhou X, Wong L, Calafat AM (2012) Concentrations of bisphenol A and seven other phenols in pooled sera from 3-11 year old children: 2001-2002 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Sci Technol 46:12664–12671. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303109c
Zhang T, Sun H, Qin X, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Ma J, Kannan K (2013) Benzophenone-type UV filters in urine and blood from children, adults, and pregnant women in China: partitioning between blood and urine as well as maternal and fetal cord blood. Sci Total Environ 461:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.074
Zhuang J, Wang S, Tan Y, Xiao R, Chen J, Wang X, Jiang L, Wang Z (2019) Degradation of sulfadimethoxine by permanganate in aquatic environment: influence factors, intermediate products and theoretical study. Sci Total Environ 671:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.277
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21607073, 21876082) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 14380137). The authors acknowledge King Saud University for funding this work through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/149), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Data and materials availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21607073, 21876082) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 14380137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wanming Cao: investigation, data curation, validation, writing—original draft; Nannan Wu: validation, data curation, writing—review and editing); Ruijuan Qu: methodology, visualization, investigation; Cheng Sun: formal analysis; Zongli Huo: visualization, investigation; Jamaan S. Ajarem: formal analysis; Ahmed A. Allam: data curation; Zunyao Wang: writing—review and editing, supervision; Feng Zhu, data curation, visualization
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ricardo Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 686 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, W., Wu, N., Qu, R. et al. Oxidation of benzophenone-3 in aqueous solution by potassium permanganate: kinetics, degradation products, reaction pathways, and toxicity assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 31301–31311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12913-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12913-x