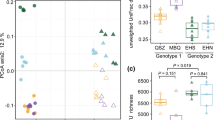
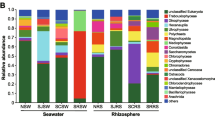
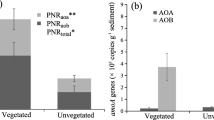
Abstract
Rhizosphere microbes are crucial to seagrass meadows because they promote plant growth and heath. However, information concerning the response of rhizosphere microorganisms in seagrass sediment in the presence of different nitrogen sources is lacking. Here, by means of high-throughput sequencing, we investigated how addition of inorganic nitrogen affects the rhizosphere microbiome of the tropical seagrass Thalassia hemperichii. A seagrass culture system was set up to conduct a nitrogen addition (ammonium and nitrate) simulation experiment. We found that the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes was increased in inorganic nitrogen-enriched samples, whereas that of Acidobacteria decreased under ammonium enrichment, especially after 35 days. High levels of inorganic nitrogen addition caused a significant decrease in the relative abundance of Desulfobacteraceae, Sulfurovaceae, and Spirochaetes, which are primarily involved in sulfur cycling. Additionally, the abundance of microbes in the seagrass rhizosphere reached the highest after the ammonium-enrichment treatment. Among the analyzed seagrass photosynthetic characteristics, seagrass leaves presented the highest light utility in treatments receiving nitrate, followed by the control groups and ammonium-enrichment groups. Moreover, 16S rRNA gene-predicted functional analysis suggested that some functions related to metabolism of amino acids and signal transduction were enriched in samples receiving high ammonium, whereas nitrate addition enriched predicted functions related to diseases. These findings provide new insights into the response of microbial communities to different types of nitrogen additions in seagrass ecosystems.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Aber J, McDowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I (1998) Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems: hypotheses revisited. BioScience 48:921–934
Alexandre A, Silva J, Santos R (2010) Inorganic nitrogen uptake and related enzymatic activity in the seagrass Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol Evol Perspect 31:539–545
Alexandre A, Silva J, Bouma TJ, Santos R (2011) Inorganic nitrogen uptake kinetics and whole-plant nitrogen budget in the seagrass Zostera noltii. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 401:7–12
Alexandre A, Silva J, Buapet P, Björk M, Santos R (2012) Effects of CO2 enrichment on photosynthesis, growth, and nitrogen metabolism of the seagrass Zostera noltii[J]. Ecol Evol 2:2625–2635
Asami H, Aida M, Watanabe K (2005) Accelerated sulfur cycle in coastal marine sediment beneath areas of intensive shellfish aquaculture. Apply Environ Microbiol 71:2925–2933
Bobbink R, Hicks K, Galloway J, Spranger T, Alkemade R, Ashmore M, Bustamante M, Cinderby S, Davidson E, Dentener F, Emmett B, Erisman JW, Fenn M, Gilliam F, Nordin A, Pardo L, de Vries W (2010) Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: a synthesis. Ecol Appl Publ Ecol Soc Am 20:30–59
Brodersen K, Koren K, Lichtenberg M, Kühl M (2016) Nanoparticle-based measurements of pH and O2 dynamics in the rhizosphere of Zostera marina L.: effects of temperature elevation and light-dark transitions. Plant Cell Environ 39:1619–1630
Burkholder J, Mason KM, Glasgow HB Jr (1992) Water-column nitrate enrichment promotes decline of eelgrass Zostera marina: evidence from seasonal mesocosm experiments. Mar Ecol Progress Ser Oldendorf 81:163–178
Burkholder JM, Tomasko DA, Touchette BW (2007) Seagrasses and eutrophication. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:46–72
Campbell BJ, Polson SW, Hanson TE, Mack MC, Schuur EA (2010) The effect of nutrient deposition on bacterial communities in Arctic tundra soil. Environ Microbiol 12:1842–1854
Cao D, Cao W, Yu K, Wu G, Yang J, Su X, Wang F (2017) Evaluation of anthropogenic influences on the Luhuitou fringing reef via spatial and temporal analyses (from isotopic values). J Geophys Res Oceans 122:4431–4443
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M, Gormley N, Gilbert JA, Smith G, Knight R (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Carvalhais LC, Dennis PG, Fedoseyenko D, Hajirezaei MR, Borriss R, von Wirén N (2011) Root exudation of sugars, amino acids, and organic acids by maize as affected by nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiency. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174:3–11
Colmer TD (2003) Long-distance transport of gases in plants: a perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots. Plant Cell Environ 26:17–36
Craine JM, Morrow C, Fierer N (2007) Microbial nitrogen limitation increases decomposition. Ecology 88:2105–2113
Cucio C, Engelen AH, Costa R et al (2016) Rhizosphere microbiomes of European seagrasses are selected by the plant, but are not species specific. Front Microbiol 7:15
Dai Y, Yan Z, Jia L, Zhang S, Gao L, Wei X, Mei Z, Liu X (2016) The composition, localization and function of low-temperature-adapted microbial communities involved in methanogenic degradations of cellulose and chitin from Qinghai- Tibetan plateau wetland soils. J Appl Microbiol 121:163–176
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Egea LG, Jiménez-Ramos R, Vergara JJ, Hernández I, Brun FG (2018) Interactive effect of temperature, acidification and ammo-nium enrichment on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Mar Pollut Bull 134:14–26
Fahimipour AK, Kardish MR, Lang JM, Green JL, Eisen JA, Stachowicz JJ (2017) Global-scale structure of the eelgrass microbiome. Appl Environ Microbiol 83
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Fierer N, Lauber CL, Ramirez KS, Zaneveld J, Bradford MA, Knight R (2012) Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME 6:1007–1017
Fourqurean JW, Duarte CM, Kennedy H, Marba N, Holmer M, Mateo MA et al (2012) Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat Geosci 5:505–509
Gacia E, Granata TC, Duarte CM (1999) An approach to measurement of particle flux and sediment retention within seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows. Aquat Bot 65:255–268
Galloway JN, Dentener F, Capone DG et al (2004) Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future[J]. Biogeochemistry 70:153–226
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892
Ge T, Li BZ, Zhu ZK, Hu YJ, Yuan HZ, Dorodnikov M et al (2017) Rice rhizodeposition and its utilization by microbial groups depends on N fertilization. Biol Fertil Soils 53:37–48
George R, Gullstrom M, Mtolera M et al (2020) Methane emission and sulfide levels increase in tropical seagrass sediments during temperature stress: a mesocosm experiment. Ecol Evol 10:1917–1928
Govers LL, Lamers LPM, Bouma TJ, de Brouwer JHF, van Katwijk MM (2014) Eutrophication threatens Caribbean seagrasses - an example from curacao and Bonaire. Mar Pollut Bull 89:481–486
Green EEP, Short FT (2003) World atlas of seagrasses. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA
Hauxwell J, Cebrian J, Valiela I (2003) Eelgrass Zostera marina loss in temperate estuaries: relationship to land-derived nitrogen loads and effect of light limitation imposed by algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 247:59–73
Hendriks IE, Olsen YS, Ramajo L, Basso L, Steckbauer A, Moore TS, Howard J, Duarte CM (2014) Photosynthetic activity buffers ocean acidification in seagrass meadows. Biogeosciences 11:333–346
Huang LM, Tan YH, Song XY, Huang XP, Wang HK, Zhang S et al (2003) The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China. Mar Pollut Bull 47:180–186
Invers O, Kraemer GP, Perez M, Romero J (2004) Effects of nitrogen addition on nitrogen metabolism and carbon reserves in the temperate seagrass Posidonia oceanica. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 303:97–114
Jensen SI, Kuhl M, Prieme A (2007) Different bacterial communities associated with the roots and bulk sediment of the seagrass Zostera marina. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:108–117
Johnson PT, Townsend AR, Cleveland CC, Glibert PM, Howarth RW, McKenzie VJ, Rejmankova E, Ward MH (2010) Linking environmental nutrient enrichment and disease emergence in humans and wildlife. Ecol Appl 20:16–29
Kaspari M, Bujan J, Weiser MD, Ning D, Michaletz ST, Zhili H, Enquist BJ, Waide RB, Zhou J, Turner BL,Wright SJ (2017) Biogeochemistry drives diversity in the prokaryotes, fungi, and invertebrates of a Panama forest. Ecology 98(8):2019–2028
Kavamura VN, Hayat R, Clark IM, Rossmann M, Mendes R, Hirsch PR, Mauchline TH (2018) Inorganic nitrogen application affects both taxonomical and predicted functional structure of wheat Rhizosphere bacterial communities. Front Microbiol 9:1074
Koren K, Brodersen KE, Jakobsen SL, Kühl M (2015) Optical sensor nanoparticles in artificial sediments–a new tool to visualize O2 dynamics around the rhizome and roots of seagrasses. Environ Sci Technol 49:2286–2292
Lamb JB, van de Water J, Bourne DG, Altier C, Hein MY, Fiorenza EA et al (2017) Seagrass ecosystems reduce exposure to bacterial pathogens of humans, fishes, and invertebrates. Science 355:731–733
Langenheder S, Szekely AJ (2011) Species sorting and neutral processes are both important during the initial assembly of bacterial communities. ISME J 5:1086–1094
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R, Beiko RG, Huttenhower C (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31:814–821
Li XB, Wang DR, Huang H, Zhang J, Lian JS, Yuan XC et al (2015) Linking benthic community structure to terrestrial runoff and upwelling in the coral reefs of northeastern Hainan Island. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 156:92–102
Liang YT, Jiang YJ, Wang F, Wen CQ, Deng Y, Xue K et al (2015) Long-term soil transplant simulating climate change with latitude significantly alters microbial temporal turnover. ISME J 9:2561–2572
Liu S, Jiang Z, Deng Y et al (2018) Effects of nutrient loading on sediment bacterial and pathogen communities within seagrass meadows. MicrobiologyOpen 7:e600
Logue JB, Lindstrom ES (2010) Species sorting affects bacterioplankton community composition as determined by 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA fingerprints. ISME J 4:729–738
Lucas R, Klaminder J, Futter M, Bishop KH, Egnell G, Laudon H et al (2011) A meta-analysis of the effects of nitrogen additions on base cations: implications for plants, soils, and streams. For Ecol Manag 262:95–104
Ma G, Kang J, Wang J, Chen Y, Lu H, Wang L, Wang C, Xie Y, Ma D, Kang G (2020) Bacterial community structure and predicted function in wheat soil from the North China plain are closely linked with soil and plant characteristics after seven years of irrigation and nitrogen application. Front Microbiol 11:506
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 27:2957–2963
Martin BC, Bougoure J, Ryan MH et al (2018) Oxygen loss from seagrass roots coincides with colonisation of sulphide-oxidising cable bacteria and reduces sulphide stress. ISME J
Martin BC, Alarcon MS, Gleeson D, Middleton JA, Fraser MW, Ryan MH, Holmer M, Kendrick GA, Kilminster K (2020) Root microbiomes as indicators of seagrass health. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 96
Mejia AY, Rotini A, Lacasella F, Bookman R, Thaller MC, Shem-Tov R, Winters G, Migliore L (2016) Assessing the ecological status of seagrasses using morphology, biochemical descriptors and microbial community analyses. A study in Halophila stipulacea (Forsk.) Aschers meadows in the northern Red Sea. Ecol Indic 60:1150–1163
Mitchell HM, Rocha GA, Kaakoush NO, O’Rourke JL, Queiroz DMM (2014) The Family Helicobacteraceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The Prokaryotes: Deltaproteobacteria and Epsilonproteobacteria. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 337–392
Moreno-Marín F, Vergara JJ, Pérez-Llorens JL, Pedersen MF, Brun FG (2016) Interaction between ammonium toxicity and green tide development over seagrass meadows: a laboratory study. PLoS One 11:e0152971
Ochieng CA, Short FT, Walker D et al (2010) Photosynthetic and morphological responses of eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) to a gradient of light conditions. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 382:117–124
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, Van Der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:789–799
Ramirez KS, Craine JM, Fierer N (2012) Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob Chang Biol 18:1918–1927
Ruiz JM, Marco-Mendez C, Sanchez-Lizaso JL (2010) Remote influence of off-shore fish farm waste on Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows. Mar Environ Res 69:118–126
Sandoval-Gil JM, Avila-Lopez MD, Camacho-Ibar VF, Hernandez-Ayon J, Zertuche-Gonzalez JA, Cabello-Pasini A (2019) Regulation of nitrate uptake by the seagrass Zostera marina during upwelling. Estuar Coasts 42:731–742
Touchette BW, Burkholder JM, Glasgow HB (2003) Variations in eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) morphology and internal nutrient composition as influenced by increased temperature and water column nitrate. Estuaries. 26:142–155
Trevathan-Tackett SM, Seymour JR, Nielsen DA, Macreadie PI, Jeffries TC, Sanderman J et al (2017) Sediment anoxia limits microbial-driven seagrass carbon remineralization under warming conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fix033
Udy JW, Dennison WC (1997) Growth and physiological responses of three seagrass species to elevated sediment nutrients in Moreton Bay, Australia[J]. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 217:253–277
Van Katwijk M, Vergeer L, Schmitz G, Roelofs J (1997) Ammonium toxicity in eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 157:159–173
Viana IG, Saavedra-Hortúa DA, Mtolera M, Teichberg M (2019) Different strategies of nitrogen acquisition in two tropical seagrasses under nitrogen enrichment[J]. New Phytol 223:1217–1229
Villazan B, Pedersen MF, Brun FG, Vergara JJ (2013) Elevated ammonium concentrations and low light form a dangerous synergy for eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 493:141–154
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJ et al (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:12377–12381
Wu CH, Sercu B, Van De Werfhorst LC, Wong J, DeSantis TZ, Brodie EL, Hazen TC, Holden PA, Andersen GL (2010) Characterization of coastal urban watershed bacterial communities leads to alternative community-based indicators. PLoS One 5:e11285
Yang XL, Zhang PD, Li WT, Hu C, Zhang X, He P (2018) Evaluation of four seagrass species as early warning indicators for nitrogen overloading: implications for eutrophic evaluation and ecosystem management. Sci Total Environ 635:1132–1143
Zahar Haichar F, Marol C, Berge O, Rangel-Castro JI, Prosser JI, Balesdent JM et al (2008) Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J 2:1221–1230
Zhang X, Wei H, Chen Q, Han X (2014) The counteractive effects of nitrogen addition and watering on soil bacterial communities in a steppe ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 72:26–34
Zhang Y, Shen H, He X, Thomas BW, Lupwayi NZ, Hao X, Thomas MC, Shi X (2017) Fertilization shapes bacterial community structure by alteration of soil pH. Front Microbiol 8:1325
Zhang X, Zhao C, Yu S, Jiang Z, Liu S, Wu Y, Huang X (2020) Rhizosphere microbial community structure is selected by habitat but not plant species in two tropical seagrass beds. Front Microbiol 11:161
Zhou J, Jiang X, Wei D, Zhao B, Ma M, Chen S, Cao F, Shen D, Guan D, Li J (2017) Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in black soils for two crop seasons in China. Sci Rep 7:3267
Zhu S, Vivanco JM, Manter DK (2016) Nitrogen fertilizer rate affects root exudation, the rhizosphere microbiome and nitrogen-use-efficiency of maize. Appl Soil Ecol 107:324–333
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all of the members of Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan for their helping work in sample collecting.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA13020300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41676163, 41406191, 41676107 and 41976147), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (201806010017), Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (GML2019ZD0402), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1406505, 2017YFC0506301 and 2018FY100105), Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISEE2018ZD02), the Guangdong Province Public Welfare Research and Capacity Building Project (2015A020216016) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2017B030314052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weiguo Zhou, Juan Ling conceived and designed the study. Weiguo Zhou collected the sample and set up a seagrass culture system with the help of Qingsong Yang and Xiancheng Lin. Junde Dong, Dewen Ding, Lijuan Long, Anning Suo, Liyun Lin, Yanying Zhang, and Juan Ling contributed to laboratory analysis and interpretation of the results. Weiguo Zhou drafted the manuscript with input from all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
N/A
Consent to participate
N/A
Consent to publish
All the authors agree for this submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Editorial Responsibility: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 78 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Dong, J., Ding, D. et al. Rhizosphere microbiome dynamics in tropical seagrass under short-term inorganic nitrogen fertilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 19021–19033 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12048-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12048-5