Abstract
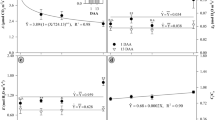
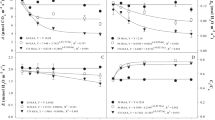
The herbicide glyphosate can cause severe ecotoxicological effects on non-target organisms. Eugenia uniflora L. (Myrtaceae) is very important for in situ environmental biomonitoring due to its wide distribution in the Atlantic Forest biome. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the response of E. uniflora leaves to glyphosate. Eight-month-old plants were exposed to an aerial application of the herbicide at concentrations of 0, 144, 432, 864, and 1440 g a. e. ha−1 (grams of acid equivalent per hectare). Evaluations were performed on the 12th day after the glyphosate application (DAA). An accumulation of shikimic acid in the leaves of E. uniflora was observed. Glyphosate altered the photosynthetic parameters of the treated plants, with a drastic decrease in the photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration, and pigment content. There was an increase in Ci/Ca, lipid peroxidation, and electrolyte extravasation levels. Glyphosate also promoted ultrastructural, anatomical and visible damage to the E. uniflora leaves. Our findings indicate that glyphosate is phytotoxic to the native species E. uniflora at the tested doses. The presence of visible damage suggests that E. uniflora has remarkable potential as a bioindicator of glyphosate in the environment, making it a possible species for future biomonitoring projects.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahsan N, Lee DG, Lee KW, Alam I, Lee SG, Bahk JD, Lee BH (2008) Glyphosate induced oxidative stress in rice leaves revealed by proteomic approach. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:1062–1070
Alves ES, Tresmondi F, Longui EL (2008) Análise estrutural de folhas de Eugenia uniflora L.(Myrtaceae) coletadas em ambientes rural e urbano, SP, Brasil. Acta Bot Bras 22:241–248
Alves ES, Moura BB, Pedroso ANV, Tresmondi F, Machado SR (2016) Cellular markers indicative of ozone stress on bioindicator plants growing in a tropical environment. Ecol Indic 67:417–424
Assis AD, Pereira OJ, Thomaz LD (2004) Fitossociologia de uma floresta de restinga no Parque Estadual Paulo César Vinha, Setiba, município de Guarapari (ES). Rev Bras Bot 27:349–361
Batista PF, Costa AC, Megguer CA, Lima JS, Silva FB, Guimarães DS, Nascimento KJT (2018) Pouteria torta: a native species of the Brazilian Cerrado as a bioindicator of glyphosate action. Braz J Biol 78:296–305
Beltrano J, Ruscitti M, Arango C, Ronco M (2013) Changes in the accumulation of shikimic acid in mycorrhized Capsicum annum grown with application of glyphosate and phosphorus. Theor Exp Plant Physiol 25:125–136
Bourguet D, Guillemaud T (2016) The hidden and external costs of pesticide use. In: Lichtfouse E (ed) Sustainable agriculture reviews. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 35–120
Boutin C (2014) Herbicides: non-target species effect. In: Jorgensen SE (ed) Encyclopedia of Environmental Management, II edn. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 1406–1417
Braz DM, Lima Jacques E, Somner GV, Silva Sylvestre L, Rosa MMT, Pereira-Moura MVL, Filho PG, Couto AVS, Amorim TA (2013) Restinga de Praia das Neves, ES, Brasil: caracterização fitofisionômica, florística e conservação. Biota Neotropica 13:315–331
Cakmak I, Yazici A, Tutus Y, Ozturk L (2009) Glyphosate reduced seed and leaf concentrations of calcium, manganese, magnesium, and iron in non Glyphosate resistant soybean. Eur J Agron 31:114–119
Christofoletti JC (1999) Considerações sobre tecnologia de aplicação nas pulverizações agrícolas e seu controle. São Paulo: Teejet South America, 15p. In: Costa AGF, Velini ED, Negrisoli E, Carbonari CA, Rossi CVS, Corrêa MR, Silva FML (2007) Efeito da intensidade do vento, da pressão e de pontas de pulverização na deriva de aplicações de herbicidas em pré-emergência. Planta Daninha. 25:203-210.
Corpas FJ, Barroso JB (2014) NADPH generating dehydrogenases: their role in the mechanism of protection against nitro oxidative stress induced by adverse environmental conditions. Front Environ Sci 2:1–5
Costa GA, Tuffi-Santos LD, Santos SA, Cruz LR, Sant Anna-Santos BF, Santos IT (2020) Efficiency of glyphosate and carfentrazone-ethyl in the control of Macroptilium atropurpureum (DC.) Urb. under different light intensities. S Afr J Bot 131:302–309
Cruz-Hipolito H, Osuna MD, Heredia A, Ruiz-Santaella JP, De Prado R (2009) Non target mechanism involved in glyphosate tolerance found in Canavalia ensiformis plants. J Agric Food Chem 57:4844–4848
Cuhra M, Bøhn T, Cuhra P (2016) Glyphosate: too much of a good thing? Front Environ Sci 4:28
Domingos M, Bulbovas P, Camargo ZSC (2015) Searching for native tree species and respective potential biomarkers for future assessment of pollution effects on the highly diverse Atlantic Forest in SE-Brazil. Environ Pollut 202:85–95
Dupont YL, Strandberg B, Damgaard C (2018) Effects of herbicide and nitrogen fertilizer on non-target plant reproduction and indirect effects on pollination in Tanacetum vulgare (Asteraceae). Agric Ecosyst Environ 262:76–82
Florencia FM, Carolina T, Enzo B, Leonrdo G (2017) Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on non-target plant native species from Chaco forest (Argentina). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:360–368
Foloni LL, Rodrigues D, Ferreira F, Miranda R, Ono EO (2005) Aplicação de glifosato em pós-emergência, em soja transgênica cultivada no Cerrado. Revista Brasileira de Herbicidas 3:47–58
Foresti ER, Nepomuceno MP, Alves PLCA (2015) Simulação da deriva de clomazone e glyphosate em mudas de laranjeira ‘Hamlin.’ Revista Brasileira de Fruticultura 37:367–376
Freitas-Silva L, Rodríguez-Ruiz M, Houmani H, da Silva LC, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (2017) Glyphosate-induced oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana affecting peroxisomal metabolism and triggers activity in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway (OxPPP) involved in NADPH generation. J Plant Physiol 218:196–205
Freitas-Silva L, Araújo TO, Nunes-Nesi A, Ribeiro C, Costa AC, Silva LC (2020) Evaluation of morphological and metabolic responses to glyphosate exposure in two neotropical plant species. Ecol Indic 113:106246
Fuchs MA, Geiger DR, Reynolds TL, Bourque JE (2002) Mechanisms of glyphosate toxicity in velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti Medikus). Pestic Biochem Physiol 74:27–39
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Gomes MP, Juneau P (2016) Oxidative stress in duckweed (Lemna minor L.) induced by glyphosate: is the mitochondrial electron transport chain a target of this herbicide? Environ Pollut 218:402–409
Gomes MP, Le Manac’h SG, Maccario S, Labrecque M, Lucotte M, Juneau P (2016a) Differential effects of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) on photosynthesis and chlorophyll metabolism in willow plants. Pestic Biochem Physiol 130:65–70
Gomes MP, Le Manac’h SG, Moingt M, Smedbol E, Paquet S, Labrecque M (2016b) Impact of phosphate on glyphosate uptake and toxicity in willow. J Hazard Mater 304:269–279
Gomes MP, Le Manac’h SG, Hénault-Ethier L, Labrecque M, Lucotte M, Juneau P (2017) Glyphosate-dependent inhibition of photosynthesis in willow. Front Plant Sci 8:207
Gove B, Power SA, Buckley GP, Ghazoul J (2007) Effects of herbicide spray drift and fertilizer overspread on selected species of woodland ground flora: comparison between short-term and long-term impact assessments and field surveys. J Appl Ecol 44:374–384
Guimarães TG, Fontes PCR, Pereira PRG, Alvarez VH, Monnerat PH (1999) Teores de clorofila determinados por medidor portátil e sua relação com formas de nitrogênio em folhas de tomateiro cultivado em dois tipos de solo. Bragantia. 58:209–210
Guo L, Ding Y, Xu Y, Li Z, Jin Y, He K, Fang Y, Zhao H (2017) Responses of Landoltia punctata to cobalt and nickel: removal, growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant system and starch metabolism. Aquat Toxicol 190:87–93
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The waterculture method for growing plants without soil. California Agricultural Experiment Station, Berkeley, p 32p
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Huang J, Silva EN, Shen Z, Jiang B, Lu H (2012) Effects of glyphosate on photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and physicochemical properties of cogongrass (Imperata cylindrical L.). Plant Omi J 5:177–183
Joly CA, Assis MA, Bernacci LC (2012) Florística e fitossociologia em parcelas permanentes da Mata Atlântica do sudeste do Brasil ao longo de um gradiente altitudinal. Biota Neotropica 12:123–145
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137–138
Kovalchuk I, Kovalchuk O (2008) Transgenic plants as sensors of environmental pollution genotoxicity. Sensors 8:1539–1558
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophyll and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In: Colowick SP (ed) 1999Methods in enzimology, 148th edn. Ademic Press, San Diego, pp 350–382
Lima DA, Müller C, Costa AC, Batista PF, Dalvi VC, Domingos M (2017) Morphoanatomical and physiological changes in Bauhinia variegata L. as indicators of herbicide diuron action. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:242–250
Lucadamo L, Corapi A, Gallo L (2018) Evaluation of glyphosate drift and anthro pogenic atmospheric trace elements contamination by means of lichen transplants in a southern Italian agricultural district. Air Qual Atmos Health 11:325–339
Lukatkin AS, Gar’kova AN, Bochkarjova AS, Olga V, Nushtaeva OV, da Silva JA (2013) Treatment with the herbicide TOPIK induces oxidative stress in cereal leaves. Pestic Biochem Physiol 105:44–49
MacFarlane GR (2003) Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a potential biomarker of zinc stress in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Bull Environ Contam 70:90–96
Mahakhode RH, Somkuwar SR (2012) Effect of spray application of herbicide gramoxone on morphoanatomical characters of weed Psoralea corylifolia L. Int J Curr Pharm Res 4:64–66
Mateos-Naranjo E, Redondo-Gómez S, Cox L, Cornejo J, Figueroa ME (2009) Effectiveness of Glyphosate and imazamox on the control of the invasive cordgrass Spartina densiflora. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1694–1700
Meschede DK, Carbonari CA, Velini ED, Trindade MLB, Gomes GLGC (2011) Efeitos do glyphosate nos teores de lignina, celulose e fibra em Brachiaria decumbens. Revista Brasileira de Herbicidas 10:57–63
Neves NR, Oliva MA, Cruz Centeno D, Costa AC, Ribas RF, Pereira EG (2009) Photosynthesis and oxidative stress in the restinga plant species Eugenia uniflora L. exposed to simulated acid rain and iron ore dust deposition: potential use in environmental risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 407:3740–3745
O’Brian PP, McCully ME (1981) The study of plants structure principles and select methods. Termarcarphi Pty. Ltda, Melbourne, p 45p
Olesen CF, Cedergreen N (2010) Glyphosate uncouples gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence. Pest Manag Sci 66:536–542
Orcaray L, Zulet A, Zabalza A, Royuela M (2012) Impairment of carbon metabolism induced by the herbicide Glyphosate. J Plant Physiol 169:27–33
Rezende-Silva SL, Costa AC, Dyszy FH, Batista PF, Crispim-Filho AJ, Nascimento KJT, Silva AA (2019) Pouteria torta is a remarkable native plant for biomonitoring the glyphosate effects on Cerrado vegetation. Ecol Indic 102:497–506
Sandmann G, Römer S, Fraser PD (2006) Understanding carotenoid metabolism as a necessity for genetic engineering of crop plants. Metab Eng 8:291–302
Santos SA, Tuffi-Santos LD, Sant’Anna-Santos BF, Tanaka FAO, Freitas-Silva L, Júnior AS (2015) Influence of shading on the leaf morphoanatomy and tolerance to Glyphosate in Commelina benghalensis L. and Cyperus rotundus L. Aust J Crop Sci 9:135–142
Schrübbers LC, Valverde BE, Sørensen JC, Cedegreen N (2014) Glyphosate spray drift in Coffea arabica—sensitivity of coffee plants and possible use of shikimic acid as a biomarker for glyphosate exposure. Pestic Biochem Physiol 115:15–22
Silva FAS, Azevedo CAV (2002) Versão do programa computacional Assistat para o sistema operacional Windows. Revista Brasileira de Produtos Agroindustriais 4:71–78
Silva LC, Oliva MA, Azevedo AA, Araújo JM, Aguiar RM (2006) Micromorphological and anatomical alterations caused by simulated acid rain in Restinga plants: Eugenia uniflora and Clusia hilariana. Water Air Soil Pollut 168:129–143
Silva LC, Araújo TO, Martinez CA, Lobo FA, Azevedo AA, Oliva MA (2015) Differential responses of C3 and CAM native Brazilian plant species to a SO2- and SPMFe- contaminated Restinga. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14007–14017 1-11
Silva FB, Vital RG, Batista PF, Costa AC, Jakelaitis A (2016a) Drift from herbicides application on cultivated and native plants: a review. Revista Brasileira de Herbicidas 15:79–88
Silva LQ, Lakelaitis A, Filho SCV, Costa AC, Araújo ACF (2016b) Morpho-anatomical changes of pequi leaves (Caryocar brasiliense Cambess.) exposed to simulates drift of glyphosate. Revista Árvore 40:669–677
Silva LC, Araújo TO, Siqueira-Silva AI, Pereira TAR, Castro LN, Silva EC, Oliva MA, Azevedo AA (2017) Clusia hilariana and Eugenia uniflora as bioindicators of atmospheric pollutants emitted by an iron pelletizing factory in Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:28026–28035
Singh BK, Shaner DL (1998) Rapid determination of glyphosate injury to plants and identification of glyphosate-resistant plants. Weed Technol 12:527–530
Szalai G, Janda T, Páldi E, Szigeti Z (1996) Role of light in the development of post chilling symptoms in maize. J Plant Physiol 148:378–383
Tuffi-Santos LD, Sant’Anna-Santos BF, Meira RMSA, Ferreira FA, Tiburcio RAS, Machado AFL (2009) Leaf anatomy and morphometry in three eucalypt clones treated with glyphosate. Braz J Biol 69:129–136
Vital RG, Jakelaitis A, Silva FB, Batista PF, Almeida GA, Costa AC, Rodrigues AA (2017) Physiological changes and in the carbohydrate content of sunflower plants submitted to sub-doses of glyphosate and trinexapac-ethyl. Bragantia. 76:33–41
Xu J, Smith S, Smith G, Wang W, Li Y (2019) Glyphosate contamination in grains and foods: An overview. Food Control 106:710
Yanniccari M, Tamussi E, Istilart C, Castro AM (2012) Glyphosate effects on gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence responses of two Lolium perenne L. biotypes with differential herbicide sensitivity. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:210–217
Zobiole LHS, Kremer RJ, Oliveira-Jr RS, Constantin J (2011) Glyphosate affects chlorophyll, nodulation and nutrient accumulation of “second generation” Glyphosate to-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Pestic Biochem Physiol 99:53–60
Acknowledgments
L. C. Silva thanks the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the Research Productivity Scholarship 309308/2018-6. The authors also thank the Departamento de Física of Universidade Federal de Viçosa for the scanning electron microscopy support.
Funding
Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES—Finance code 001). Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) granted a scholarship to Carlos Eduardo Souza Cruz during the research development and granted the Research Productivity Scholarship 309308/2018-6 to Luzimar Campos da Silva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CESC, LFS, CR, and LCS conceived and designed the research. CES conducted the experiments; CESC and LFS conducted the biochemical analyses. CESC, LFS, CR, and LCS discussed the results. LFS wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cruz, C.E.S., de Freitas-Silva, L., Ribeiro, C. et al. Physiological and morphoanatomical effects of glyphosate in Eugenia uniflora, a Brazilian plant species native to the Atlantic Forest biome. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 21334–21346 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12003-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12003-4