Abstract
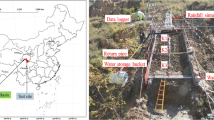
Slope failure is a one of major process that causes severe landform variation and environment variation, and slope failure has become a major hidden danger to human settlement and urban construction in this vast loess region. The physical model of slope failure as induced by artificial rainfall was constructed in the field, and monitored the pore water pressure (PWP), earth stress (ES), volumetric water content (VWC), electrical conductivity (EC), and temperature (T) of the soil using this physical simulation. The surface morphology of slope started to occur in the slope as a result of erosion caused by rainfall and rainwater infiltration at the beginning of the experiment; concurrently, PWP, ES, VWC, and EC were increased gradually. Meanwhile, the saturated weight of the soil rose. In the middle of the experiment, PWP, ES, VWC, and EC were increased rapidly as the artificial rainfall continued, and the ratio of soil pore the soil fell. The slope landform was obviously occurred during the experiment, when it was noted that PWP, ES, VWC, and EC of the soil rapidly decreased. Afterwards, slope failure evolved into a debris flow; eventually, the landform was entirely changed in the slope. The soil became more compact toward the end of the experiment, and PWP, ES, VWC, and EC were slowly increased; these factors indicated that the loess slope was temporarily stable. This study could potentially be used to provide the relevant parameters for numerical simulations of landform variation in loess regions, and provide reference for regional land use planning and environmental development.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya G, Cochrane T, Davies T, Bowman E (2011) Quantifying and modeling post-failure sediment yields from laboratory-scale soil erosion and shallow landslide experiments with silty loess. Geomorphology 129:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.01.012
Anderson SA, Sitar N (1995) Analysis of rainfall-induced debris flows. J Geotech Eng 121:544–552. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1995)121:7(544)
Batunacun WR, Lakes T, Yunfeng H, Nendel C (2019) Identifying drivers of land degradation in Xilingol, China, between 1975 and 2015. Land Use Policy 83:543–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.02.013
Berti M, Simoni A (2012) Observation and analysis of near-surface pore-pressure measurements in clay-shales slopes. Hydrol Process 26:2187–2205. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7981
Cai F, Ugai K (2004) Numerical analysis of rainfall effects on slope stability. Int J Geomech 4:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2004)4:2(69)
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Sorbino G (2010) Modeling of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of the flow-type. J Geotech Geoenviron 136:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000182
Cassiani G, Binley A (2005) Modeling unsaturated flow in a layered formation under quasi-steady state conditions using geophysical data constraints. Adv Water Resour 28:467–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2004.12.007
Chen G, Meng X, Qiao L, Zhang Y, Wang S (2018) Response of a loess landslide to rainfall: observations from a field artificial rainfall experiment in Bailong River basin, China. Landslides 15:895–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0924-6
Ching-Chuan H, Yih-Jang J, Lih-Kang H, Jin-Long L (2009) Internal soil moisture and piezometric responses to rainfall-induced shallow slope failures. J Hydrol 370:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.02.051
Choi CE, Ng CWW, Au-Yeung SCH, Goodwin GR (2015) Froude characteristics of both dense granular and water flows in flume modelling. Landslides 12:1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0628-8
Crosta GB, Dal Negro P, Frattini P (2010) Soil slips and debris flows on terraced slopes. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 3:31–42. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-3-31-2003
Derbyshire E (2001) Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth Sci Rev 54:231–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-8252(01)00050-2
Gao G (1986) Formation and development of the structure of collapsing loess in China. Eng Geol 25:236–246
García-Quintana A, García-Hidalgo JF, Martin-Duque JF, Pedraza J, González-Martin JA (2004) Geological factors of the Guadalajara landscapes (Central Spain) and their relevance to landscape studies. Landsc Urban Plan 69:417–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2003.12.001
Gvirtzman H, Shalev E, Dahan O, Hatzor YH (2008) Large-scale infiltration experiments into unsaturated stratified loess sediments: monitoring and modeling. J Hydrol 349:214–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.002
Harp EL, Wells WG, Sarmiento JG (1990) Pore pressure response during failure in soils. Bull Geol Soc Am 102:428–438. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1990)102<0428:PPRDFI>2.3.CO;2
Hessel R, Van Asch T (2003) Modelling gully erosion for a small catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 54:131–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00061-4
Hino M, Odaka Y, Nadaoka K, Sato A (1988) Effect of initial soil moisture content on the vertical infiltration process—a guide to the problem of runoff-ratio and loss. J Hydrol 102:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(88)90102-3
Hu W, Dong XJ, Xu Q, Wang GH, van Asch TWJ, Hicher PY (2016) Initiation processes for run-off generated debris flows in the Wenchuan earthquake area of China. Geomorphology 253:468–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.10.024
Huang CC, Yuin SC (2010) Experimental investigation of rainfall criteria for shallow slope failures. Geomorphology 120:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.04.006
Huang CC, Lo CL, Jang JS, Hwu LK (2008) Internal soil moisture response to rainfall-induced slope failures and debris discharge. Eng Geol 101:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.04.009
Iverson RM (2005) Regulation of landslide motion by dilatancy and pore pressure feedback. J Geophys Res 110:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JF000268
Iverson RM (2015) Scaling and design of landslide and debris-flow experiments. Geomorphology 244:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.02.033
Kovacevic N, Jardine RJ, Potts DM, Clukey CE, Brand JR, Spikula DR (2012) A numerical simulation of underwater slope failures generated by salt diapirism combined with active sedimentation. Geotechnique 62:777–786. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.12.OG.004
Kowalsky MB, Finsterle S, Rubin Y (2004) Estimating flow parameter distributions using ground-penetrating radar and hydrological measurements during transient flow in the vadose zone. Adv Water Resour 27:583–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2004.03.003
Krahn J, Fredlund DG, Klassen MJ (1989) Effect of soil suction on slope stability at Notch Hill. Can Geotech J 26:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-036
Li LC, Tang CA, Zhu WC, Liang ZZ (2009) Numerical analysis of slope stability based on the gravity increase method. Comput Geotech 36:1246–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.06.004
Lin C-W, Liu S-H, Lee S-Y, Liu C-C (2006) Impacts of the chi-chi earthquake on subsequent rainfall-induced landslides in Central Taiwan. Eng Geol 86:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.02.010
Liu DS (1985) Loess and environment. Science Press, Beijing, pp:1–43 (in Chinese)
Liu X, Wang Y, Li DQ (2019) Investigation of slope failure mode evolution during large deformation in spatially variable soils by random limit equilibrium and material point methods. Comput Geotech 111:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.03.022
Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Crosta, G.B., Corominas, J., Azzam, R., Wasowski, J., Sciarra, N., 2015. Engineering geology for society and territory—Volume 2: Landslide processes. 1–2177. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09057-3
Londono AC (2006) Discussion of “Response of a residual soil slope to rainfall”. Can Geotech J 43:979–983. https://doi.org/10.1139/t06-084
Lu Y, Liu S, Alonso E, Wang L, Xu L, Li Z (2019) Volume changes and mechanical degradation of a compacted expansive soil under freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 157:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.10.008
Lu Y, Liu S, Zhang Y, Li Z, Xu L (2020) Freeze-thaw performance of a cement-treated expansive soil. Cold Reg Sci Technol 170:102926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102926
Moriwaki H, Inokuchi T, Hattanji T, Sassa K, Ochiai H, Wang G (2004) Failure processes in a full-scale landslide experiment using a rainfall simulator. Landslides 1:277–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0034-0
Okada Y, Ochiai H, Furuya G, Okura Y, Matsui T, Sammori T, Terajima T, Sassa K (2004) A fluidized landslide on a natural slope by artificial rainfall. Landslides 1:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0030-4
Okura Y, Kitahara H, Ochiai H, Sammori T, Kawanami A (2002) Landslide fluidization process by flume experiments. Eng Geol 66:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00032-7
Olivares L, Damiano E (2007) Postfailure mechanics of landslides: laboratory investigation of flowslides in pyroclastic soils. J Geotech Geoenviron 133:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:1(51)
P. Orense, R., Shimoma, S., Maeda, K., Towhata, I., 2004. Instrumented model slope failure due to water seepage. J Nat Disaster Sci 26, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.2328/jnds.26.15
Pourkhosravani A, Kalantari B (2011) A review of current methods for slope stability evaluation. Electron J Geotech Eng 16(L):1245–1254
Rosenau M, Lohrmann J, Oncken O (2009) Shocks in a box: an analogue model of subduction earthquake cycles with application to seismotectonic forearc evolution. J Geophys Res 114:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB005665
Rui X, Nie L, Xu Y, Wang H (2019) Land degeneration due to water infiltration and sub-erosion: a case study of soil slope failure at the National Geological Park of Qian-an mud Forest, China. Sustainability 11:4709. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174709
Scheidl C, Chiari M, Kaitna R, Müllegger M, Krawtschuk A, Zimmermann T, Proske D (2013) Analysing debris-flow impact models, based on a small scale modelling approach. Surv Geophys 34:121–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-012-9199-6
Schulz WH, McKenna JP, Kibler JD, Biavati G (2009) Relations between hydrology and velocity of a continuously moving landslide-evidence of pore-pressure feedback regulating landslide motion? Landslides 6:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0157-4
Shi JS, Wu LZ, Wu SR, Li B, Wang T, Xin P (2016) Analysis of the causes of large-scale loess landslides in Baoji, China. Geomorphology 264:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.04.013
Shu H, Ma J, Yu H, Hürlimann M, Zhang P, Liu F, Qi S (2018) Effect of density and Total weight on flow depth, velocity, and stresses in loess debris flows. Water 10:1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121784
Shu H, Hürlimann M, Molowny-Horas R, González M, Pinyol J, Ma J (2019a) Relation between land cover and landslide susceptibility in Val d’Aran, Pyrenees (Spain): historical aspects, present situation and forward prediction. Sci Total Environ 693:1–14
Shu H, Ma J, Zhang P, Yu H, Ren S, Qi S, Yang H (2019b) Debris-flow risk assessment: from catchment to regional scale: a case study from southern Gansu Province, China. Ekoloji 28:2319–2333
Singh TN, Gulati A, Dontha L, Bhardwaj V (2008) Evaluating cut slope failure by numerical analysis—a case study. Nat Hazards 47:263–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-008-9219-5
Tecca PR, Galgaro A, Genevois R, Deganutti AM (2003) Development of a remotely controlled debris flow monitoring system in the Dolomites (Acquabona, Italy). Hydrol Process 17:1771–1784. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1212
Trandafir AC, Sidle RC, Gomi T, Kamai T (2008) Monitored and simulated variations in matric suction during rainfall in a residual soil slope. Environ Geol 55:951–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1045-7
Tsaparas I, Rahardjo H, Toll DG, Leong EC (2003) Infiltration characteristics of two instrumented residual soil slopes. Can Geotech J 40:1012–1032. https://doi.org/10.1139/t03-049
Tu XB, Kwong AKL, Dai FC, Tham LG, Min H (2009) Field monitoring of rainfall infiltration in a loess slope and analysis of failure mechanism of rainfall-induced landslides. Eng Geol 105:134–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.11.011
Walker JP, Willgoose GR, Kalma JD (2004) In situ measurement of soil moisture: a comparison of techniques. J Hydrol 293:85–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.01.008
Wang G, Sassa K (2003) Pore-pressure generation and movement of rainfall-induced landslides: effects of grain size and fine-particle content. Eng Geol 69:109–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00268-5
Wang JJ, Liang Y, Zhang HP, Wu Y, Lin X (2014) A loess landslide induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 11:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0418-0
Wang D, Chen Z, He S, Liu Y, Tang H (2018) Measuring and estimating the impact pressure of debris flows on bridge piers based on large-scale laboratory experiments. Landslides 15:1331–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0944-x
Wu LZ, Zhou Y, Sun P, Shi JS, Liu GG, Bai LY (2017) Laboratory characterization of rainfall-induced loess slope failure. Catena 150:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.002
Xu L, Dai FC, Tham LG, Tu XB, Min H, Zhou YF, Wu CX, Xu K (2011) Field testing of irrigation effects on the stability of a cliff edge in loess, north-west China. Eng Geol 120:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.03.007
Xu L, Qiao X, Wu C, Iqbal J, Dai F (2012) Causes of landslide recurrence in a loess platform with respect to hydrological processes. Nat Hazards 64:1657–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0326-y
Yang W, Wu S, Zhang Y, Shi J, Xiang L (2007) Research on formation mechanism of the debris flow on slope induced by rainfall. Earth Sci Front 14:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-5791(08)60011-1
Yu L, Peng C, Regmi AD, Murray V, Pasuto A, Titti G, Shafique M, Priyadarshana T (2018) An international program on silk road disaster risk reduction–a belt and road initiative (2016–2020). J Mt Sci 15:1383–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-4842-4
Zeng RQ, Meng XM, Zhang FY, Wang SY, Cui ZJ, Zhang MS, Zhang Y, Chen G (2016) Characterizing hydrological processes on loess slopes using electrical resistivity tomography—a case study of the Heifangtai terrace, Northwest China. J Hydrol 541:742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.07.033
Zhang F, Huang X (2018) Trend and spatiotemporal distribution of fatal landslides triggered by non-seismic effects in China. Landslides 15:1663–1674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1007-z
Zhang D, Wang G (2007) Study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake-induced landslides in loess (China). Eng Geol 94:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.07.007
Zhang F, Pei X, Chen W, Liu G, Liang S (2014) Spatial variation in geotechnical properties and topographic attributes on the different types of shallow landslides in a loess catchment, China. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 18:470–488. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2014.881754
Zhang F, Kang C, Chan D, Zhang X, Pei X, Peng J (2017) A study of a flowslide with significant entrainment in loess areas in China. Earth Surf Process Landf 42:2295–2305. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.4184
Zhang F, Yan B, Feng X, Lan H, Kang C, Lin X, Zhu X, Ma W (2019) A rapid loess mudflow triggered by the check dam failure in a bulldoze mountain area, Lanzhou, China. Landslides 16:1981–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01219-2
Zhao JK, Wang D, Chen JH (2015) Experimental study on slope sliding and debris flow evolution with and without barrier. Water Sci Eng 8:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2015.01.003
Zhou BB, Wu J, Anderies JM (2019) Sustainable landscapes and landscape sustainability: a tale of two concepts. Landsc Urban Plan 189:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2019.05.005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. lzujbky-2020-kb54), the 111 Project (No. BP2018001), the Foundation for Excellent Youth Scholars of the “Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources”, CAS (Grant No. FEYS2019013), and the State Key Laboratory of Frozen Soil Engineering (Grant No. SKLFSE-ZQ-56).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, H., Ma, J., Guo, J. et al. Effects of rainfall on surface environment and morphological characteristics in the Loess Plateau. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 37455–37467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10365-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10365-3