Abstract
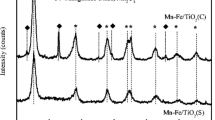
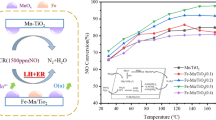
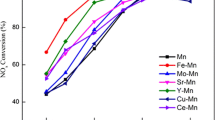
Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts were prepared through the wet impregnation process to selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 at low temperature, and series of experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of key precursors on their SCR performance. Ferric nitrate, ferrous sulfate, and ferrous chloride were chosen as Fe precursors while manganese nitrate, manganese acetate, and manganese chloride as Mn precursors. These precursors had been commonly used to prepare Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts by numerous researchers. The results showed that there were distinct differences in NO conversion efficiencies at low temperature of catalysts prepared with different precursors. Catalysts prepared with ferric nitrate and manganese nitrate precursors exhibited the best catalytic performance at low temperature, while three kinds of catalysts prepared with manganese chloride precursors exhibited significantly low catalytic activity. All catalysts were characterized by XRD, SEM, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD, and XPS. The results indicated that when the catalysts were prepared with manganese nitrate or manganese acetate as precursors, Mn4+ contents and Oβ/(Oβ + Oα) ratios decreased in an order of ferric nitrate > ferrous sulfate > ferrous chloride, which was consistent with the change of catalytic activities of the corresponding catalysts at low temperature. It can be found that the excellent catalytic performance of Fe(A)-Mn(a)/TiO2 was ascribed to high redox property and enrichment of Mn4+species and surface chemical labile oxygen groups.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cimino S, Lisi L, Tortorelli M (2016) Low temperature SCR on supported MnOx catalysts for marine exhaust gas cleaning: effect of KCl poisoning. Chem Eng J 283:223–230
Chen L, Yuan F, Li Z, Niu X, Zhu Y (2018) Synergistic effect between the redox property and acidity on enhancing the low temperature NH3-SCR activity for NO removal over the Co0.2CexMn0.8-xTi10 (x = 0–0.40) oxides catalysts. Chem Eng J 354:393–406
Deng S, Zhuang K, Xu B, Ding Y, Yu L, Fan Y (2016) Promotional effect of iron oxide on the catalytic properties of Fe-MnOx/TiO2 (anatase) catalysts for the SCR reaction at low temperatures. Catal Sci Technol 6:1772–1778
Fan Y, Ling W, Huang B, Dong L, Yu C, Xi H (2017) The synergistic effects of cerium presence in the framework and the surface resistance to SO2 and H2O in NH3-SCR. J Ind Eng Chem 56:108–119
Gao Y, Luan T, Zhang S, Jiang W, Feng W, Jiang H (2019) Comprehensive comparison between nanocatalysts of Mn-Co/TiO2 and Mn-Fe/TiO2 for NO catalytic conversion: an insight from nanostructure, performance, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Catalysts 9:175
Geng Y, Shan W, Yang S, Liu F (2018) W-modified Mn-Ti mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:9112–9119
Grossale A, Nova I, Tronconi E (2009) Ammonia blocking of the “fast SCR” reactivity over a commercial Fe-zeolite catalyst for diesel exhaust after treatment. J Catal 265:141–147
Han Z, Yu Q, Teng Z, Wu B, Xue Z, Qin Q (2019) Effects of manganese content and calcination temperature on Mn/Zr-PILM catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 in metallurgical sintering flue gas. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:12920–12927
Huang J, Huang H, Liu L, Jiang H (2018) Revisit the effect of manganese oxidation state on activity in low-temperature NO-SCR. Catal Today 446:49–57
Huang J, Huang H, Jiang H, Liu L (2019) The promotional role of Nd on Mn/TiO2 catalyst for the low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal Today 332:49–58
Hwang S, Jo SH, Kim J, Shin MC, Chun HH, Park H, Lee H (2016) Catalytic activity of MnOx/TiO2 catalysts synthesized with different manganese precursors for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides. React Kinet Mech Catal 117:583–591
Kantcheva M (2001) Identification, stability, and reactivity of NOx species adsorbed on titania-supported manganese catalysts. J Catal 204:479–494
Kapteijn F, Vanlangeveld AD, Moulijn JA, Andreini A, Vuurman MA, Turek AM, Wachs IE (1994) Alumina-supported manganese oxide catalysts: I. characterization: effect of precursor and loading. J Catal 150:94–104
Li J, Chen J, Ke R, Luo C, Hao J (2007) Effects of precursors on the surface Mn species and the activities for NO reduction over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts. Catal Commun 8:1896–1900
Li L, Sun B, Sun J, Yu S, Ge C, Tang C, Dong L (2017) Novel MnOx-CeO2 nanosphere catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Catal Commun 100:98–102
Li F, Xie J, Qi K, Gong P, He F (2019) Evaluating the intermetallic interaction of Fe or Cu doped Mn/TiO2 catalysts: SCR activity and sulfur tolerance. Catal Lett 149:788–797
Lin L, Lee C, Zhang Y, Bai H (2018) Aerosol-assisted deposition of Mn-Fe oxide catalyst on TiO2 for superior selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Catal Commun 111:36–41
Liu K, He H, Yu Y, Yan Z, Yang W, Shan W (2019) Quantitative study of the NH3-SCR pathway and the active site distribution over CeWOx at low temperatures. J Catal 369:372–381
Mu J, Li X, Sun W, Fan S, Wang X, Wang L, Zhang D (2018) Enhancement of low-temperature catalytic activity over a highly dispersed Fe-Mn/Ti catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:10159–10169
Nova I, Ciardelli C, Tronconi E, Chatterjee D, Bandl KB (2006) NH3-SCR of NO over a V-based catalyst: low-T redox kinetics with NH3 inhibition. AICHE J 52(9):3222–3233
Pan Y, Shen Y, Jin Q, Zhu S (2018) Promotional effect of Ba additives on MnCeOx/TiO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR of NO at low temperature. J Mater Res 33:2414–2422
Pârvulescu V, Grange P, Delmon B (1998) Catalytic removal of NO. Catal Today 46:233–316
Pena DA, Uphade BS, Smirniotis PG (2004) TiO2-supported metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: I. evaluation and characterization of first row transition metals. J Catal 221:421–431
Putluru SSR, Schill L, Jensen AD, Siret B, Tabaries F, Fehrmann R (2015) Mn/TiO2 and Mn-Fe/TiO2 catalysts synthesized by deposition precipitation—promising for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl Catal B-Environ 165:628–635
Qi G, Yang RT (2003) Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron and manganese oxides supported on titania. Appl Catal B-Environ 44:217–225
Qiu L, Wang Y, Pang D, Ouyang F, Zhang C, Cao G (2016) Characterization and catalytic activity of Mn-Co/TiO2 catalysts for NO oxidation to NO2 at low temperature. Catalysts 6:9
Sun C, Liu H, Chen W, Chen D, Yu S, Liu A, Feng S (2018) Insights into the Sm/Zr co-doping effects on N2 selectivity and SO2 resistance of a MnOx-TiO2 catalyst for the NH3-SCR reaction. Chem Eng J 347:27–40
Tang C, Zhang H, Dong L (2016) Ceria-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal Sci Technol 6:1248–1264
Wang H, Chen X, Gao S, Wu Z, Liu Y, Weng X (2013) Deactivation mechanism of Ce/TiO2 selective catalytic reduction catalysts by the loading of sodium and calcium salts. Catal Sci Technol 3:715–722
Wang T, Wan Z, Yang X, Zhang X, Niu X, Sun B (2018) Promotional effect of iron modification on the catalytic properties of Mn-Fe/ZSM-5 catalysts in the fast SCR reaction. Fuel Process Technol 169:112–121
Wang Q, Xu H, Huang W, Pan Z, Zhou H (2019a) Metal organic frameworks-assisted fabrication of CuO/Cu2O for enhanced selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 at low temperatures. J Hazard Mater 364:499–508
Wang D, Yao Q, Hui S, Niu Y (2019b) Source of N and O in N2O formation during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over MnOx/TiO2. Fuel 2019:23–29
Wu Z, Jiang B, Liu Y, Zhao W, Guan B (2007) Experimental study on a low-temperature SCR catalyst based on MnOx/TiO2 prepared by sol-gel method. J Hazard Mater 145:488–494
Wu Z, Jiang B, Liu Y (2008) Effect of transition metals addition on the catalyst of manganese/titania for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Appl Catal B-Environ 79:347–355
Wu S, Zhang L, Wang X, Zou W, Cao Y, Sun J, Dong L (2015) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of FeMnTiOx mixed oxides catalyst prepared by a CTAB-assisted process for mid-low temperature NH3-SCR. Appl Catal A-Gen 505:235–242
Wu X, Feng Y, Du Y, Liu X, Zou C, Li Z (2019) Enhancing deNOx performance of CoMnAl mixed metal oxides in low-temperature NH3-SCR by optimizing layered double hydroxides (LDHs) precursor template. Appl Surf Sci 467:802–810
Xiong Y, Tang C, Yao X, Zhang L, Li L, Wang X, Deng Y, Gao F, Dong L (2015) Effect of metal ions doping (M=Ti4+, Sn4+) on the catalytic performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl Catal A-Gen 495:206–216
Xu H, Liu S, Wang Y, Lin Q, Lin C, Lan L, Chen Y (2018a) Promotional effect of Al2O3 on WO3/CeO2-ZrO2 monolithic catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia after hydrothermal aging treatment. Appl Surf Sci 427:656–669
Xu W, Zhang G, Chen H, Zhang G, Han Y, Chang Y, Gong P (2018b) Mn/beta and Mn/ZSM-5 for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia: effect of manganese precursors. Chin J Catal 39:118–127
Yang N, Guo R, Pan W, Chen Q, Wang Q, Lu C (2016) The promotion effect of Sb on the Na resistance of Mn/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Fuel 169:87–92
Yang G, Zhao H, Luo X, Shi K, Zhao H, Wang W, Wu T (2019) Promotion effect and mechanism of the addition of Mo on the enhanced low temperature SCR of NOx by NH3 over MnOx/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Appl Catal B-Environ 245:743–752
Zhang Z, Yu H, Liao B, Huang H, Chen Y (2012) Influence of iron precursors on NH3-SCR behavior of Fe/β catalyst. Chin J Catal 33:576–580
Zhang S, Zhao Y, Yang J, Zhang J, Zheng C (2018) Fe-modified MnOx/TiO2 as the SCR catalyst for simultaneous removal of NO and mercury from coal combustion flue gas. Chem Eng J 348:618–629
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Xiao R, Huang T, Shen K (2017) Novel holmium-modified Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts with a broad temperature window and high sulfur dioxide tolerance for low-temperature SCR. Catal Commun 88:64–67
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51779024) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grants 3132019032 and 3132019330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The effects of Fe and Mn precursors on NH3-SCR performance were investigated.
• The catalyst prepared using ferric nitrate and manganese nitrate precursors exhibited the best catalytic activity at low temperature, while the catalysts prepared with chloride precursors exhibited much lower catalytic activities.
• The choice of Fe and Mn precursors was crucial for preparing Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts, which would probably affect the redox property, Mn4+ content, the surface chemisorbed labile oxygen content, and the dispersion of active species over support.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 877 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Han, Z., Wang, Q. et al. Effects of ferric and manganese precursors on catalytic activity of Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalysts for selective reduction of NO with ammonia at low temperature. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 40870–40881 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10073-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10073-y