Abstract
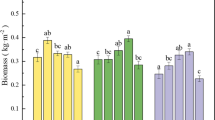
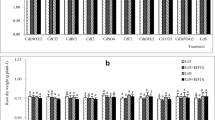
Phytoextraction has been considered an effective and environment-friendly method for removing heavy metals from contaminated soil. However, the efficiency, mechanism, and adaptability of phytoextraction by hyperaccumulators in Cd-polluted weakly alkaline soil have not been investigated in detail. In this study, pot experiments were conducted to evaluate the enhanced effects of S,S-ethylenediamine disuccinic acid (EDDS) on phytoextraction in alkaline soil by measuring the degradation kinetic characteristics of EDDS and Cd absorption dynamics of Tagetes patula L. (T. patula) and Phytolacca americana L. (P. americana) for a period of 55 days. Results showed that the half-life of EDDS varied from 4.20–7.07 days and 3.35–4.36 days for T. patula and P. americana, respectively. EDDS-activated Cd reached saturation at a low dosage (1 mM) and a single application of EDDS was found to be better than double applications. The activation of EDDS on Cd applied before 45 days of harvest was better than that before 15 days of harvest, and disappeared after a 35-day application. Correspondingly, the Cd concentration in P. americana and T. patula leaves increased significantly after 3 days of the EDDS application. However, T. patula had a biomass 2.57 times and Cd absorption capacity 10.06 times higher than P. americana. EDDS showed almost no influence on the stem and leaf biomass of T. patula; however, the root weight decreased by 9.44–71.77%. The Cd concentration in T. patula leaves of all the treatments was 1.00–1.81 times that of the control group. In comparison with other treatments, the EDDS application (3 mM) before 15 days of harvest extracted the highest amount of Cd (601.45 μg/pot) in T. patula shoots, reaching 1.40 times that in the control group. Therefore, T. patula might be a more suitable phytoremediator for Cd-polluted alkaline soil than P. americana; the most effective method was the EDDS application (3 mM) before 15 days of harvest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Guo D, Arockiam Jeyasundar PGS, Li YM, Xiao R, Du J, Li RH, Zhang ZQ (2019) Application of wood biochar in polluted soils stabilized the toxic metals and enhanced wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth and soil enzymatic activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109635
Ashraf S, Ali Q, Zahir ZA, Ashraf S, Asghar HN (2019) Phytoremediation: environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:714–727
Beesley L, Moreno-Jimenez E, Gomez-Eyles JL, Harris E, Robinson B, Sizmur T (2011) A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:3269–3282
Cao Y, Feng HY, Sun D, Xu GH, Rathinasabapathi B, Chen YS, Ma LQ (2019) Heterologous expression of Pteris vittata phosphate transporter PvPht1;3 enhances arsenic translocation to and accumulation in tobacco shoots. Environ Sci Technol 53:10636–10644
Chen YR, Zhang QF, Fu BS, Cai SB, Wu JZ, Chen YH (2017) Differences of lead, cadmium and zinc accumulation among Chinese wheat mini-core collections germplasms and screening for low Pb, Cd and Zn accumulative cultivars in grains. J Nanjing Agric Univ 40:393–399 (in Chinese)
Chen R, Zhang CB, Zhao YL, Huang YC, Liu ZQ (2018) Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2361–2368
Fu YZ, Lei WR, Shen ZG, Luo CL (2015) Permeability of plant young root endodermis to Cu ions and Cu-citrate complexes in corn and soybean. Int J Phytoremediation 17:822–834
Guo JM, Lei M, Yang JX, Yang J, Wan XM, Chen TB, Zhou XY, Gu SP, Guo GH (2017) Effect of fertilizers on the Cd uptake of two sedum species (Sedum spectabile Boreau and Sedum aizoon L.) as potential Cd accumulators. Ecol Eng 106:409–414
Guo GH, Lei M, Wang YW, Song B, Yang J (2018) Accumulation of As, Cd, and Pb in sixteen wheat cultivars grown in contaminated soils and associated health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2601
Guo D, Ali A, Ren CY, Du J, Li RH, Lahori AH, Xiao R, Zhang ZY, Zhang ZQ (2019) EDTA and organic acids assisted phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from a smelter contaminated soil by potherb mustard (Brassica juncea, Coss) and evaluation of its bioindicators. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:396–403
Hseu ZY, Jien SH, Wang SH, Deng HW (2013) Using EDDS and NTA for enhanced phytoextraction of Cd by water spinach. J Environ Manag 117:58–64
Hu N, Lang T, Ding DX, Hu JS, Li CW, Zhang H, Li GY (2019) Enhancement of repeated applications of chelates on phytoremediation of uranium contaminated soil by Macleaya cordata. J Environ Radioact 199-200:58–65
Huang QQ, Xu YM, Liu YY, Qin X, Huang R, Liang XF (2018) Selenium application alters soil cadmium bioavailability and reduces its accumulation in rice grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:31175–31182
Lei L, Lv H, Yu Y, Hu RG, Wang RG, Xu YM, Ding YZ, Feng RW, Fan ZL (2018) Performances of water management, foliage dressing, and variation screening in controlling the accumulation of As and Cd and maintaining the concentrations of essential elements in the grains of rice plant. Front Environ Sci 6:3
Li JR, Xu YM (2015) Immobilization of Cd in a paddy soil using moisture management and amendment. Chemosphere 122:131–136
Li XF, Zhou DM (2019) A meta-analysis on phenotypic variation in cadmium accumulation of rice and wheat: implications for food cadmium risk control. Pedosphere 29:545–553
Li TQ, Di ZZ, Islam E, Jiang H, Yang XE (2011) Rhizosphere characteristics of zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii involved in zinc accumulation. J Hazard Mater 185:818–823
Li CW, Hu N, Ding DX, Hu JS, Li GY, Wang YD (2015) Phytoextraction of uranium from contaminated soil by Macleaya cordata before and after application of EDDS and CA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6155–6163
Li ZW, Zhang RS, Zhang HM (2018) Effects of plant growth regulators (DA-6 and 6-BA) and EDDS chelator on phytoextraction and detoxification of cadmium by Amaranthus hybridus Linn. Int J Phytoremediation 20:1121–1128
Li J, Zhang PY, Ye JP, Zhang GM, Cai YJ (2019) Simultaneous in-situ remediation and fertilization of Cd-contaminated weak-alkaline farmland for wheat production. J Environ Manag 250:109528
Liang XF, Li N, He LZ, Xu YM, Huang QQ, Xie ZL, Yang F (2019) Inhibition of Cd accumulation in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in alkaline soil using mercapto-modified attapulgite. Sci Total Environ 688:818–826
Liu XQ, Peng KJ, Wang AG, Lian CL, Shen ZG (2010) Cadmium accumulation and distribution in populations of Phytolacca americana L. and the role of transpiration. Chemosphere 78:1136–1141
Liu X, Fu JW, Da Silva E, Shi XX, Cao Y, Rathinasabapathi B, Ma LQ (2017) Microbial siderophores and root exudates enhanced goethite dissolution and Fe/As uptake by As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Environ Pollut 223:230–237
Liu ZL, Chen W, He XY (2018) Evaluation of hyperaccumulation potentials to cadmium (Cd) in six ornamental species (compositae). Int J Phytoremediation 20:1464–1469
Luo CL, Shen ZG, Li XD (2005) Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere 59:1–11
Luo JP, Liu YY, Tao Q, Hou Q, Wu KR, Song YC, Liu YK, Guo XY, Li JX, Hashmi M, Liang YC, Li TQ (2019) Successive phytoextraction alters ammonia oxidation and associated microbial communities in heavy metal contaminated agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 664:616–625
McBride MB, Zhou YT (2019) Cadmium and zinc bioaccumulation by Phytolacca americana from hydroponic media and contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 21:1215–1224
Meers E, Ruttens A, Hopgood MJ, Samson D, Tack FMG (2005) Comparison of EDTA and EDDS as potential soil amendments for enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals. Chemosphere 58:1011–1122
Meers E, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2008) Degradability of ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid (EDDS) in metal contaminated soils: implications for its use soil remediation. Chemosphere 70:358–363
Moslehi A, Feizian M, Higueras P, Eisvand HR (2019) Assessment of EDDS and vermicompost for the phytoextraction of Cd and Pb by sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Int J Phytoremediation 21:191–199
Norvell WA (1984) Comparison of chelating agents as extractants for metals in diverse soil materials. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1285–1292
Peng KJ, Luo CL, You WX, Lian CL, Li XD, Shen ZG (2008) Manganese uptake and interactions with cadmium in the hyperaccumulator-Phytolacca Americana L. J Hazard Mater 154:674–681
Qian TT, Wu P, Qin QY, Huang YN, Wang YJ, Zhou DM (2019) Screening of wheat straw biochars for the remediation of soils polluted with Zn (II) and Cd (II). J Hazard Mater 362:311–317
Qu CD, Shi W, Guo J, Fang BB, Wang S, Giesy JP, Holm PE (2016) China’s soil pollution control: choices and challenges. Environ Sci Technol 50:13181–13183
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Zia Ur Rehman M, Waris AA (2019) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Saifullah SN, Bibi S, Ahmad M, Sik Ok Y (2013) Effectiveness of zinc application to minimize cadmium toxicity and accumulation in wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Environ Earth Sci 71:1663–1672
Salt DE, Prince RC, Pickering IJ, Raskin I (1995) Mechanisms of cadmium mobility and accumulation in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 109:1427–1433
Sun YB, Zhou QX, An J, Liu WT, Liu R (2009) Chelator-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil irrigated by industrial wastewater with the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii Hance). Geoderma 150:106–112
Sun YB, Zhou QX, Xu YM, Wang L, Liang XF (2011) Phytoremediation for co-contaminated soils of benzo [a] pyrene (B [a]P) and heavy metals using ornamental plant Tagetes patula. J Hazard Mater 186:2075–2082
Sun RL, Sun QQ, Wang RQ, Cao LD (2018) Cadmium accumulation and main rhizosphere characteristics of seven French marigold (Tagetes patula L.) cultivars. Int J Phytoremediation 20:1171–1178
Talebi M, Tabatabaei BES, Akbarzadeh H (2019) Hyperaccumulation of Cu, Zn, Ni, and Cd in Azolla species inducing expression of methallothionein and phytochelatin synthase genes. Chemosphere 230:488–497
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack AB (2006) Uptake of metals during chelant-assisted phytoextraction with EDDS related to the solubilized metal concentration. Environ Sci Technol 40:2753–2758
Wang X, Wang Y, Mahmood Q, Islam E, Jin XF, Li TQ, Yang XE, Liu D (2009) The effect of EDDS addition on the phytoextraction efficiency from Pb contaminated soil by Sedum alfredii Hance. J Hazard Mater 168:530–535
Wang K, Liu YH, Song ZG, Wang D, Qiu WW (2019) Chelator complexes enhanced Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. phytoremediation efficiency in Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 237:124480–124488
Wei JL, Lai HY, Chen ZS (2012) Chelator effects on bioconcentration and translocation of cadmium by hyperaccumulators, Tagetes patula and Impatiens walleriana. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:173–178
Xu Y, Yamaji N, Shen RF, Ma JF (2007) Sorghum roots are inefficient in uptake of EDTA-chelated lead. Ann Bot 99:869–875
Xu Y, Liang XF, Xu YM, Qin X, Huang QQ, Wang L, Sun YB (2017) Remediation of heavy metal-polluted agricultural soils using clay minerals: a review. Pedosphere 27:193–204
Yang L, Wang GP, Cheng ZN, Liu Y, Shen ZG, Luo CL (2013) Influence of the application of chelant EDDS on soil enzymatic activity and microbial community structure. J Hazard Mater 262:561–570
Yang W, Dai HP, Skuza L, Wei SH (2019) Strengthening role and the mechanism of optimum nitrogen addition in relation to Solanum nigrum L. Cd hyperaccumulation in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 182:109444–109450
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project from the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (No. CAASXTCX-xym-2018), and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-03-25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 77 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Qin, X. et al. Effects of EDDS on the Cd uptake and growth of Tagetes patula L. and Phytolacca americana L. in Cd-contaminated alkaline soil in northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 25248–25260 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08877-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08877-z