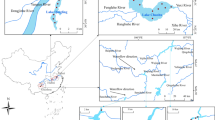
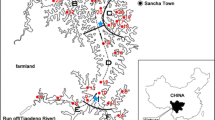
Abstract
Oxidation of surface sediments is an important means for altering phosphorus (P) exchanges across sediment–water interface (SWI) in shallow lakes. In this study, the potential and composition of regenerated oxidation capacity (OC) of surface sediments were evaluated in three large shallow lakes (Tai Lake, Chao Lake, and Dianchi Lake) in China; the transformation of sedimentary P was quantified through P fractionation scheme. The composition of the regenerated OC differed among these three lakes, with Fe(III) and SO42− dominant in Dianchi Lake, Mn(IV) and Fe(III) in Chao Lake and Tai Lake. Oxidation of sediments enhanced the transformation of sedimentary P and altered P exchanges across the SWI. In Chao Lake, the HCl-P was transformed to BD-P; in Tai Lake, the NaOH-P was involved too, and transformed to BD-P; whereas in Dianchi Lake, an increase in NH4Cl-P was also observed except for the transformation from HCl-P to BD-P. The sediment-to-water flux of P was enhanced with 0.17 mg/g DW in Dianchi Lake and 0.08 mg/g DW in Chao Lake, while a contrary water-to-sediment flux of P was observed in Tai Lake, reaching 0.01 mg/g DW. This study advances our knowledge on the impacts of sediment oxidation on P cycles in lakes, which will be beneficial to eutrophication control.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aeschbacher M, Vergari D, Schwarzenbach RP, Sander M (2011) Electrochemical analysis of proton and electron transfer equilibria of the reducible moieties in humic acids. Environ Sci Technol 45:8385–8394
Antelo J, Avena M, Fiol S, López R, Arce F (2005) Effects of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate at the goethite–water interface. J Colloid Interface Sci 285:476–486
Breemen NV, Mulder J, Driscoll CT (1983) Acidification and alkalinization of soils. Plant Soil 75:283–308
Chen C, Wei L, Guo X, Guo S, Yan G (2014) Investigation of heavy oil refinery wastewater treatment by integrated ozone and activated carbon-supported manganese oxides. Fuel Process Technol 124:165–173
Chen M, Ding S, Chen X, Sun Q, Fan X, Lin J, Ren M, Yang L, Zhang C (2018) Mechanisms driving phosphorus release during algal blooms based on hourly changes in iron and phosphorus concentrations in sediments. Water Res 133:153
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (2002) The monitoring analysis method of water and waste water. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Devereux R, Lehrter JC, Jr DLB, Yates DF, Jarvis BM (2015) Manganese, iron, and sulfur cycling in Louisiana continental shelf sediments. Cont Shelf Res 99:46–56
Frederichs T, Dobeneck TV, Bleil U, Dekkers MJ (2003) Towards the identification of siderite, rhodochrosite, and vivianite in sediments by their low-temperature magnetic properties. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/b/c 28:669–679
Fu YQ, Zhou YY, Li JQ (2000) Sequential fractionation of reactive phosphorus in the sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake-Donghu Lake, China. J Environ Sci (China), 12:57–62
Geelhoed JS, Hiemstra T, Riemsdijk WHV (1997) Phosphate and sulfate adsorption on goethite: single anion and competitive adsorption. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:2389–2396
Golterman HL, De Graaf Bierbrauwer-Würtz IM (1992) Colorimetric determination of sulphate in freshwater with a chromate reagent. Hydrobiologia, 228:111–115
Hupfer M, Gächter R, Giovanoli R (1995) Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat Sci 57:305–324
Hupfer M, Lewandowski J (2008) Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments–a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. Int Rev Hydrobiol 93:415–432
Jiao Y, Yang C, He W, Liu W-X, Xu F-L (2018) The spatial distribution of phosphorus and their correlations in surface sediments and pore water in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:25906–25915
Jin C-W, Du S-T, Dong W-Y, Wang J-H, Shen C, Zhang Y-S (2013) Aquatic plant debris improve phosphorus sorption into sediment under anoxic condition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8237–8244
Joshi SR, Kukkadapu RK, Burdige DJ, Bowden ME, Sparks DL, Jaisi DP (2015) Organic matter remineralization predominates phosphorus cycling in the mid-bay sediments in the Chesapeake Bay. Environ Sci Technol 49:5887
Keitel J, Zak D, Hupfer M (2016) Water level fluctuations in a tropical reservoir: the impact of sediment drying, aquatic macrophyte dieback, and oxygen availability on phosphorus mobilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:6883–6894
Lamers LPM, Tomassen HBM, Roelofs JGM (1998) Sulfate-induced eutrophication and phytotoxicity in freshwater wetlands. Environ Sci Technol 32:199–205
Li EH, Li W, Wang XL, Xue HP, Xiao F (2010) Experiment of emergent macrophytes growing in contaminated sludge: implication for sediment purification and lake restoration. Ecol Eng 36:427–434
Li M, Liu J, Xu Y, Qian G (2016) Phosphate adsorption on metal oxides and metal hydroxides: a comparative review. Environ Rev 24:319–332
Liu J, Luo X, Zhang N, Wu Y (2016) Phosphorus released from sediment of Dianchi Lake and its effect on growth of microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16321–16328
Luo SS, Wan GJ, Schmidt R (2001) Characters of cycle and transference of iron and manganese at interface between sediment-water in Wallersee, Austria. Agro-environmental Protection of China, 20: 137–140.
Lyngkilde J, Christensen TH (1992) Redox zones of a landfill leachate pollution plume (Vejen, Denmark). J Contam Hydrol 10:273–289
Morse JW, Arvidson RS, Andreas L (2007) Calcium carbonate formation and dissolution. Chem Rev 107:342–381
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nay M, ., Snozzi M, ., Zehnder AJ (1999): Fate and behavior of organic compounds in an artificial saturated subsoil under controlled redox conditions: the sequential soil column system. Biodegradation 10, 75–82
Oldham VE, Jones MR, Tebo BM, Luther GW (2017) Oxidative and reductive processes contributing to manganese cycling at oxic-anoxic interfaces. Mar Chem 195:122–128
Pakhomova SV, Hall POJ, Kononets MY, Rozanov AG, Tengberg A, Vershinin AV (2007) Fluxes of iron and manganese across the sediment–water interface under various redox conditions. Mar Chem 107:319–331
Li QM, Zhang W, Wang XX, Zhou YY, Yang H, Ji GL (2007) Phosphorus in interstitial water induced by redox potential in sediment of Dianchi Lake, China. Pedosphere 17:739–746
Richardson G (2014) Lab-scale experiment for assessing the effect of resuspension and oxygenation on sediment oxygen demand. Dissertations & Theses - Gradworks
Rietra RP, Hiemstra T, van Riemsdijk WH (2001) Interaction between calcium and phosphate adsorption on goethite. Environ Sci Technol 35:3369
Ruttenberg KC (1992) Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 37:1460–1482
Shen L, Lin GF, Tan JW, Shen JH (2000) Genotoxicity of surface water samples from Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, Eastern China. Chemosphere 41:129–132
Sulu-Gambari F, Seitaj D, Meysman FJ, Schauer R, Polerecky L, Slomp CP (2015) Cable bacteria control iron-phosphorus dynamics in sediments of a coastal hypoxic basin. Environ Sci Technol 50:1227
Svensson J, Leonardson L (2010) Effects of bioturbation by tube-dwelling chironomid larvae on oxygen uptake and denitrification in eutrophic lake sediments. Freshw Biol 35:289–300
Vaněk V, Šilha J, Němeček R (2003) The level of soil nitrate content at different management of organic fertilizers application. Plant Soil Environ 49:197–202
Wang C, Qi Y, Pei Y (2012a) Laboratory investigation of phosphorus immobilization in lake sediments using water treatment residuals. Chem Eng J 209:379–385
Wang JZ, Zhang K, Liang B (2012b) Tracing urban sewage pollution in Chaohu Lake (China) using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) as a molecular marker. Sci Total Environ 414:356–363
Yamanaka M, Nakano T, Norio (2007) Sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in anoxic confined aquifers in the northeastern Osaka Basin, Japan. J Hydrol 335:55–67
Yin H, Yun Y, Zhang Y, Fan C (2011) Phosphate removal from wastewaters by a naturally occurring, calcium-rich sepiolite. J Hazard Mater 198:362–369
Yu H, Xi B, Jiang J, Heaphy MJ, Wang H, Li D (2011) Environmental heterogeneity analysis, assessment of trophic state and source identification in Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1333–1342
Yücel M, Konovalov SK, Moore TS, Janzen CP, Luther GW (2010) Sulfur speciation in the upper Black Sea sediments. Chem Geol 269:364–375
Zhang S, Yi Q, Buyang S, Cui H, Zhang S (2019) Enrichment of bioavailable phosphorus in fine particles when sediment resuspension hinders the ecological restoration of shallow eutrophic lakes. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135672
Zhou J, Qin B, Casenave C, Han X, Yang G, Wu T, Wu P, Ma J (2015) Effects of wind wave turbulence on the phytoplankton community composition in large, shallow Lake Taihu. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12737–12746
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Honghai Ma for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41877397, 51709181, and 51979171).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Shi, W. Effects of sediment oxidation on phosphorus transformation in three large shallow eutrophic lakes in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 25925–25932 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07510-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07510-y