Abstract
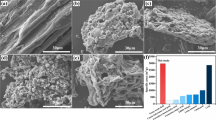
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) occur broadly in natural media due to its extensive use, and it has systematic effects on our ecosystem and human immunity. In this study, long-root Eichhornia crassipes was reclaimed as a multi-functional activated carbon (MFAC) to remove fluoroquinolones (FQs) from contaminated water. To get insight into the adsorption mechanism, multiple measurements, including FTIR and XPS analyses, were employed to investigate the adsorption processes of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin as well as the experiments of effect of exogenous factors on adsorption performances. The results confirmed that the adsorption of FQs by MFAC was mainly attributed to the electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bond interaction, and electronic-donor-acceptor (EDA) interaction. In addition, the kinetics and thermodynamics experiments demonstrated that the MFAC possessed great adsorption performance for FQs. According to the Langmuir model, the saturated adsorption capacities exceeded 145.0 mg/g and 135.1 mg/g for CIP and NOR at 303.15 K, respectively. The column experiments were conducted to explore the application performance of MFAC on the advanced treatment of synthetic water at different flow rates and bed depths. The adsorption capacity of CIP on MFAC was estimated by the Thomas models and the bed-depth service time (BDST) models, reaching 127.56 mg/g and 11,999.52 mg/L, respectively. These results also provide a valid approach for the resource recycling of the redundant long-root Eichhornia crassipes plants.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnieszka C, Rama P, Kaur BS, Patrick D, Mausam V, Surampalli RY (2018) Fluoroquinolones metal complexation and its environmental impacts. Coord Chem Rev 376:46–61
Ahmed MJ, Theydan SK (2014) Fluoroquinolones antibiotics adsorption onto microporous activated carbon from lignocellulosic biomass by microwave pyrolysis. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:219–226
Baginska E, Haiss A, Kümmerer K (2015) Biodegradation screening of chemicals in an artificial matrix simulating the water-sediment interface. Chemosphere 119:1240–1246
Behera SK, Oh SY, Park HS (2010) Sorption of triclosan onto activated carbon, kaolinite and montmorillonite: effects of pH, ionic strength, and humic acid. J Hazard Mater 179:684–691
Cao F, Lian C, Yu J, Yang H, Lin S (2019) Study on the adsorption performance and competitive mechanism for heavy metal contaminants removal using novel multi-pore activated carbons derived from recyclable long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Bioresour Technol 276:211–218
Carabineiro SA, Thavorn-Amornsri T, Pereira MF, Figueiredo JL (2011) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on surface-modified carbon materials. Water Res 45:4583–4591
Crespo-Alonso M, Nurchi VM, Biesuz R, Alberti G, Spano N, Pilo MI, Sanna G (2013) Biomass against emerging pollution in wastewater: ability of cork for the removal of ofloxacin from aqueous solutions at different pH. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1199–1204
Cuypers WL, Jacobs J, Wong V, Klemm EJ, Deborggraeve S, Van SP (2018) Fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella: insights by whole-genome sequencing. Microb Genomics 4:1–9
Darweesh TM, Ahmed MJ (2017) Batch and fixed bed adsorption of levofloxacin on granular activated carbon from date ( Phoenix dactylifera L) stones by KOH chemical activation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 50:159–166
Dong S, Sun Y, Wu J, Wu B, Creamer AE, Gao B (2016) Graphene oxide as filter media to remove levofloxacin and lead from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 150:759–764
Dorivalgarcía N, Zafragómez A, Navalón A, González J, Vílchez JL (2013) Removal of quinolone antibiotics from wastewaters by sorption and biological degradation in laboratory-scale membrane bioreactors. Sci Total Environ 442:317–328
Duan W, Wang N, Xiao W, Zhao Y, Zheng Y (2018) Ciprofloxacin adsorption onto different micro-structured tourmaline, halloysite and biotite. J Mol Liq 269:874–881
Eishafey E, Allawati H, Alsumri AS (2012) Ciprofloxacin adsorption from aqueous solution onto chemically prepared carbon from date palm leaflets. J Environ Sci 24:1579–1586
Fan B, Ryan C, Weiguo S, Ming D (2013) Spatial risk assessment of alien invasive plants in China. Environ Sci Technol 47:7624–7632
Fan Y, Ji Y, Kong D, Lu J, Zhou Q (2015) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of the degradation of sulfamethazine in heat-activated persulfate oxidation process. J Hazard Mater 300:39–47
Fan S, Jie T, Yi W, Hui L, Hao Z, Tang J, Zhen W, Li X (2016) Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Mol Liq 220:432–441
Feng W, Xiao K, Zhou W, Zhu D, Zhou Y, Yu Y, Xiao N, Wan X, Hua Y, Zhao J (2017) Analysis of utilization technologies for Eichhornia crassipes biomass harvested after restoration of wastewater. Bioresour Technol 223:287–295
Fida H, Guo S, Zhang G (2015) Preparation and characterization of bifunctional Ti-Fe kaolinite composite for Cr (VI) removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 442:30–38
Fu Y, Peng L, Zeng Q, Yang Y, Song H, Shao J, Liu S, Gu J (2015) High efficient removal of tetracycline from solution by degradation and flocculation with nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chem Eng J 270:631–640
González JA, Bafico JG, Villanueva ME, Giorgieri SA, Copello GJ (2018) Continuous flow adsorption of ciprofloxacin by using a nanostructured chitin/graphene oxide hybrid material. Carbohydr Polym 188:213–220
Gordon MA (2008) Salmonella infections in immunocompromised adults. J Infect 56:413–422
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG (2005) Sorption of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environ Sci Technol 39:9166–9173
Guo S, Zhang G (2016) Green synthesis of bifunctional Fe-montmorillonite composite during Fenton degradation process and its enhanced adsorption and heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalytic properties. RSC Adv 6:2537–2545
Jiang LH, Liu YG, Zeng GM, Xiao FY, Hu XJ, Hu X, Wang H, Li TT, Zhou L, Tan XF (2016) Removal of 17β-estradiol by few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions: external influence and adsorption mechanism. Chem Eng J 284:93–102
Li S, Hu J (2016) Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline: effect of humic acid on degradation kinetics and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 318:134–144
Li H, Zhang D, Han X, Xing B (2014) Adsorption of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on carbon nanotubes: pH dependence and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 95:150–155
Li JR, Wang YX, Wang X, Yuan B, Fu ML (2015) Intercalation and adsorption of ciprofloxacin by layered chalcogenides and kinetics study. J Colloid Interface Sci 453:69–78
Li MF, Liu YG, Liu SB, Shu D, Zeng GM, Hu XJ, Tan XF, Jiang LH, Yan ZL, Cai XX (2017) Cu (II)-influenced adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by magnetic graphene oxide/nitrilotriacetic acid nanocomposite: competition and enhancement mechanisms. Chem Eng J 319:219–228
Li J, Yu G, Pan L, Li C, You F, Xie S, Yin W, Ma J, Shang X (2018) Study of ciprofloxacin removal by biochar obtained from used tea leaves. J Environ Sci 73:24–34
Lin S, Wang G, Na Z, Lu D, Liu Z (2012) Long-root Eichhornia crassipes as a biodegradable adsorbent for aqueous As (III) and As(V). Chem Eng J 183:365–371
Lin Y, Xu S, Li J (2013) Fast and highly efficient tetracyclines removal from environmental waters by graphene oxide functionalized magnetic particles. Chem Eng J 225:679–685
Lin S, Yang H, Na Z, Lin K (2017) A novel biodegradable arsenic adsorbent by immobilization of iron oxyhydroxide (FeOOH) on the root powder of long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 192:258
Liu L, Hu S, Shen G, Farooq U, Zhang W, Lin S, Lin K (2018) Adsorption dynamics and mechanism of aqueous sulfachloropyridazine and analogues using the root powder of recyclable long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 196:409–417
Lv YY, Xinhai T, Yan S-T, Dahlquist J, Erik (2012) Experimental studies on simultaneous removal of CO2 and SO2 in a polypropylene hollow fiber membrane contactor. Appl Energy 97:283–288
Ma J, Sun Y, Zhang M, Yang M, Gong X, Yu F, Zheng J (2017) Comparative study of graphene hydrogels and aerogels reveals the important role of buried water in pollutant adsorption. Environ Sci Technol 51:12283–12292
Mirzaei A, Ebadi A, Khajavi P (2013) Kinetic and equilibrium modeling of single and binary adsorption of methyl tert -butyl ether (MTBE) and tert -butyl alcohol (TBA) onto nano-perfluorooctyl alumina. Chem Eng J 231:550–560
Nurchi VM, Crespo-Alonso M, Pilo MI, Spano N, Sanna G, Toniolo R (2015) Sorption of ofloxacin and chrysoidine by grape stalk. A representative case of biomass removal of emerging pollutants from wastewater. Arab J Chem 256:727–734
Oleszczuk P, Pan B, Xing B (2010) Adsorption and desorption of oxytetracycline and carbamazepine by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 44:9167–9173
Pei Z, Shan XQ, Kong J, Wen B, Owens G (2010) Coadsorption of ciprofloxacin and Cu (II) on montmorillonite and kaolinite as affected by solution pH. Environ Sci Technol 44:915–920
Peng L, Zhan Z, Dai J, Wu X, Zhang W, Wang K, Yuan S (2013) Adsorption of tetracycline and chloramphenicol in aqueous solutions by bamboo charcoal: a batch and fixed-bed column study. Chem Eng J 228:496–505
Picó Y, Andreu V (2007) Fluoroquinolones in soil--risks and challenges. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1287–1299
Prieto A, Möder M, Rodil R, Adrian L, Marco-Urrea E (2011) Degradation of the antibiotics norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin by a white-rot fungus and identification of degradation products. Bioresour Technol 102:10987–10995
Qaiser S, Saleemi AR, Umar M (2009) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solution by Ficus religiosa leaves: batch and column study. J Hazard Mater 166:998–1005
Ruiz J, Pons MJ, Gomes C (2012) Transferable mechanisms of quinolone resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents 40:196–203
Singla P, Goel N, Singhal S (2016) Affinity of boron nitride nanomaterials towards antibiotics established by exhaustive experimental and theoretical investigations. Chem Eng J 299:403–414
Sui M, Zhou Y, Sheng L, Duan B (2012) Adsorption of norfloxacin in aqueous solution by Mg–Al layered double hydroxides with variable metal composition and interlayer anions. Chem Eng J 210:451–460
Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, Pulcini C, Kahlmeter G, Kluytmans J, Carmeli Y (2017) Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis 18:318–327
Tran VS, Ngo HH, Guo W, Zhang J, Liang S, Ton-That C, Zhang X (2015) Typical low cost biosorbents for adsorptive removal of specific organic pollutants from water. Bioresour Technol 182:353–363
Versporten A, Zarb P, Caniaux I, Gros MF, Drapier N, Miller M, Jarlier V, Nathwani D, Goossens H, Network GP (2018) Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in adult hospital inpatients in 53 countries: results of an internet-based global point prevalence survey. Lancet Glob Health 6:619–629
Wallis SC, Gahan LR, Charles BG, Hambley TW, Duckworth PA (1996) Copper (II) complexes of the fluoroquinolone antimicrobial ciprofloxacin. Synthesis, X-ray structural characterization, and potentiometric study. J Inorg Biochem 62:1–16
Wan X, Zhan Y, Long Z, Zeng G, Yi H (2017) Core@double-shell structured magnetic halloysite nanotube nano-hybrid as efficient recyclable adsorbent for methylene blue removal. Chem Eng J 330:491–504
Wang CJ, Li Z, Jiang WT, Jean JS, Liu CC (2010) Cation exchange interaction between antibiotic ciprofloxacin and montmorillonite. J Hazard Mater 183:309–314
Wang CJ, Li Z, Jiang WT (2011) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on 2:1 dioctahedral clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 53:723–728
Wang W, Ma Y, Li A, Zhou Q, Zhou W, Jin J (2015) Two novel multi-functional magnetic adsorbents for effective removal of hydrophilic and hydrophobic nitroaromatic compounds. J Hazard Mater 294:158–167
Wang B, Jiang YS, Li FY, Yang DY (2017) Preparation of biochar by simultaneous carbonization, magnetization and activation for norfloxacin removal in water. Bioresour Technol 233:159–165
Wu Q, Li Z, Hong H, Yin K, Tie L (2010) Adsorption and intercalation of ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 50:204–211
Yan B, Niu CH (2017) Modeling and site energy distribution analysis of levofloxacin sorption by biosorbents. Chem Eng J 307:631–642
Yan W, Zhang J, Jing C (2013) Adsorption of enrofloxacin on montmorillonite: two-dimensional correlation ATR/FTIR spectroscopy study. J Colloid Interface Sci 390:196–203
Yang W, Lu Y, Zheng F, Xue X, Li N, Liu D (2012) Adsorption behavior and mechanisms of norfloxacin onto porous resins and carbon nanotube. Chem Eng J 179:112–118
Zhan Y, He S, Wan X, Zhang J, Liu B, Wang J, Li Z (2018) Easy-handling bamboo-like polypyrrole nanofibrous mats with high adsorption capacity for hexavalent chromium removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 529:385–395
Zhang R, Yang Y, Huang CH, Zhao L, Sun P (2016) Kinetics and modeling of sulfonamide antibiotic degradation in wastewater and human urine by UV/H2O2 and UV/PDS. Water Res 103:283–292
Zhang WT, Yang L, Kurths Y, Juergen (2017) Event-triggering containment control for a class of multi-agent networks with fixed and switching topologies. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I-Regul Papers 64:619–629
Zhao G, Li J, Ren X, Chen C, Wang X (2011) Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ Sci Technol 45:10454–10462
Zheng JC, Liu HQ, Feng HM, Li WW, Lam MH, Lam PK, Yu HQ (2016) Competitive sorption of heavy metals by water hyacinth roots. Environ Pollut 219:837–845
Zhou L, Ji L, Ma PC, Shao Y, Zhang H, Gao W, Li Y (2014) Development of carbon nanotubes/CoFe2O4 magnetic hybrid material for removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and Pb(II). J Hazard Mater 265:104–114
Zhou Y, Gao Y, Pang S, Jiang J, Yang Y, Ma J, Yang Y, Duan J, Guo Q (2016) Oxidation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics by peroxymonosulfate without activation: kinetics, products, and antibacterial deactivation. Water Res 106:507–517
Zhuang Y, Yu F, Ma J, Chen J (2017) Enhanced adsorption removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by modified alginate/graphene double network porous hydrogel. J Colloid Interface Sci 507:250–259
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771513, 41001316, 51704121), the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment in China (2017ZX07202006, 2014ZX07104-006), and the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1901000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 164 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Chen, X., Wang, Z. et al. Removal of aqueous fluoroquinolones with multi-functional activated carbon (MFAC) derived from recycled long-root Eichhornia crassipes: batch and column studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34345–34356 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06173-z