Abstract
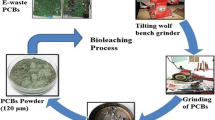
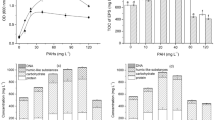
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) extracted from fungal mycelium by four chemical methods (NaOH, H2SO4, formaldehyde-NaOH, glutaraldehyde-NaOH), three physical methods (heating, ultrasound, vibration), and a control method (centrifugation alone) were investigated. Results indicated formaldehyde-NaOH outperformed other methods with 186.6 ± 8.0 mg/g of polysaccharides and 23.2 ± 4.6 mg/g of protein extracted and ensured little contamination by intracellular substances. Thereafter, this method was applied in extracting EPS from a mixed fungal culture in the adaptation process with 0.5% (w/v) waste printed circuit boards (PCBs). With the four adaptation stages continuing, the culture tended to become more sensitive to respond to the external toxic environment characterized by secreting EPS more easily and quickly. The maximum amount of polysaccharides and protein could be achieved in only 3 days both at the 3rd and 4th adaptation stage. Three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectrum indicated the peaks obtained for EPS were mainly associated to soluble microbial by-product-like and aromatic protein-like compounds. Transmission electron microscopic observation illustrated that although metal ions penetrated into hypha cells, parts of them could be absorbed by EPS, implying that EPS secretion may be a primary protective strategy adopted by the culture.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J Hazard Mater 154:1120–1126
Amiri F, Yaghmaei S, Mousavi SM, Sheibani S (2011) Recovery of metals from spent refinery hydrocracking catalyst using adapted Aspergillus niger. Hydrometallurgy 109:65–71
Bai J, Chao Y, Chen Y, Wang S, Qiu R (2017) Immobilization of Cu by Bacillus subtilis DBM and the role of extracellular polymeric substances. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:86
Baker A (2001) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environ Sci Technol 35:948–953
Beech WB, Sunner J (2004) Biocorrosion: towards understanding interactions between biofilms and metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:181–186
Bellion M, Courbot M, Jacob C, Blaudez D, Chalot M (2006) Extracellular and cellular mechanisms sustaining metal tolerance in ectomycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:173–181
Burgstaller W, Schinner F (1993) Leaching of metals with fungi. J Biotechnol 27:91–116
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710
Chen X, Shi J, Chen Y, Xu X, Xu S, Wang Y (2006) Tolerance and biosorption of copper and zinc by Pseudomonas putida CZ1 isolated from metal-polluted soil. Can J Microbiol 52:308–316
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006a) Relations between extraction protocols for activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and complexation properties of Pb and Cd with EPS part II. Consequences of EPS extraction methods on Pb2+ and Cd2+ complexation. Enzym Microb Technol 38:246–252
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006b) Relations between extraction protocols for activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and EPS complexation properties part I. Comparison of the efficiency of eight EPS extraction methods. Enzym Microb Technol 38:237–245
d'Abzac P, Bordas F, van Hullebusch E, Lens PNL, Guibaud G (2010) Effects of extraction procedures on metal binding properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from anaerobic granular sludges. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 80:161–168
Domínguez L, Rodríguez M, Prats D (2010) Effect of different extraction methods on bound EPS from MBR sludges. Part I: influence of extraction methods over three-dimensional EEM fluorescence spectroscopy fingerprint. Desalination 261:19–26
Gong AS, Bolster CH, Benavides M, Walker SL (2009) Extraction and analysis of extracellular polymeric substances: comparison of methods and extracellular polymeric substance levels in Salmonella pullorum SA 1685. Environ Eng Sci 26:1523–1532
Jablonski JE, Fu T-J, Jackson LS, Gendel SM (2010) Determination of protein levels in soy and peanut oils by colorimetric assay and ELISA. J AOAC Int 93:213–220
Kelleher BP, Simpson AJ (2006) Humic substances in soils: are they really chemically distinct? Environ Sci Technol 40:4605–4611
Kinzler K, Gehrke T, Telegdi J, Sand W (2003) Bioleaching - a result of interfacial processes caused by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Hydrometallurgy 71:83–88
Kleber M, Johnson MG (2010) Chapter 3 – advances in understanding the molecular structure of soil organic matter : implications for interactions in the environment. Adv Agron 106:77–142
Liu H, Fang HHP (2002) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J Biotechnol 95:249–256
Liu Y, Tay J-H (2004) State of the art of biogranulation technology for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:533–563
Lu Q, Chang M, Yu Z, Zhou S (2015) The effects of three commonly used extraction methods on the redox properties of extracellular polymeric substances from activated sludge. Environ Technol 36:2884–2891
McSwain BS, Irvine RL, Hausner M, Wilderer PA (2005) Composition and distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic flocs and granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1051–1057
Pal A, Paul AK (2008) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: central elements in heavy metal bioremediation. Indian J Microbiol 48:49–64
Peng TJ, Zhou D, Liu YN, Yu RL, Qiu GZ, Zeng WM (2019): Effects of pH value on the expression of key iron/sulfur oxidation genes during bioleaching of chalcopyrite on thermophilic condition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-019-01453-y
Santamaria M, Diaz-Marrero AR, Hernandez J, Gutierrez-Navarro AM, Corzo J (2003) Effect of thorium on the growth and capsule morphology of Bradyrhizobium. Environ Microbiol 5:916–924
Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q, Li X-Y (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Yu Z (2005) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:125–130
Sobeck DC, Higgins MJ (2002) Examination of three theories for mechanisms of cation-induced bioflocculation. Water Res 36:527–538
Tan SN, Chen M (2012) Early stage adsorption behaviour of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on minerals I: an experimental approach. Hydrometallurgy 119:87–94
Urrutia MM, Beveridge TJ (1993) Remobilization of heavy metals retained as oxyhydroxides or silicates by Bacillus subtilis cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4323–4329
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 45-53
Wu XL, Wu XY, Shen L, Li JK, Yu RL, Liu YD, Qiu GZ, Zeng WM (2019): Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomics analyses of Pandoraea sp. XY-2, a new species capable of biodegrade tetracycline. Front Microbiol 10
Xia M, Wang Y, Peng T, Shen L, Yu R, Liu Y, Chen M, Li J, Wu X, Zeng W (2017) Recycling of metals from pretreated waste printed circuit boards effectively in stirred tank reactor by a moderately thermophilic culture. J Biosci Bioeng 123:714–721
Xia M, Bao P, Liu A, Wang M, Shen L, Yu R, Liu Y, Chen M, Li J, Wu X (2018) Bioleaching of low-grade waste printed circuit boards by mixed fungal culture and its community structure analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 136:267–275
Yu R, Hou C, Liu A, Peng T, Xia M, Wu X, Shen L, Liu Y, Li J, Yang F, Qiu G, Chen M, Zeng W (2018) Extracellular DNA enhances the adsorption of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans strain ST on chalcopyrite surface. Hydrometallurgy 176:97–103
Yu RL, Liu A, Liu Y, Yu Z, Peng T, Wu X, Shen L, Liu Y, Li J, Liu X, Qiu G, Chen M, Zeng W (2017) Evolution of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans secreting alginate during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate. J Appl Microbiol 122:1586–1594
Zeng W, Qiu G, Zhou H, Liu X, Chen M, Chao W, Zhang C, Peng J (2010) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances extracted during the bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 100:177–180
Zhang L, Ren H, Ding L (2012) Comparison of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extraction from two different activated sludges. Water Sci Technol 66:1558–1564
Zhang X, Bishop PL (2003) Biodegradability of biofilm extracellular polymeric substances. Chemosphere 50:63–69
Zheng Y, Zhao X, Jia K, Li J, Wang L, Wang R, Lu X, Zhang D (2018) bifA regulates biofilm development of Pseudomonas putidaMnB1 as a primary response to H2O2and Mn2+. Front Microbiol 9:1490
Zhu L, Qi H, Lv M, Kong Y, Yu Y, Xu X (2012) Component analysis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during aerobic sludge granulation using FTIR and 3D-EEM technologies. Bioresour Technol 124:455–459
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470230, 51320105006, 51604308), the Youth Talent Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No.2017RS3003), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No.2018JJ2486), and Key Research and Development Projects in Hunan Province (2018WK2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, M., Bao, P., Zhang, S. et al. Extraction and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from a mixed fungal culture during the adaptation process with waste printed circuit boards. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 22137–22146 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05234-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05234-7