Abstract
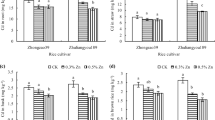
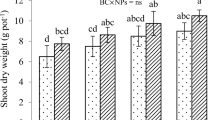
The contamination of large areas of arable land with cadmium (Cd) is a serious concern worldwide and environmentally feasible amendments are necessary to minimize Cd accumulation in cereals such as rice (Oryza sativa L.). A pot study was, therefore, conducted to evaluate the efficiency of foliar spray of different levels (0, 50, 75, 100 mg/L) of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) alone or combined with biochar (1.0% w/w) on Cd content in rice plants grown on an aged Cd-polluted soil. The results showed that ZnO NPs alone or combined with biochar improved the biomass and photosynthesis of rice plant. The ZnO NPs significantly diminished the Cd concentration and enhanced the Zn concentrations in shoots and roots either alone or in combination with biochar. Foliar spray of 100 mg/L ZnO NPs significantly diminished the Cd content in rice shoot and rice roots by 30% and 31%, respectively. The Cd concentrations in rice shoot and root diminished by 39% and 38% after 100 mg/L ZnO NPs combined with biochar, respectively. The ZnO NPs in combination with biochar increased the soil pH from 8.03 to 8.23 units. Soil AB-DTPA-extractable Cd significantly reduced with the amendments applied over the control. Foliar spray of ZnO NPs combined with biochar could be used to grow rice plants especially in areas where Cd concentration is high and Zn deficiency is high.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Mahmood A, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF (2018) Biochar application increased the growth and yield and reduced cadmium in drought stressed wheat grown in an aged contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:825–833
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Abbas F, Hannan F, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:37–47
Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One 10:1–23
Ali B, Tao Q, Zhou Y, Gill RA, Ali S, Rafiq MT, Xu L, Zhou W (2013) 5-Aminolevolinic acid mitigates the cadmium-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by the biochemical and ultra-structural evaluation of roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:271–280
Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Ibrahim M, Riaz M, Arif MS, Hafeez F, Al-Wabel MI, Shahzad AN (2017) Biochar soil amendment on alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12700–12712
Amacher MC (1996) Nickel, cadmium and lead. p. 739–768. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods, 3rd edn. SSSA/ASA, Madison
Bashir A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Ishaque W, Riaz MA, Maqbool A (2018) Effect of foliar-applied iron complexed with lysine on growth and cadmium (cd) uptake in rice under cd stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20691–20699
Baycu G, Gevrek-Kürüm N, Moustaka J, Csatári I, Rognes SE, Moustakas M (2017) Cadmium-zinc accumulation and photosystem II responses of Noccaea caerulescens to cd and Zn exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2840–2850
Beesley L, Marmiroli M (2011) The immobilisation and retention of soluble arsenic, cadmium and zinc by biochar. Environ Pollut 159:474–480
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle- size analyses of soils. Agron J 54:464–465
Cakmak I, Kutman UB (2018) Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur J Soil Sci 69:172–180
Dapkekar A, Deshpande P, Oak MD, Paknikar KM, Rajwade JM (2018) Zinc use efficiency is enhanced in wheat through nanofertilization. Sci Rep 8:1–10
Dimkpa CO, White JC, Elmer WH, Gardea-Torresdey J (2017) Nanoparticle and ionic Zn promote nutrient loading of sorghum grain under low NPK fertilization. J Agric Food Chem 65:8552–8559
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gao X, Mohr RM, McLaren DL, Grant CA (2011) Grain cadmium and zinc concentrations in wheat as affected by genotypic variation and potassium chloride fertilization. Field Crop Res 122:95–103
García-Gómez C, Obrador A, González D, Babín M, Fernández MD (2018) Comparative study of the phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles and Zn accumulation in nine crops grown in a calcareous soil and an acidic soil. Sci Total Environ 644:770–780
Gil-Diaz M, Pinilla P, Alonso J, Lobo MC (2017) Viability of a nanoremediation process in single or multi-metal (loid) contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 321:812–819
Huang G, Ding C, Zhou Z, Zhang T, Wang X (2019) A tillering application of zinc fertilizer based on basal stabilization reduces cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:338–344
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM cu. Planta 241:847–860
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Li C, Wang P, Lombi E, Cheng M, Tang C, Howard DL, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2018a) Absorption of foliar-applied Zn fertilizers by trichomes in soybean and tomato. J Exp Bot 69:2717–2729
Li C, Wang P, Lombi E, Wu J, Blamey FP, Fernández V, Howard DL, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2018b) Absorption of foliar applied Zn is decreased in Zn deficient sunflower (Helianthus annuus) due to changes in leaf properties. Plant Soil 433:309–322
Li S, Wang M, Zhao Z, Li X, Han Y, Chen S (2018c) Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity to wheat is associated with cd re-distribution in soil aggregates as affected by amendments. RSC Adv 8:17426–17434
Liu J, Cai H, Mei C, Wang M (2015) Effects of nano-silicon and common silicon on lead uptake and translocation in two rice cultivars. Front Environ Sci Eng 9:905–911
Moodie CD, Smith HW, McCreery RA (1959) Laboratory manual for soil fertility. Washington State College Mimeograph, Washington
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
O'Connor D, Peng T, Zhang J, Tsang DC, Alessi DS, Shen Z, Bolan NS, Hou D (2018) Biochar application for the remediation of heavy metal polluted land: a review of in situ field trials. Sci Total Environ 619:815–826
Pandey VC (2012) Phytoremediation of heavy metals from fly ash pond by Azolla caroliniana. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:8–12
Pullagurala VL, Adisa IO, Rawat S, Kim B, Barrios AC, Medina-Velo IA, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2018) Finding the conditions for the beneficial use of ZnO nanoparticles towards plants-a review. Environ Pollut 241:1175–1181
Qayyum MF, Rehman MZ, Ali S, Rizwan M, Naeem A, Maqsood MA, Khalid H, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field. Chemosphere 174:515–523
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soils and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ali S, Naeem A, Yousaf B, Lui G, Azhar M (2018) A field study investigating the potential use of phosphorus combined with organic amendments on cadmium accumulation by wheat and subsequent rice. Arab J Geosci 11:1–10
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016a) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Rehman MZ, Waris AA (2019a) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Rizwan M, Ali S, Hussain A, Ali Q, Shakoor MB, Rehman MZ, Farid M, Asma M (2017a) Effect of zinc-lysine on growth, yield and cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 187:35–42
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016b) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Farid M, Abbas F (2017b) Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 322:2–16
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Maqbool A (2019b) A critical review on the effects of zinc at toxic levels of cadmium in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04174-6
Saifulah JH, Naeem A, Rengel Z, Dahlawi S (2016) Timing of foliar Zn application plays a vital role in minimizing cd accumulation in wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 223:16432–16439
Soltanpour PN (1985) Use of AB-DTPA soil test to evaluate elemental availability and toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 16:323–338
Sturikova H, Krystofova O, Huska D, Adam V (2018) Zinc, zinc nanoparticles and plants. J Hazard Mater 349:101–110
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2015) Silicon nanoparticles (SiNp) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 96:189–198
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining in soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic soil titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang H, Xu C, Luo ZC, Zhu HH, Wang S, Zhu QH, Huang DY, Zhang YZ, Xiong J, He YB (2018) Foliar application of Zn can reduce cd concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29287–29294
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S (2015) Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2837–2845
Funding
Financial support was received from the Government College University, Faisalabad and Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan under NRPU Project No. 5634/Punjab/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2016. Funding was received from Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University to the Research Group number (RG-199).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Rizwan, M., Noureen, S. et al. Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 11288–11299 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04554-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04554-y