Abstract
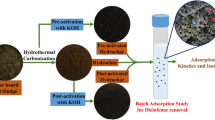
Pharmaceutically active compounds like diclofenac (DFS), ibuprofen (IBP), and other drugs that persist in the environment are listed as emerging contaminants. These escape from normal wastewater treatment plants and find their way to water streams; therefore, alternate treatment processes are needed. Herein, a sorbent material is reported that is prepared through hydrotermal carbonization from dried fruit powder of Zizipus mauritiana L. (HTC-ZM) and applied for simultaneous removal of DFS and IBP. Carbonized material (HTC-ZM) was found as agglomerates of approximately 1 μm particle size with surface area of 1160 m2/g having oxygen functional groups (e.g., COO, O, C=O) on surface. Simultaneous removal of IBP and DFS onto HTC-ZM was studied using response surface methodology with a set of 18 experiments using factors such as pH, amount of sorbent, contact time, and sorbate concentration. Maximum removal efficiency was obtained 88% and 97% for DFS and for IBP, respectively, with adsorption capacity of 2.03 mmol g−1 for DFS and 2.54 mmol g−1 for IBP. Kinetics modeling and “mean free energy” values predicted that sorption is mainly governed by physical interactions followed by “pore filling” mechanism for uptake of DFS and IBP.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 March 2019
The original publication of this paper contain typographical mistakes.
References
Alatalo SM, Mäkilä E, Repo E, Heinonen M, Salonen J, Kukk E, Sillanpää M, Titirici MM (2016) Meso-and microporous soft templated hydrotermal carbons for dye removal from water. Green Chem 18:1137–1146
Ahmed MB, Zhou JL, Ngo HH, Guo W (2015) Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water and wastewater: progress and challenges. Sci Total Environ 532:112–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.130
Anonymous (2011) Economic survey of Pakistan Government of Pakistan. Ministry of Food and Agriculture, Islamabad. http://www.parc.gov.pk/. Accessed 23 Nov 2015
Arora RK SAACRCNAKSAJSRWS Fruits for the future 2: ber Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Field manual for extension workers. Crops for the future. pp-77
Azam-Ali S, Bonkoungou E, Bowe C, DeKok C, Godara A, Williams JT (eds) ( 2006) Ber and other jujubes. In: Fruits for the future. Southampton Centre for Underutilized Crops, Southhampton, pp 18–23
Boeije G (1999) Chemical fate prediction for use in geo-referenced environmental exposure assessment. PhD Thesis, University of Ghent, Belgium
Brodin T, Fick J, Jonsson M, Klaminder J (2013) Dilute concentrations of a psychiatric drug alter behavior of fish from natural populations. Science 339:814–815. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1226850
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM, Llompart M, Garcı́a JC, Rodrı́guez I, Gómez M, Ternes T (2004) Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res 38:2918–2926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.03.029
Cleuvers M (2003) Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol Lett 142:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00068-7
Cleuvers M (2004) Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00141-6
Dąbrowski A (2001) Adsorption—from theory to practice. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 93:135–224
Deshmane CA, Wright MW, Lachgar A, Rohlfing M, Liu Z, Le J, Hanson BE (2013) A comparative study of solid carbon acid catalysts for the esterification of free fatty acids for biodiesel production. Evidence for the leaching of colloidal carbon. Bioresour Technol 147:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortec.2013.08.073
Dong L, Guo S, Zhu S, Xu D, Zang L, uo M, Yang X (2011) Sunlight responsive BiVO4photocatalyst: effects of pH on L-cysteine-assisted hydrotermal treatment and enhanced degradation of ofloxacin. Catal Commun 16:250–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.05.005
Falco C, Baccile N, Titirici M-M (2011) Morphological and structural differences between glucose, cellulose and lignocellulosic biomass derived hydrotermal carbons. Green Chem 13:3273–3281
Fan W, Gao W, Zhang C, Tjiu WW, Pan J, Liu T (2012) Hybridization of graphene sheets and carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a synergistic adsorbent of organic dyes. J Mater Chem 22:25108–25115. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm35609k
Fernandez M, Ledesma B, Román S, Bonelli P, Cukierman A (2015) Development and characterization of activated hydrochars from orange peels as potential adsorbents for emerging organic contaminants. Bioresour Technol 183:221–228
Funke A, Ziegler F (2010) Hydrotermal carbonization of biomass: a summary and discussion of chemical mechanisms for process engineering. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 4:160–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.198
Grassi M, Kaykioglu G, Belgiorno V, Lofrano G (2012) Removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by adsorption process. In: Lofrano G (ed) Emerging compounds removal from wastewater: natural and solar based treatments. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 15–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3916-1_2
Hamdaoui O, Naffrecoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chloropenols onto granular activated carbon: part II. Models with more than two parameters. J Hazard Mater 147:401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jazmat.2007.01.023
Hasan Z, Jhung S (2015) Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J Hazard Mater 283:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jazmat.2014.09.046
Jain A, Balasubramanian R, Srinivasan MP (2015) Production of high surface area mesoporous activated carbons from waste biomass using hydrogen peroxide-mediated hydrotermal treatment for adsorption applications. Chem Eng J 273:622–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.111
Jjemba PK (2006) Excretion and ecotoxicity of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.11.011
Langford K, Thomas KV (2009) Determination of pharmaceutical compounds in hospital effluents and their contribution to wastewater treatment works. Environ Int 35:766–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.02.007
Luo L, Xu C, Chen Z, Zhang S (2015) Properties of biomass-derived biocars: combined effects of operating conditions and biomass types. Bioresour Technol 192:83–89
Malghani S, Gleixner G, Trumbore SE (2013) Chars produced by slow pyrolysis and hydrotermal carbonization vary in carbon sequestration potential and greenhouse gases emissions. Soil Biol Biochem 62:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.03.013
Memon AA, Memon N, Bhanger MI, Luthria DL (2013) Assay of phenolic compounds from four species of ber (Ziziphus mauritiana L.) fruits: comparison of three base hydrolysis procedure for quantification of total phenolic acids. Food Chem 139:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcem.2013.01.065
Mestre AS, Pires RA, Aroso I, Fernandes EM, Pinto ML, Reis RL, Andrade MA, Pires J, Silva SP, Carvalo AP (2014) Activated carbons prepared from industrial pre-treated cork: sustainable adsorbents for pharmaceutical compounds removal. Chem Eng J 253:408–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.051
Mestre AS, Tyszko E, Andrade MA, Galhetas M, Freire C, Carvalo AP (2015) Sustainable activated carbons prepared from a sucrose-derived hydrochar: remarkable adsorbents for pharmaceutical compounds. RSC Adv 5:19696–19707. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra14495c
Mi Y, u W, Dan Y, Liu Y (2008) Synthesis of carbon micro-spheres by a glucose hydrotermal method. Mater Lett 62:1194–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.08.011
Oaks JL, Gilbert M, Virani MZ, Watson RT, Meteyer CU, Rideout BA, Sivaprasad L, Amed S, Iqbal Caudry MJ, Arsad M, Mamood S, Ali A, Amed Kan A (2004) Diclofenac residues as the cause of vulture population decline in Pakistan. Nature 427(6975):630–633. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v427/n6975/suppinfo/nature02317_S1.tml
Oliveira I, Blöhse D, Ramke HG (2013) Hydrotermal carbonization of agricultural residues. Bioresour Technol 142:138–146
Pailler JY, Krein A, Pfister L, offmann L, Guignard C (2009) Solid phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatograpy-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, analgesics and hormones in surface water and wastewater in Luxembourg. Sci Total Environ 407:4736–4743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.042
Pobudkowska A, Domańska U (2014) Study of pH-dependent drugs solubility in water. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 20:115–126
Qu K, Wang J, Ren J, Qu X (2013) Carbon dots prepared by hydrotermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem Eur J 19:7243–7249. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.201300042
Quresi T, Memon N, Memon SQ, Shaik H (2014) Determination of ibuprofen drug in aqueous environmental samples by gas chromatograpy–mass spectrometry without derivatization. Am J Modern Chromatogr 1:45–54
Ragugnetti M, Adams ML, Guimarães ATB, Sponchiado G, de Vasconcelos EC, de Oliveira CMR (2011) Ibuprofen genotoxicity in aquatic environment: an experimental model using Oreochromis niloticus. Water Air Soil Pollut 218:361–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0698-0
Regmi P, Garcia Moscoso JL, Kumar S, Cao X, Mao J, Schafran G (2012) Removal of copper and cadmium from aqueous solution using switcgrass biocar produced via hydrotermal carbonization process. J Environ Manag 109:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.04.047
Rillig MC et al (2010) Material derived from hydrotermal carbonization: effects on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Appl Soil Ecol 45:238–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.04.011
Roman S, Nabais JV, Ledesma B, González J, Laginhas C, Titirici M (2013) Production of low-cost adsorbents with tunable surface chemistry by conjunction of hydrotermal carbonization and activation processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 165:127–133
Shaik H, Memon N, Bhanger M, Nizamani S (2014) GC/MS based non-target screening of organic contaminants in river Indus and its tributaries in Sindh (Pakistan). Pakistan J Anal Environ Chem 15:42–65
Scheurell M, Franke S, Shah R, Hünerfuss H (2009) Occurrence of diclofenac and its metabolites in surface water and effluent samples from Karachi. Pakistan Chemosphere 77:870–876
Shi Y, Zang X, Liu G (2015) Activated carbons derived from hydrotermally carbonized sucrose: remarkable adsorbents for adsorptive desulfurization. ACS Sustain Chemistry Eng 3:2237–2246. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuscemeng.5b00670
Suarez S, Lema JM, Omil F (2009) Pre-treatment of hospital wastewater by coagulation–flocculation and flotation. Bioresour Technol 100:2138–2146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortec.2008.11.015
Ternes TA, Meisenheimer M, McDowell D, Sacher F, Brauch HJ, Haist-Gulde B, Preuss G, Wilme U, Zulei-Seibert N (2002) Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 36:3855–3863. https://doi.org/10.1021/es015757k
Titirici M-M (2012) Chapter 12 - hydrotermal carbons: synthesis, characterization, and applications A2 - Tascón. In: Juan MD (ed) Novel carbon adsorbents. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 351–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097744-7.00012-0
Titirici M-M (2013) Sustainable carbon materials from hydrotermal processes. Wiley, Oxford
Titirici MM, Thomas A, Yu S, Müller J-O, Antonietti M (2007) A direct synthesis of mesoporous carbons with bicontinuous pore morphology from crude plant material by hydrotermal carbonization. Chem Mater 19:4205–4212. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0707408
Titirici M-M, Antonietti M, Baccile N (2008) Hydrotermal carbon from biomass: a comparison of the local structure from poly- to monosaccarides and pentoses/exoses. Green Chem 10:1204–1212. https://doi.org/10.1039/b807009a
Wang S, Gao B, Zimmerman AR, Li Y, Ma L, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015) Pyhsicocemical and sorptive properties of biochars derived from woody and erbaceous biomass. Chemosphere 134:257–262
Wu M, Janssen S (2010) Dosed without prescription: a framework for preventing pharmaceutical contamination of our nation’s drinking water. Environ Sci Technol 45:366–367
Funding
Financial support from Pak-US Science and Technology Cooperation Program, Phase VI (Project No. 6/6/PAK-US/EC/2015/06) is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised:
The original publication of this paper contain typographical mistakes.
The published paper had missed letter ‘H’ in some parts of text, references and figure captions. These changes does not affect the findings of paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qureshi, T., Memon, N., Memon, S.Q. et al. Evaluation of hydrochar efficiency for simultaneous removal of diclofenac and ibuprofen from aqueous system using surface response methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 9796–9804 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04359-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04359-z