Abstract
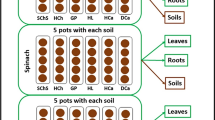
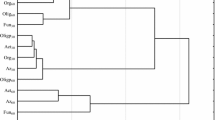
Soils can be contaminated by pharmaceuticals. The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of soil conditions (influencing sorption and persistence of pharmaceuticals in soils) and plant type on the root uptake of selected pharmaceuticals and their transformation in plant-soil systems. Four plants (lamb’s lettuce, spinach, arugula, radish) planted in 3 soils were irrigated for 20 days (26) with water contaminated by one of 3 pharmaceuticals (carbamazepine, atenolol, sulfamethoxazole) or their mixture. The concentrations of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in soils and plant tissues were evaluated after the harvest. Sulfamethoxazole and atenolol dissipated rapidly from soils. The larger concentrations of both compounds and an atenolol metabolite were found in roots than in leaves. Sulfamethoxazole metabolites were below the limits of quantifications. Carbamazepine was stable in soils, easily uptaken, accumulated, and metabolized in plant leaves. The efficiency of radish and arugula (both family Brassicaceae) in metabolizing was very low contrary to the high and moderate efficiencies of lamb’s lettuce and spinach, respectively. Compounds’ transformations mostly masked the soil impact on their accumulation in plant tissues. The negative relationships were found between the carbamazepine sorption coefficients and its concentrations in roots of radish, lamb’s lettuce, and spinach.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Ahmed MBM, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Vu NT, Kim IS, Kang HM, Lee SS, Ok YS (2015) Distribution and accumulative pattern of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in edible vegetables of cucumber, tomato, and lettuce. J Agric Food Chem 63(2):398–405. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5034637
Bower CA, Hatcher JT (1966) Simultaneous determination of surface area and cation exchange capacity. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 30:525–527
Calderón-Preciado D, Matamoros V, Savé R, Muñoz P, Biel C, Bayona JM (2013) Uptake of microcontaminants by crops irrigated with reclaimed water and groundwater under real field greenhouse conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3629–3638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1509-0
Carter LJ, Williams M, Böttcher C, Kookana RS (2015) Uptake of pharmaceuticals influences plant development and affects nutrient and hormone homeostasis. Environ Sci Technol 49(20):2509–12518 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03468
Chung HS, Lee Y-J, Rahman MM, El-Aty AMA, Lee HS, Kabir MH, Kim SW, Park B-J, Kim J-E, Hacımüftüoğlu F, Nahar N, Shin H-C, Shim JH (2017) Uptake of the veterinary antibiotics chlortetracycline, enrofloxacin, and sulphathiazole from soil by radish. Sci Total Environ 605–606:322–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.231
Dodgen LK, Li J, Parker D, Gan JJ (2013) Uptake and accumulation of four PPCP/EDCs in two leafy vegetables. Environ Pollut 182:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.06.038
Dodgen LK, Ueda A, Wu X, Parker DR, Gan J (2015) Effect of transpiration on plant accumulation and translocation of PPCP/EDCs. Environ Pollut 198:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.002
Droge STJ, Goss KU (2013) Sorption of organic cations to phyllosilicate clay minerals: CEC-normalization, salt dependency, and the role of electrostatic and hydrophobic effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:14224–14232. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403187w
Edgington L (1981) Structural requirements of systemic fungicides. Annu Rev Phytopathol 19:107–124
Fedorova G, Randak T, Golovko O, Kodes V, Grabicova K, Grabic R (2014) A passive sampling method for detecting analgesics, psycholeptics, antidepressants and illicit drugs in aquatic environments in the Czech Republic. Sci Total Environ 487:681–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.091
Fér M, Kodešová R, Golovko O, Schmidtová Z, Klement A, Kočárek M, Grabic R (2018) Sorption of atenolol, sulfamethoxazole and carbamazepine onto soil aggregates from the illuvial horizon of the Haplic Luvisol on loess. Soil Water Res 13(3):177–183. https://doi.org/10.17221/82/2018-SWR
Figueroa-Diva RA, Vasudevan D, Mackay AA (2010) Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere 79:786–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.017
Gee GW, Or D (2002) Particle-size analysis. In: Dane JH, Topp GC (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 4. Physical Methods. Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 255–294
Goldstein G, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2014) Insights into the uptake processes of wastewater-borne pharmaceuticals by vegetables. Environ Sci Technol 48(10):5593–5600. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5008615
Golovko O, Kumar V, Fedorova G, Randak T, Grabic R (2014) Seasonal changes in antibiotics, antidepressants/psychiatric drugs, antihistamines and lipid regulators in a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 111:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.132
Golovko O, Koba O, Kodešová R, Fedorova G, Kumar V, Grabic R (2016) Development of fast and robust multiresidual LC-MS/MS method for determination of pharmaceuticals in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(14):14068–14077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6487-6
Grabicova K, Stanova AV, Ucun OK, Borik A, Randak T, Grabic R (2018) Development of a robust extraction procedure for the HPLC-ESI-HRPS determination of multi-residual pharmaceuticals in biota samples. Anal Chim Acta 1022:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.011
Holling CS, Bailey JL, Heuvel BV, Kinney CA (2012) Uptake of human pharmaceuticals and personal care products by cabbage from fortified and biosolids-amended soils. J Environ Monit 14(11):3029–3036. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em30456b
Hurtado C, Domínguez C, Pérez-Babace L, Cañameras N, Comas J, Bayon JM (2016) Estimate of uptake and translocation of emerging organic contaminants from irrigation water concentration in lettuce grown under controlled conditions. J Hazard Mater 305:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.11.039
International Organization of Standardization (1995) Soil quality – Determination of total nitrogen – Modified Kjeldahl method (ISO 11261:1995). https://www.iso.org/standard/19239.html. Accessed 10 March 2018
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2002) Aquatic environmental assessment of the top 25 English prescription pharmaceuticals. Water Res 36:5013–5022. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(02)00227-0
Klement A, Kodešová R, Bauerová M, Golovko O, Kočárek M, Fér M, Koba O, Nikodem A, Grabic R (2018) Sorption of citalopram, irbesartan and fexofenadine in soils: estimation of sorption coefficients from soil properties. Chemosphere 195:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.098
Klute M (1996) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Koba O, Golovko O, Kodešová R, Klement A, Grabic R (2016) Transformation of atenolol, metoprolol, and carbamazepine in soils: the identification, quantification, and stability of the transformation products and further implications for the environment. Environ Pollut 218:574–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.041
Koba O, Golovko O, Kodešová R, Fér M, Grabic R (2017) Antibiotics degradation in soil: a case of clindamycin, trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole and their transformation products. Environ Pollut 220:1251–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.007
Kočárek M, Kodešová R, Vondráčková L, Golovko O, Fér M, Klement A, Nikodem A, Jakšík O, Grabic R (2016) Simultaneous sorption of four ionizable pharmaceuticals in different horizons of three soil types. Environ Pollut 218:563–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.039
Kodešová R, Grabic R, Kočárek M, Klement A, Golovko O, Fér M, Nikodem A, Jakšík O (2015) Pharmaceuticals’ sorptions relative to properties of thirteen different soils. Sci Total Environ 511:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.088
Kodešová R, Kočárek M, Klement A, Golovko O, Koba O, Fér M, Nikodem A, Vondráčková L, Jakšík O, Grabic R (2016) An analysis of the dissipation of pharmaceuticals under thirteen different soil conditions. Sci Total Environ 544:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.088
Kumar K, Gupta SC (2016) A framework to predict uptake of trace organic compounds by plants. J Environ Qual 45(2):555–564. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2015.06.0261
Loeppert R, Suarez D (1996) Carbonate and gypsum. Methods soil anal. Part 3—chemical methods. SSSA B, Ser No 5, pp 437–475
Loos R, Locoro G, Comero S, Contini S, Schwesig D, Werres F, Balsaa P, Gans O, Weiss C, Blaha L, Bolchi M, Gawlik BM (2010) Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res 44:4115–4126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.032
Loos R, Carvalho R, António DC, Comero S, Locoro G, Tavazzi S, Paracchini B, Ghiani M, Lettieri T, Blaha L, Jarosova B, Voorspoels S, Servaes K, Haglund P, Fick J, Lindberg RH, Schwesig D, Gawlik BM (2013) EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res 47:6475–6487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.024
Lucida H, Parkin JE, Sunderland VB (2000) Kinetic study of the reaction of sulfamethoxazole and glucose under acidic conditions—I. Effect of pH and temperature. Int J Pharm 202(1–2):47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00413-0
Malchi T, Maor Y, Tadmor G, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2014) Irrigation of root vegetables with treated wastewater: evaluating uptake of pharmaceuticals and the associated human health risks. Environ Sci Technol 48(16):9325–9333. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5017894
Mehlich A (1984) Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: a modification of Mehlich-2 extractant. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628409367568
Montemurro N, Postigo C, Lonigro A, Perez S, Barceló D (2017) Development and validation of an analytical method based on liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry detection for the simultaneous determination of 13 relevant wastewater-derived contaminants in lettuce. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:5375–5387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0363-1
Mordechay EB, Tarchitzky J, Chen Y, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2018) Composted biosolids and treated wastewater as sources of pharmaceuticals and personal care products for plant uptake: a case study with carbamazepine. Environ Pollut 232:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.029
Mullen RA, Wigginton KR, Noe-Hays A, Nace K, Love NG, Bott CB, Aga DS (2017) Optimizing extraction and analysis of pharmaceuticals in human urine, struvite, food crops, soil, and lysimeter water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 9:5952–5962. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay01801k
O'Neil MJ (ed) (2001) The Merck Index—an Encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals, 13th edn. Merck and Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, p 147
Oppel J, Broll G, Loffler D, Meller M, Rombke J, Ternes T (2005) Leaching behaviour of pharmaceuticals in soil-testing-systems: a part of an environmental risk assessment for groundwater protection. Sci Total Environ 328:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.02.004
Paltiel O, Fedorova G, Tadmor G, Kleinstern G, Maor Y, Chefetz B (2016) Human exposure to wastewater-derived pharmaceuticals in fresh produce: a randomized controlled trial focusing on carbamazepine. Environ Sci Technol 50:4476–4482. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b06256
Rhoades JD (1996) Salinity: electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 417–435
Riemenschneider C, Seiwert B, Moeder M, Schwarz D, Reemtsma T (2017) Extensive transformation of the pharmaceutical carbamazepine following uptake into intact tomato plants. Environ Sci Technol 51(11):6100–6109. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b06485
Schaffer M, Licha T (2015) A framework for assessing the retardation of organic molecules in groundwater: implications of the species distribution for the sorption influenced transport. Sci Total Environ 524–525:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.006
Shenker M, Harush D, Ben-Ari J, Chefetz B (2011) Uptake of carbamazepine by cucumber plants—a case study related to irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 82:905–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.052
Skjemstad JO, Baldock JA (2008) Total and organic carbon. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and method of analysis. Taylor and Francis Group, Abingdon, pp 225–237
Thiele-Bruhn S (2003) Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds, in soils—a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:145–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200390023
Verlicchi P, Zambello E (2015) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in untreated and treated sewage sludge: occurrence and environmental risk in the case of application on soil—a critical review. Sci Total Environ 538:750–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.108
Williams M, Martin S, Kookana RS (2015) Sorption and plant uptake of pharmaceuticals from an artificially contaminated soil amended with biochars. Plant Soil 395:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2421-9
Winke M, Clements J, Reich M, Gulyas H, Otterpohl R (2010) Ryegrass uptake of carbamazepine and ibuprofen applied by urine fertilization. Sci Total Environ 408:1902–1908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.01.028
Wu CX, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Czajkowski KP (2010) Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 44:6157–6161. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1011115
Wu X, Conkle JL, Gan J (2012a) Multi-residue determination of pharmaceutical and personal care products in vegetables. J Chromatogr A 1254:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.041
Wu CX, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Sridha BBM (2012b) Transfer of wastewater associated pharmaceuticals and personal care products to crop plants from biosolids treated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.08.007
Wu X, Ernst F, Conkle JL, Gan J (2013) Comparative uptake and translocation of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) by common vegetables. Environ Int 60:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.07.015
Wu X, Dodgen LK, Conkle JL, Gan J (2015) Plant uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products from recycled water and biosolids: a review. Sci Total Environ 536:655–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.129
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Czech Science Foundation project No. 17-08937S, Behavior of pharmaceuticals in soil-water-plant system, and partly also our previous project No. 13-12477S, Transport of pharmaceuticals in soils. Pharmaceutical concentrations were measured using devices financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic, projects CENAKVA (No. CZ.1.05/2.1.00/01.0024), CENAKVA Center Development (No. CZ.1.05/2.1.00/19.0380) and CENAKVA II (No. LO1205 under the NPU I program). The work was also supported by European Regional Development Fund, project Centre for the investigation of synthesis and transformation of nutritional substances in the food chain in interaction with potentially harmful substances of anthropogenic origin: comprehensive assessment of soil contamination risks for the quality of agricultural products (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000845).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental material 1
: additional information (3 figures and 5 tables referred in the manuscript) (PDF 880 kb)
Supplemental material 2
: The results of initial method validation and documentation of QA/QC (PDF 817 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodešová, R., Klement, A., Golovko, O. et al. Root uptake of atenolol, sulfamethoxazole and carbamazepine, and their transformation in three soils and four plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 9876–9891 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04333-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04333-9