Abstract
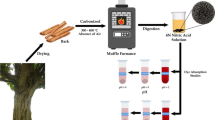
This study addressed the removal performance of RR2 from aqueous solutions in adsorption columns experiments by comparing the potential of activated carbon alone (ACA) and microbially inoculated (MIAC), prepared from barks of a largely available tree in Brazilian Cerrado biome, Hymenaea courbaril L. or “Jatobá,” presenting the kinetics, isotherms, breakthrough curves, and dissolved organic carbon removal. ACA presented strong interaction to RR2 dye, evidenced at the first 20 min when absorbance already attained 66.4%. The removal percentage gradually increased with time and the equilibrium occurred around 91.7% within 120 min. Langmuir model best fitted the isotherm data, indicating a maximum adsorption capacity of 4.068 mg g−1 for the amount of 0.5 g of adsorbent. The Langmuir’s model parameters KL, RL, and R2 corresponded to 0.0234 L mg−1, 0.4159, and 0.9663, respectively, indicating a favorable adsorption process (0 < RL < 1). The experiments in adsorption columns revealed maximum adsorption capacities of 14.38 and 11.43 mg g−1 for MIAC and ACA, respectively, where the microbial activity favorably retarded the adsorption breakpoint in approximately 20 min and enhanced the RR2 consumption in 25.8%. Effectiveness of DOC removal attained above 90% for both ACA and MIAC, reducing the content from 86.1 to 7.84 mg L−1 and 4.82 mg L−1, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Abd ES, Salah H, Nachida KM, Djilali T, Tibor S, Klára H, László N (2016) Using central composite experimental design to optimize the degradation of tylosin from aqueous solution by photo-fenton reaction. Materials 9(6):428–439
Araújo CST, Alves VN, Rezende HC, Almeida ILS, Assunção RMN, Tarley CRT, Segatelli MG, Coelho NMM (2010) Characterization and use of Moringa oleifera seeds as biosorbent for removing metal ions from aqueous effluents. Water Sci Technol 62:2198–2203
Araújo DA, Curbelo FDS, Braga RM, Garnica AIC (2017) Remoção do óleo da água produzida utilizando carvão ativado comercial. Holos 8:12–31
Baghapour MA, Dehghani M (2016) Evaluation of Fenton process in removal of direct red 81. J Health Sci Surveill Syst 4(1):14–21
Bhatnagar A, Minocha AK (2010) Biosorption optimization of nickel removal from water using Punica granatum peel waste. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 76:544–548
Brazil (2005) CONAMA: Brazilian National Counselor of Environment Regulation N° 357. Access in 20 may 2015. Available in: http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=459
Brock TD, Madigan MT (1991) Biology of microorganisms. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Cahan R, Stein M, Anker Y, Langzam Y, Nitzan Y (2013) Innovative utilization of coal bottom ash for bioremediation of toxic organic pollutants. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 85:421–428
Chen KM, Chu HC (2002) Reuse of activated sludge biomass: I. Removal of basic dyes from wastewater by biomass. Process Biochem 37:595–600
Chernicharo CAL (1997) Reatores anaeróbios: princípios do tratamento biológico de águas residuárias. Polytécnica, Belo Horizonte
Conceição V, Freire FB, Carvalho KQ (2013) Treatment of textile effluent containing indigo blue dye by a UASB reactor coupled with pottery clay adsorption. Acta Sci Technol 35(1):53–58
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97(9):1061–1085
Da Silva A, Mariani VC, De Souza AAU, Souza SMAGU (2005) Numerical study of n-pentane separation using adsorption column. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:267–274
Da Silva RTS, Dervanoski A, Haupenthal LD, Souza SMAGU, Souza AAU, Da Luz C (2015) Simulação numérica e ensaios experimentais da remoção de Fe (III) da água para utilização nas indústrias alimentícias. Eng Sanit Ambient 20(4):653–663
Edwards SJ, Kjellerup BV (2013) Applications of biofilms in bioremediation and biotransformation of persistent organic pollutants, pharmaceuticals/personal care products, and heavy metals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9909–9921
Hafshejani MK, Ogugbue CJ, Morad N (2014) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of decolorization and mineralization of triazo dye Direct Blue 71 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3 Biotech 4(6):605–619
Kah M, Sigmund G, Xiao F, Hofmann T (2017) Sorption of ionizable and ionic organic compounds to biochar, activated carbon and other carbonaceous materials. Water Res 124:63–692
Keller JU, Staudt R (2005) Gas adsorption equilibria: experimental methods and adsorptive isotherms. Springer, Boston, MA
Lafrance P, Mazet M, Villessot D (1983) Bacterial growth on granular activated carbon. An examination by scanning electron microscopy. Water Res 17(10):1467–1470
Lee YH, Pavlostathis SG (2004) Decolorization and toxicity of reactive anthraquinone textile dyes under methanogenic conditions. Water Res 38:1838–1852
Ling CP, Ai I, Tan W, Lik L, Lim P (2016) Fixed-bed column study for adsorption of cadmium on oil palm shell-derived activated carbon. J Appl Sci Proc Eng 3(2):60–71
McCabe WL, Smith JC, Harriott P (1993) Unit operations of chemical engineering. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math, USA
Mousavi SA, Khashij M, Shahbazi P (2016) Adsorption isotherm study and factor affected on methylene blue decolorization using activated carbon powder prepared grapevine leaf. J Saf Promot Inj Prev 3(4):249–256
Muthana SM, Ayad FA, Luma MA, Falah HH (2011) Zinc oxide assisted photocatalytic decolorization of reactive red 2 dye. Int J Chem Sci 9(3):969–979
Onat TA, Gümüşdere HT, Güvenç A, Dönmez G, Mehmetoğlu U (2010) Decolorization of textile azo dyes by ultrasonication and microbial removal. Desalination 255:154–158
Pereira L, Pereira R, Pereira MFR, van der Zee FP, Cervantes FJ, Alves MM (2010) Thermal modification of activated carbon surface chemistry improves its capacity as redox mediator for azo dye reduction. J Hazard Mater 183:931–939
Rahmani AR, Zarrabi M, Samarghandi MR, Afkhami A, Ghaffari HR (2010) Degradation of azo dye Reactive Black 5 and acid orange 7 by Fenton-like mechanism. Iran J Chem Eng 7(1):87–94
Reck IM, Paixão RN, Bergamasco R, Vieira MF, Vieira AMS (2018) Removal of tartrazine from aqueous solutions using adsorbents based on activated carbon and Moringa oleifera seeds. J Clean Prod 171:85–97
Salmani LR, Akram G, Saeid A, Maryam D, Nasrin N (2016) Removal of reactive red 141 dye from synthetic wastewater by electrocoagulation process: investigation of operational parameters. Iran J Health Saf Environ 3(1):403–411
Seitenfus N, Ortigara ARC, Bento AP, Scaratti D, Sezerino PH (2007) Biofiltro aerado submerso como alternativa de tratamento do efluente do Núcleo Biotecnológico da Unoesc Campus de Videira. Evidência - Ciência e Biotecnologia 7(1):25–36
Seyyed AM, Parastoo S, Parviz M, Seyyed MDN (2016) Investigation of the efficiency of UV/H2O2 process on the removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solutions. Intl Res J Appl Basic Sci 10(5):456–459
Shakoor S, Nasar A (2016) Removal of methylene blue dye from artificially contaminated water using citrus limetta peel waste as a very low-cost adsorbent. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 66:154–163
Shen J, Huang G, An C, Xin X, Huang C, Rosendahl S (2018) Removal of Tetrabromobisphenol A by adsorption on pinecone-derived activated charcoals: synchrotron FTIR, kinetics and surface functionality analyses. Bioresour Technol 247:812–820
Shimp RJ, Pfaender FK (1982) Effects of surface area and flow rate on marine bacterial growth in activated carbon columns. Appl Environ Microbiol 44(2):471–477
Slejko FL (1985) Adsorption technology. A step-by-step approach to process evaluation and application. Dekker, New York
Smaranda C, Bulgariu D, Gavrilescu M (2009) An investigation of the sorption of acid orange 7 from aqueous solution onto soil. Environ Eng Manag J 8:1391–1402
Sungthong R, Tauler M, Grifoll M, Ortega-Calvo JJ (2017) Mycelium-enhanced bacterial degradation of organic pollutants under bioavailability restrictions. Environ Sci Technol 51:11935–11942
Tuty EA, Yourdan WA, Febrian M (2016) Degradation of reactive red 2 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation processes. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 11(8):5227–5231
Vasques AR (2012) Caracterização de adsorventes obtidos por combustão e pirólise de lodo residual e aplicação no tratamento de efluentes têxteis. Tese de doutorado. Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina. Florianópolis. Access in: 25 may 2015. Available in: https://repositorio.ufsc.br/handle/123456789/100696
Vasques AR, Guelli USSMA, Weissenberg L, Souza AAU, Valle JAB (2011) Adsorção dos corantes RO16, RR2 e RR141 utilizando lodo residual da indústria têxtil. Eng San Ambient 16:245–252
Vieira GEG, Nunes AP, Teixeira LF, Colen AGN (2014) Biomassa: uma visão dos processos de pirólise. Revista Liberato 15:168–177
Viswanathan B, Indra P, Varadarajan TK (2009) Methods of activation and specific application of carbon materials. Chennai: Indian Institute of Technology Madras. Edition: E book, Publisher: NCCR IIT Madras
von Sperling M (2007) Basic principles of wastewater treatment. IWA Publishing, London
Wang L, Huang Z, Zhang M, Chai B (2012) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution on modified ACFs by chemical vapor deposition. Chem Eng J 189:168–174
Yang Y-Y, Li Z-L, Wang G, Zhao X-P, Crowley DE, Zhao Y-H (2012) Computational identification and analysis of the key biosorbent characteristics for the biosorption process of reactive black 5 onto fungal biomass. PLoS One 7(3):1–9
Acknowledgements
The authors thank LDPQ, LAMP, and LMC laboratory staff, from the University of Brasilia, for helping develop this study. Enormous appreciation goes to the editors and reviewers who took the time to review our work and make enriching suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Diane Purchase
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendonça, A.R.V., Zanardi, G.B., Brum, S.S. et al. RR2 dye adsorption to Hymenaea courbaril L. bark activated carbon associated with biofilm. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 28524–28532 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3786-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3786-0