Abstract
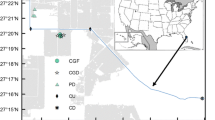
Nutrients in runoff degrade water quality. The development of schemes to mitigate such degradation requires a characterization of the underlying dynamic processes of nutrient loss. The drinking-water source protection area in the Lake Hongfeng watershed of Guiyang City, the capital of Guizhou Province, China, has been delimited for effective conservation. However, no systematic observations have provided data on nutrient losses from these areas that could support optimal management. We selected one typical watershed in the area. Automatic gauges were installed to record the water levels and calculate runoff rates during 2010 and 2011. A total of 1523 runoff samples were collected at an interval of 3 h during a day; total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and chemical oxygen demand (COD) were tested. The results indicated that surface runoff rates were primarily less than 15 L/s but rapidly increased 1–30 times 15 L/s when it rained. TN, TP, and COD concentrations primarily fluctuated between 0.06 and 18.79 mg/L, between 0.01 and 1.57 mg/L, and between 0.01 and 160 mg/L, respectively. TN and COD concentrations in 98.98% and 52.04% of the runoff samples, respectively, exceeded the upper limit required by the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (EQSSW) in China. Conversely, 94.29% of the runoff samples had lower concentrations than the upper limit of TP concentration. Surface runoff has been seriously polluted by nitrogen and organic pollutants. The occurrence frequency of different runoff rates and TP and COD concentrations showed different distributions, but TN concentrations had a normal distribution. There was a significant relationship between runoff rates and TP concentration and TN, TP, or COD loss. TN, TP, and COD loss primarily occurred on vegetable lands, rice fields, and residential sites. Effectively controlling nitrogen fertilizer that is applied on vegetable lands and paddy fields and managing wastewater and solid waste are urgent. The results reported here will also provide references for many other regions facing similar problems.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts EE, Schuman GE, Burwell RE (1978) Seasonal runoff losses of nitrogen and phosphorus from Missouri Valley loess watersheds. J Envir Qual 7:203–208. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1978.00472425000700020010x
Alexander RB, Murdoch PS, Smith RA (1996) Streamflow-induced variations in nitrate flux in tributaries to the Atlantic coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 33:149–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181070
Berry SR (2005) Non-point source pollution with specific reference to the Mkabela catchment. Master thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg
Buda AR, Kleinman PJ, Srinivasan MS, Bryant RB, Feyereisen GW (2009) Effects of hydrology and field management on phosphorus transport in surface runoff. J Environ Qual 38:2273–2284. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2008.0501
Chun JA, Cooke RA, Kang MS, Minha C, Timlin D (2010) Runoff losses of suspended sediment, nitrogen, and phosphorus from a small watershed in Korea. J Environ Qual 39:981–990. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0226
Ferreira CSS, Keizer JJ, Santos LMB, Serpa D, Silva V, Cerqueira M, Ferreira AJD, Abrantes N (2018) Runoff, sediment and nutrient exports from a Mediterranean vineyard under integrated production: an experiment at plot scale. Agric Ecosyst Environ 256:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.01.015
Fu B (2018) Preface for special issue, ecotechnologies for controlling non-point source pollution and protecting aquatic ecosystem (ENPE-2017). Sci Total Environ 618:1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.085
Fujii S, Shivakoti BR, Shichi K, Songprasert P, Ihara H, Moriya M, Kitpati S, Tanaka S (2006) Analysis of parameter variations in L-Q equations for river runoff processes from the viewpoint of spatial and temporal conditions. Wat Sci Technol 53:141–152. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2006.307
Geng RZ, Yin PH, Ma Q (2017) Drinking water source divisions based on identification of critical source areas. Res Environ Sci 30:329–339. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.01.72
Holzmann S, Puhlmann H, Wilpert K (2016) Impact of anthropogenic induced nitrogen input and liming on phosphorus leaching in forest soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 18:17876–17453. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201500552
Jaeheon C (2013) Comparison of surface runoff quality between dry and wet period and characteristics of pollutant runoff in a lake watershed. Int J Environ Sci Dev 4:143–147
Kim JS, Oh SY, Oh KY (2006) Nutrient runoff from a Korean rice paddy watershed during multiple storm events in the growing season. J Hydrol 327:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.062
Li PP, Bian XM, Zhang XG, Tan LJ, Chen X (1995) Production function analysis of national composition of inorganic N, P, K and organic fertilizers for relayed spring corn. J Nanjing Agric Univ 18:19–24
Li HP, Liu XM, Huang WY (2004) The non-point output of different land use types in Zhexi hydraulic region of Taihu Basin. Acta Geograph Sin 59:401–408. https://doi.org/10.11821/xb200403010
Liu MX, Zhou JG, Huang X, Xie KJ, Li J, Lü DQ, Li YY (2017) Analysis of the COD load and impact factor in subtropical watersheds. Res Agric Modern 38:168–175. https://doi.org/10.13872/j.1000-0275.2016.0149
Lu HM, Yin CQ, Wang XH, Zhou Y (2008) Comparison of nitrogen loss via surface runoff from two agricultural catchments in semi-arid China. Environ Sci 29:2690–2695
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (2002a) Analysis methods of water and wastewater. China Environment Science, Beijing
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (2002b) Environmental quality standard for surface water in China. China Environment Science, Beijing
Ministry of Urban and Rural Construction (1993) National standards for municipal wastewater discharge measurement rectangular notch thin-plate weir (CJ/T3008.2-1993)
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR (2001) Soil and water assessment tool users’ manual version 2000. Blackland Research Center, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Temple
Núñez JH, Verbist K, Wallis JR, Schaefer MG, Morales L, Cornelis WM (2011) Regional frequency analysis for mapping drought events in north-central Chile. J Hydrol 405:352–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.035
Randall GW, Iragavarapu TK (1995) Impact of long term tillage systems for continuous corn on nitrate leaching to tile drainage. J Environ Qual 24:360–366. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1995.00472425002400020020x
Sun TW, Chen JJ, Shi ZT, Wang H (2010) Investigation on non-point sources pollution of a typical village and pollution loads of the runoff in Baiyang Lake watershed. J Anhui Agric Sci 38:16991–16993
Surbeck CQ (2005) Dynamics of point and non-point source fecal pollution from an urban watershed in Southern California. 372:2115–2123
Tiemeyer B, Kahle P, Lennartz B (2006) Nutrients losses from artificially drained catchments in north-eastern Germany at different scales. Agric Water Manag 85:47–57
Tomer MD, Meek DW, Jaynes DB, Hatfield JL (2003) Evaluation of nitrate nitrogen fluxes from a tile-drained watershed in central Iowa. J Envir Qual 32:642–653. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.0642
Udawatta RP, Motavalli PP (2006) Nitrogen losses in runoff from three adjacent agricultural watersheds with claypan soils. Agric Ecosyst Environ 117:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2006.03.002
Uusitalo R, Turtola E, Kauppila T, Lilja T (2001) Particulate phosphorus and sediment in surface runoff and drainflow from clayey soils. J Environ Qual 30:589–595. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2001.302589x
Vogel T, Dohnal M, Votrubova J (2011) Modeling heat fluxes in macroporous soil under sparse young forest of temperate humid climate. J Hydrol 402:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.030
Wang KQ, Song ZF, Li TX, Li YJ (2009) The contribution of non-point pollution in the Jianshan River watershed,the first branch of Fuxian Lake. Acta Sci Circumst 29:1321–1328
Wang X, Hao F, Cheng H, Yang S, Zhang X (2011) Estimating non-point source pollutant loads for the large-scale basin of the Yangtze River in China. Environ Earth Sci 63:1079–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0783-0
Wendt RC, Corey RB (1980) Phosphorus variations in surface runoff from agricultural lands as a function of land use. J Environ Qual 9:130–136. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1980.00472425000900010028x
Wesström I, Joel A, Messing I (2014) Controlled drainage and subirrigation—a water management option to reduce non-point source pollution from agricultural land. Agric Ecosyst Environ 198:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.03.017
William EJ, Michael DC (2011) Transport of phosphorus and nitrogen in surface runoff in a corn silage system: paired watershed methodology and calibration period results. Can J Soil Sci 91:479–491. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss09095
Xu CM, Wang ZH, Yin XL, Cai XL (2012) Study on nitrogen leaching in soils of different land utilization type in the Dachong watershed. Guizhou Agr Sci 40:146–150
Yang TQ, Yu YH, Liu HY (2016) Agricultural non-point source pollution in drinking water protection area of Hongfeng Lake, Guiyang. Guizhou Agric Sci 44:161–165
Young RA (1989) AGNPS: a non-point source pollution model for evaluating agricultural watersheds. J Soil Water Conserv 44:168–173
Yu WT, Guan Y, Li JD, Zhang L, Ma Q (2005) Recycling rate of N and P through a feeding-composting cycle and their recoveries in agro-ecosystems. Chin J Appl Ecol 16:1563–1565
Yu D, Sun LN, Yu JF, Wang ZH (2012) Simulation on soil erosion and streamflow in Maotiaohe watershed of Guizhou Province based on SWAT model. Chin Agric Sci Bull 28:256–261
Yuan ZL, Mu ZJ (2010) Research on N and P discharge load of typical agricultural small watershed in TGP reservoir area. Yangtz Riv 41:94–98
Zhang MJ (2012) Main pollutant loads in surface runoff from different lands and their influence factors in Dachong watershed. Master thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang
Zhang WL, Wu SX, Ji HJ, Kolbe H (2004) Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviating strategies. I. Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China in early 21 century. Sci Agric Sin 37:1008–1017
Zhang RB, Yao Q, Yong J, Wang P (2005) A study on law of non point source pollutant loss in a typical small watershed of Taihu Basin—a case study at Meilin watershed in Yixing City of Jiangsu Province. Res Environ Yangtz Bas 14:94–98
Zhang Z, Fukushima T, Onda Y, Gomi T, Fukuyama T, Sidle R, Kosugi K, Matsushige K (2007) Nutrient runoff from forested watersheds in central Japan during typhoon storms: implications for understanding runoff mechanisms during storm events. Hydrol Process 21:1167–1178. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6677
Zhang RY, Wang LY, Chen JA (2014) Physical-chemical characteristics and phosphorus distribution in soils of the Lake Hongfeng watershed in dry seasons. Earth Environ 42:719–725
Zhu ZL (2008) Research on soil nitrogen in China. Acta Pedol Sin 45:778–783
Zhu W, Tan YQ, Wang RC, Feng GY, Chen HM, Liu YF, Li M (2018) The trend of water quality variation and analysis in typical area of Lake Taihu, 2010-2017. J Lake Sci 30:296–305. https://doi.org/10.18307/2018.0202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z.H., Yin, X.L., Wan, L. et al. Dynamics of nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic pollutant losses from a small watershed in the drinking-water source protection area in Guiyang City of Southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 1791–1808 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3721-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3721-4