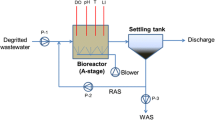
Abstract
Conventional activated sludge (CAS) process is one of the most commonly applied processes for municipal wastewater treatment. However, it requires a high energy input and does not promote energy recovery. Currently, high-rate activated sludge (HRAS) process is gaining importance as a good option to reduce the energy demand of wastewater treatment and to capture organic matter for valorizing through anaerobic digestion (AD). Besides, food waste addition to wastewater can help to increase the organic matter content of wastewater and thus, energy recovery in AD. The objective of this study is to evaluate the applicability of co-treatment of municipal wastewater and food waste in a pilot-scale HRAS system as well as to test the minimal hydraulic retention times (HRTs) such as 60 and 30 min. Food waste addition to the wastewater resulted in a 10% increase in chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration of influent. In the following stages of the study, the pilot-scale system was operated with wastewater solely under the HRTs of 60 and 30 min. With the decrease of HRT, particulate COD removal increased; however, soluble COD removal decreased. The results demonstrated that if the settling process is optimized, more particulate matter can be diverted to sludge stream.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
anaerobic digestion
- AnMBR:
-
anaerobic membrane bioreactor
- BOD:
-
biological oxygen demand
- CAS:
-
conventional activated sludge
- cCOD:
-
colloidal chemical oxygen demand
- COD:
-
chemical oxygen demand
- DO:
-
dissolved oxygen
- F/M:
-
food/microorganisms ratio (kg COD/kg VSS day)
- FOG:
-
fat, oils, and grease
- HRAS:
-
high-rate activated sludge
- HRT:
-
hydraulic retention time
- pCOD:
-
particulate chemical oxygen demand
- PSD:
-
particle size distribution
- RAS:
-
return activated sludge
- SCADA:
-
supervisory control and data acquisition
- sCOD:
-
soluble chemical oxygen demand
- SRT:
-
solids retention time
- SVI:
-
sludge volume index
- TN:
-
total nitrogen
- TP:
-
total phosphorus
- TS:
-
total solids
- TSS:
-
total suspended solids
- VLR:
-
volumetric loading rate (kg COD/m3 day)
- VS:
-
volatile solids
- VSS:
-
volatile suspended solids
- WAS:
-
waste activated sludge
- WWTP:
-
wastewater treatment plant
- ZSV:
-
zone settling velocity
References
Almeida-Naranjo CE, Espinoza-Montero PJ, Muñoz-Rodríguez MI, Villamar-Ayala CA (2017) Hydraulic retention time influence on improving flocculation in the activated sludge processes through polyelectrolytes. Water Air Soil Pollut 228
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Batstone DJ, Hulsen T, Mehta CM, Keller J (2015) Platforms for energy and nutrient recovery from domestic wastewater: a review. Chemosphere 140:2–11
Battistoni P, Fatone F, Passacantando D, Bolzonella D (2007) Application of food waste disposers and alternate cycles process in small-decentralized towns: a case study. Water Res 41:893–903
Bernstad Saraiva A, Davidsson A, Bissmont M (2016) Lifecycle assessment of a system for food waste disposers to tank - a full-scale system evaluation. Waste Manag 54:169–177
Bolzonella D, Pavan P, Battistoni P, Cecchi F (2003) The under sink garbage grinder: a friendly technology for the environment. Environ Technol 24:354–359
de Graaff MS, van den Brand TPH, Roest K, Zandvoort MH, Duin O, van Loosdrecht MCM (2016) Full-scale highly-loaded wastewater treatment processes (A-stage) to increase energy production from wastewater: performance and design guidelines. Environ Eng Sci 33:571–577
Diamantis V, Eftaxias A, Bundervoet B, Verstraete W (2014) Performance of the biosorptive activated sludge (BAS) as pre-treatment to UF for decentralized wastewater reuse. Bioresour Technol 156:314–321
Diggelman C, Ham RK (2003) Household food waste to wastewater or to solid waste? That is the question. Waste Manag Res 21:501–514
Dionisi D, Rasheed AA (2018) Maximisation of the organic load rate and minimisation of oxygen consumption in aerobic biological wastewater treatment processes by manipulation of the hydraulic and solids residence time. J Water Process Eng 22:138–146
Evans TD, Andersson P, Wievegg Å, Carlsson I (2010) Surahammar: a case study of the impacts of installing food waste disposers in 50% of households. Water Environ J 24:309–319
Fang F, Qiao LL, Ni BJ, Cao JS, Yu HQ (2017) Quantitative evaluation on the characteristics of activated sludge granules and flocs using a fuzzy entropy-based approach. Sci Rep 7:42910
Faust L, Temmink H, Zwijnenburg A, Kemperman AJ, Rijnaarts HH (2014) High loaded MBRs for organic matter recovery from sewage: effect of solids retention time on bioflocculation and on the role of extracellular polymers. Water Res 56:258–266
Ge H, Batstone DJ, Mouiche M, Hu S, Keller J (2017) Nutrient removal and energy recovery from high-rate activated sludge processes - impact of sludge age. Bioresour Technol 245:1155–1161
Giokas DL, Daigger GT, Mv S, Kim Y, Paraskevas PA (2003) Comparison and evaluation of empirical zone settling velocity parameters based on sludge volume index using a unified settling characteristics database. Water Res 37:3821–3836
Gude VG (2015) Energy and water autarky of wastewater treatment and power generation systems. Renew Sust Energ Rev 45:52–68
Guven H, Dereli RK, Ozgun H, Ersahin ME, Ozturk I (2019) Towards sustainable and energy efficient municipal wastewater treatment by up-concentration of organics. Prog Energy Combust Sci 70:145–168
Hreiz R, Latifi MA, Roche N (2015) Optimal design and operation of activated sludge processes: state-of-the-art. Chem Eng J 281:900–920
Iacovidou E, Ohandja D-G, Gronow J, Voulvoulis N (2012) The household use of food waste disposal units as a waste management option: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:1485–1508
Jimenez J, Miller M, Bott C, Murthy S, De Clippeleir H, Wett B (2015) High-rate activated sludge system for carbon management--evaluation of crucial process mechanisms and design parameters. Water Res 87:476–482
Kalbar PP, Karmakar S, Asolekar SR (2012) Selection of an appropriate wastewater treatment technology: a scenario-based multiple-attribute decision-making approach. J Environ Manag 113:158–169
Kim M, Chowdhury MM, Nakhla G, Keleman M (2015) Characterization of typical household food wastes from disposers: fractionation of constituents and implications for resource recovery at wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 183:61–69
Kinyua MN, Elliott M, Wett B, Murthy S, Chandran K, Bott CB (2017) The role of extracellular polymeric substances on carbon capture in a high rate activated sludge A-stage system. Chem Eng J 322:428–434
Li Y, Huang Z, Ruan W, Ren H, Zhao M (2015) ANAMMOX performance, granulation, and microbial response under COD disturbance. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:139–148
Li Z, Lu P, Zhang D, Chen G, Zeng S, He Q (2016) Population balance modeling of activated sludge flocculation: investigating the influence of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) content and zeta potential on flocculation dynamics. Sep Purif Technol 162:91–100
Lijo L, Malamis S, Gonzalez-Garcia S, Moreira MT, Fatone F, Katsou E (2017) Decentralised schemes for integrated management of wastewater and domestic organic waste: the case of a small community. J Environ Manag 203:732–740
Ma Y, Yin Y, Liu Y (2017a) New insights into co-digestion of activated sludge and food waste: biogas versus biofertilizer. Bioresour Technol 241:448–453
Ma Y, Yin Y, Liu Y (2017b) A holistic approach for food waste management towards zero-solid disposal and energy/resource recovery. Bioresour Technol 228:56–61
Marashlian N, El-Fadel M (2005) The effect of food waste disposers on municipal waste and wastewater management. Waste Manag Res 23:20–31
Mata-Alvarez J, Dosta J, Romero-Güiza MS, Fonoll X, Peces M, Astals S (2014) A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010 and 2013. Renew Sust Energ Rev 36:412–427
Meerburg FA, Boon N, Van Winckel T, Vercamer JA, Nopens I, Vlaeminck SE (2015) Toward energy-neutral wastewater treatment: a high-rate contact stabilization process to maximally recover sewage organics. Bioresour Technol 179:373–381
Metcalf&Eddy (2014) Wastewater engineering: treatment and resource recovery, 5th edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Miller MW, Elliott M, Jimenez J, Murthy S, Wett B, Bott CB (2015) Adsorption-style high-rate activated sludge for carbon management and diversion. Proc Water Environ Fed 2015:3723–3728
Miller MW, Armond JD, Elliott M, Kinyua M, Kinnear D, Wett B, Murthy S, Bott CB (2016) Settling and dewatering characteristics of an A-stage activated sludge process proceeded by shortcut biological nitrogen removal. Int J Water Wastewater Treat 2:1–8
Monino P, Jimenez E, Barat R, Aguado D, Seco A, Ferrer J (2016) Potential use of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste in anaerobic co-digestion with wastewater in submerged anaerobic membrane technology. Waste Manag 56:158–165
Monino P, Aguado D, Barat R, Jimenez E, Gimenez JB, Seco A, Ferrer J (2017) A new strategy to maximize organic matter valorization in municipalities: combination of urban wastewater with kitchen food waste and its treatment with AnMBR technology. Waste Manag 62:274–289
Muga HE, Mihelcic JR (2008) Sustainability of wastewater treatment technologies. J Environ Manag 88:437–447
Nansubuga I, Banadda N, Ronsse F, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2015) Digestion of high rate activated sludge coupled to biochar formation for soil improvement in the tropics. Water Res 81:216–222
Nieuwenhuis E, Langeveld J, Clemens F (2018) The relationship between fat, oil and grease (FOG) deposits in building drainage systems and FOG disposal patterns. Water Sci Technol 77:2388–2396
Nogaj TM, Randall AA, Jimenez JA, Takacs I, Bott CB, Miller MW, Murthy S, Wett B (2013) Mathematical modeling of carbon removal in the high-rate activated sludge system: model presentation and application, WEFTEC
Orhon D (2015) Evolution of the activated sludge process: the first 50 years. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:608–640
Panepinto D, Fiore S, Zappone M, Genon G, Meucci L (2016) Evaluation of the energy efficiency of a large wastewater treatment plant in Italy. Appl Energy 161:404–411
Sankai T, Ding G, Emori N, Kitamura S, Katada K, Koshio A, Maruyama T, Kudo K, Inamori Y (1997) Treatment of domestic wastewater mixed with crushed garbage and garbage washing water by advanced Gappei-Shori Johkaso. Water Sci Technol 36:175–182
Trzcinski AP, Wang C, Zhang D, Ang WS, Lin LL, Niwa T, Fukuzaki Y, Ng WJ (2017) Performance of A-stage process treating combined municipal-industrial wastewater. Water Sci Technol 75:228–238
von Sperling M (2007) Activated sludge and aerobic biofilm reactors. IWA Publishing, New Delhi
Xu G, Zhou Y, Yang Q, Lee ZM, Gu J, Lay W, Cao Y, Liu Y (2015) The challenges of mainstream deammonification process for municipal used water treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2485–2490
Zhang W, Yang P, Xiao P, Xu S, Liu Y, Liu F, Wang D (2015) Dynamic variation in physicochemical properties of activated sludge floc from different WWTPs and its influence on sludge dewaterability and settleability. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 467:124–134
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Industry and Technology of Turkey, and Istanbul Environment Management Industry and Trade Company (ISTAC) (Project no. 0534.STZ.2013-2), and Istanbul Technical University Scientific Research Projects Office (Project no. 38833).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 470 kb)
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guven, H., Ozgun, H., Ersahin, M.E. et al. High-rate activated sludge processes for municipal wastewater treatment: the effect of food waste addition and hydraulic limits of the system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 1770–1780 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3665-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3665-8