Abstract
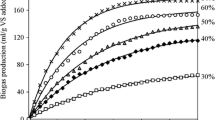
In order to enhance the efficiency and benefits of the sludge anaerobic digestion process, K2FeO4 was added to a sludge anaerobic digestion system, and its effects on the system were comprehensively investigated. Results showed that sludge anaerobic digestion was greatly improved by adding 500 mg/L K2FeO4. Biogas and methane productions were increased by 26.6 and 28.4%, respectively. Sludge reduction, protein removal, and the conversion efficiency of dissolved organics were all improved. The mechanism revealed that the disintegration of sludge flocs, enhancement of protease activity, and decrease of soluble sulfide toxicity on microorganisms contributed to biogas production and sludge reduction. Biogas quality was improved, benefitting from the decreasing H2S content in biogas; as additionally, the cost of biogas desulfuration was reduced. In the biogas slurry treatment, the PO43−-P concentrations were decreased by 39%, which also reduced the cost of the dephosphorization processes at certain extent.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Abbott T, Eskicioglu C (2015) Effects of metal salt addition on odor and process stability during the anaerobic digestion of municipal waste sludge. Waste Manag 46:449–458
Appels L, Baeyens J, Degrève J, Dewil R (2008) Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog Energy Combust Sci 34(6):755–781
Appels L, Degrève J, Van der Bruggen B, Van lmpe J, Dewil R (2010) Influence of low temperature thermal pre-treatment on sludge solubilisation, heavy metal release and anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 101(15):5743–5748
Appels L, Van Assche A, Willems K, Degrève J, Impe J, Dewil R (2011) Peracetic acid oxidation as an alternative pre-treatment for the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 102(5):4124–4130
Appels L, Houtmeyers S, Degrève J, Impe J, Dewil R (2013) Influence of microwave pre-treatment on sludge solubilization and pilot scale semi-continuous anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 128(1):598–603
Carrera-Chapela F, Donoso-Bravo A, Jeison D, Diaz I, Gonzalez J, Ruiz-Filippi G (2016) Development, identification and validation of a mathematical model of anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge focusing on H2S formation and transfer. Biochem Eng J 112:13–19
Carrère H, Dumas C, Battimelli A, Batstone DJ, Delgenès JP, Steyer JP (2010) Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: a review. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):1–15
Cheng X, Chen B, Cui Y, Sun D, Wang X (2015) Iron (III) reduction-induced phosphate precipitation during anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Sep Purif Technol 143:6–11
Chi Y, Li Y, Fei X, Wang S, Yuan H (2011) Enhancement of thermophilic anaerobic digestion of thickened waste activated sludge by combined microwave and alkaline pretreatment. J Environ Sci 23(8):1257–1265
Clesscerl L, Greenberg A, Eaton A (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In: American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC
Devlin DC, Esteves SRR, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ (2011) The effect of acid pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion and dewatering of waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 102(5):4076–4082
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (2002) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Fang W, Zhang P, Zhang G, Jin S, Li D, Zhang M, Xu X (2014) Effect of alkaline addition on aerobic sludge digestion with combined pretreatment of alkaline and high pressure homogenization. Bioresour Technol 168(3):167–172
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Quan X, Chen S (2014) Enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge digestion by the addition of zero valent iron. Water Res 52(4):242–250
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Chen S, Quan X (2015) Enhanced production of methane from waste activated sludge by the combination of high-solid anaerobic digestion and microbial electrolysis cell with iron–graphite electrode. Chem Eng J 259:787–794
Gallipoli A, Gianico A, Gagliano MC, Braguglia CM (2014) Potential of high-frequency ultrasounds to improve sludge anaerobic conversion and surfactants removal at different food/inoculum ratio. Bioresour Technol 159(2):207–214
Gayathri T, Kavitha S, Kumar SA, Kaliappan S, YeoM LT, Banu JR (2015) Effect of citric acid induced deflocculation on the ultrasonic pretreatment efficiency of dairy waste activated sludge. Ultrason Sonochem 22:333–340
He C, Li X, Sharma VK, Li S (2009) Elimination of sludge odor by oxidizing sulfur-containing compounds with ferrate (VI). Environ Sci Technol 43(15):5890–5895
Houtmeyers S, Degrève J, Willems K, Dewil R, Apples L (2014) Comparing the influence of low power ultrasonic and microwave pre-treatments on the solubilisation and semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 171:44–49
Jang JH, Ahn JH (2013) Effect of microwave pretreatment in presence of NaOH on mesophilic anaerobic digestion of thickened waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 131(2):437–442
Jiang JQ (2014) Advances in the development and application of ferrate (VI) for water and wastewater treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89(2):165–177
Jiang JQ, Lloyd B (2002) Progress in the development and use of ferrate (VI) salt as an oxidant and coagulant for water and wastewater treatment. Water Res 36(6):1397–1408
Lee WS, Chua ASM, Yeoh HK, Ngoh GC (2014) A review of the production and applications of waste-derived volatile fatty acids. Chem Eng J 235:83–99
Li Y, Zhang R, Liu X, Chen C, Xiao X, Feng L, He Y, Liu G (2013) Evaluating methane production from anaerobic mono- and co-digestion of kitchen waste, corn stover, and chicken manure. Energy Fuel 27(4):2085–2091
Li X, Dai X, Takahashi J, Li N, Jin J, Dai L, Dong B (2014) New insight into chemical changes of dissolved organic matter during anaerobic digestion of dewatered sewage sludge using EEM-PARAFAC and two-dimensional FTIR correlation spectroscopy. Bioresour Technol 159(6):412–420
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein determination with Folin reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Müller JA (2000) Pretreatment processes for the recycling and reuse of sewage sludge. Water Sci Technol 42(9):167–174
Park CM, Novak JT (2013) The effect of direct addition of iron (III) on anaerobic digestion efficiency and odor causing compounds. Water Sci Technol 68(11):2391–2396
Park B, Ahn JH, Kim J, Hwang S (2004) Use of microwave pretreatment for enhanced anaerobiosis of secondary sludge. Water Sci Technol 50(9):17–23
Ruffino B, Campo G, Genon G, Lorenzi E, Novarino D, Scibilia G, Zanetti M (2014) Improvement of anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge in a wastewater treatment plant by means of mechanical and thermal pre-treatments: performance, energy and economical assessment. Bioresour Technol 175:298–308
Sharma VK, Bloom JT, Joshi VNJ (1998) Oxidation of ammonia by ferrate (VI). J Environ Sci Heal A 33(4):635–650
Stabnikov VP, Tay STL, Tay DK, Ivanov VN (2004) Effect of iron hydroxide on phosphate removal during anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. Appl Biochem Microbiol 40(4):376–380
Su L, Zhao Y (2013) Chemical reduction of odour in fresh sewage sludge in the presence of ferric hydroxide. Environ Technol 34(1–4):165–172
Wang D, Zhao J, Zeng G, Chen Y, Bond PL, Li X (2015) How does poly (hydroxyalkanoate) affect methane production from the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge? Environ Sci Technol 49:12253–12262
Wu C, Jin L, Zhang P, Zhang G (2015) Effects of potassium ferrate oxidation on sludge disintegration, dewaterability and anaerobic biodegradation. Int Biodeteri Biodegr 102:137–142
Yang G, Zhang G, Wang H (2015a) Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Res 78:60–73
Yang G, Zhang P, Zhang G, Wang Y, Yang A (2015b) Degradation properties of protein and carbohydrate during sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 192:126–130
Yang G, Zhang G, Zhuan R, Yang A, Wang Y (2016) Transformations, inhibition, and inhibition control methods of sulfur in sludge anaerobic digestion: a review. Curr Org Chem 20(999):2780–2789
Ye F, Ji H, Ye Y (2012) Effect of potassium ferrate on disintegration of waste activated sludge (WAS). J. Hazard. Mater. s219–220(12):164–168
Yu S, Zhang G, Li J, Zhao Z, Kang X (2013) Effect of endogenous hydrolytic enzymes pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of sludge. Bioresour Technol 146(10):758–761
Yu B, Lou Z, Zhang D, Shan A, Yuan H, Zhu N, Zhang K (2015) Variations of organic matters and microbial community in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge with the addition of ferric salts. Bioresour Technol 179:291–298
Yuan H, Xu C, Zhu N (2014) Disinhibition of the ammonium nitrogen in autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion for sewage sludge by chemical precipitation. Bioresour Technol 169(5):686–691
Zhang S, Zhang P, Zhang G, Fan J, Zhang Y (2012) Enhancement of anaerobic sludge digestion by high-pressure homogenization. Bioresour Technol 118:496–501
Zhang Y, Feng Y, Yu Q, Xu Z, Quan X (2014) Enhanced high-solids anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by the addition of scrap iron. Bioresour Technol 159(5):297–304
Zhang S, Guo H, Du L, Liang J, Lu X, Li N, Zhang K (2015) Influence of NaOH and thermal pretreatment on dewatered activated sludge solubilisation and subsequent anaerobic digestion: focused on high-solid state. Bioresour Technol 185:171–177
Zhao J, Gui L, Wang Q, Liu Y, Wang D, Ni B-J, Li X, Xu R, Zeng G, Yang Q (2017) Aged refuse enhances anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Res 123:724–733
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51708214 and No. 51608117), the High-level Personnel Research Startup Project of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (No. 40550 and No. 40619), and the Treatment Technology Integration and Demonstration for Domestic Sewage of Typical Villages and Towns in Henan Province (No. 161100310700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Yang, G., Fu, J. et al. Synchronously enhancing biogas production, sludge reduction, biogas desulfurization, and digestate treatment in sludge anaerobic digestion by adding K2FeO4. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 35154–35163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3438-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3438-4