Abstract
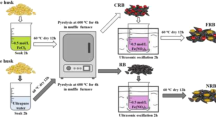
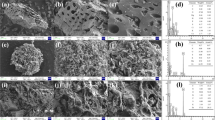
Red mud-modified biochar (RM-BC) has been produced to be utilized as a novel adsorbent to remove As because it can effectively combine the beneficial features of red mud (rich metal oxide composition and porous structure) and biochar (large surface area and porous structure properties). SEM-EDS and XRD analyses demonstrated that red mud had loaded successfully on the surface of biochar. With the increasing of pH in solution, arsenate (As(V)) adsorption on RM-BC decreased while arsenite (As(III)) increased. Arsenate adsorption kinetics process on RM-BC fitted the pseudo-second-order model, while that of As(III) favored the Elovich model. All sorption isotherms produced superior fits with the Langmuir model. RM-BC exhibited improved As removal capabilities, with a maximum adsorption capacity (Qmax) for As(V) of 5923 μg g−1, approximately ten times greater than that of the untreated BC (552.0 μg g−1). Furthermore, it has been indicated that the adsorption of As(V) on RM-BC may be strongly associated with iron oxides (hematite and magnetite) and aluminum oxides (gibbsite) by X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES), which was possibly because of surface complexation and electrostatic interactions. RM-BC may be used as a valuable adsorbent for removing As in the environment due to the waste materials being relatively abundant.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adra A, Morin G, Nguema GO, Brest J (2015) Arsenate and arsenite adsorption onto Al-containing ferrihydrites implications for arsenic immobilization after neutralization of acid mine drainage. Appl Geochem 64:2–9
Altundogan HS, Altundogan S, Tumen F, Bildik M (2000) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on red mud. Waste Manag 20:761–767
Bai YH, Yang TT, Liang JS, Qu JH (2016) The role of biogenic Fe-Mn oxides formed in situ for arsenic oxidation and adsorption in aquatic ecosystems. Water Res 98:119–127
Baig SA, Zhu J, Muhammad N, Sheng T, Xu X (2014) Effect of synthesis methods on magnetic Kans grass biochar for enhanced As(III, V) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Biomass Bioenergy 71:299–310
Castaldi P, Silvetti M, Enzo S, Melis P (2010) Study of sorption processes and FT-IR analysis of arsenate sorbed onto red muds (a bauxite ore processing waste). J Hazard Mater 175:172–178
Chen Z, Wang YP, Jiang XL, Fu D, Xia D, Wang HT, Dong GW, Li QB (2017) Dual roles of AQDS as electron shuttles for microbes and dissolved organic matter involved in arsenic and iron mobilization in the arsenic-rich sediment. Sci Total Environ 574:1684–1694
Cheng Q, Huang Q, Khan S, Liu Y, Liao Z, Li G, Ok YS (2016) Adsorption of cd by peanut husks and peanut husk biochar from aqueous solutions. Ecol Eng 87:240–245
Ding ZC, Fu FL, Cheng ZH, Lu JW, Tang B (2017) Novel mesoporous Fe-Al bimetal oxides for As(III) removal: performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 169:297–307
Feng Y, Xue L, Yang B, Liu Y, Duan J, He S, Yang L (2015) Adsorption of As from aqueous solution by lanthanum oxide-loaded biochar:process and mechanisms. J Agro-Environ Sci 34:2190–2197
Gimenez J, Martinez M, Depabio J, Rovira M, Duro L (2007) Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite, and goethite. J Hazard Mater 141:575–580
Guo H, Guo HM, Yang LJ (2014) Simultaneous removal of fluoride and arsenic from aqueous solution using activated red mud. Sep Sci Technol 49:2412–2425
Hartley W, Riby P, Waterson J (2016) Effects of three different biochars on aggregate stability, organic carbon mobility and micronutrient bioavailability. J Environ Manag 181:770–778
Hua YM, Heal KV, Hanl WF (2017) The use of red mud as an immobiliser for metal/metalloid-contaminated soil: a review. J Hazard Mater 325:17–30
Jadhav SV, Bringas E, Yadav GD, Rathod VK, Ortiz I, Marathe KV (2015) Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: a review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J Environ Manag 162:306–325
Khan S, Cai C, Waqa M, Arp HPH, Zhu YG (2013) Sewage sludge biochar influence upon rice (Oryza sativa L) yield, metal bioaccumulation and greenhouse gas emissions from acidic paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 47:8624–8632
Kim EJ, Yoo J, Baek K (2014) Arsenic speciation and bioaccessibility in arsenic-contaminated soils: sequential extraction and mineralogical investigation. Environ Pollut 186:29–35
Kong XF, Guo Y, Xue SG, Hartley W, Wu C, Ye YZ, Cheng QY (2017a) Natural evolution of alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue. J Clean Prod 143:224–230
Kong XF, Li M, Xue SG, Hartley W, Chen CR, Wu C, Li XF, Li YW (2017b) Acid transformation of bauxite residue: conversion of its alkaline characteristics. J Hazard Mater 324:382–390
Ladeira ACQ, Ciminelli VST, Duarte HA, Alves MCM, Ramos AY (2001) Mechanism of anion retention from EXAFS and density functional calculations: arsenic (V) adsorbed on gibbsite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 8:1211–1217
Li R, Wang JJ, Zhou B, Awasthi MK, Ali A, Zhang Z, Gaston LA, Lahori AH, Mahar A (2016) Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci Total Environ 559:121–129
Liu Y, Naidu R (2014) Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): recovery of metals. Waste Manag 34:2662–2673
Lone AH, Najar GR, Ganie MA, Sofi JA, Ali T (2015) Biochar for sustainable soil health: a review of prospects and concerns. Pedosphere 25:639–653
Lu KP, Yang X, Gielen G, Bolan N, Okd YS, Niazi NK, Xu S, Yuan GD, Chen X, Zhang XK, Liu D, Song ZL, Liu XY, Wang HL (2017) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 186:285–292
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Hurel C, Marmier N, Roméo M (2011) Arsenic (V) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: effects of pH, concentration and reversibility. Desalination 281:93–99
Manju GN, Raji C, Anirudhan TS (1998) Evaluation of coconut husk carbon for the removal of arsenic from water. Water Res 32:3062–3070
Mohan D, Rajput S, Singh VK, Steele PH, Pittman CU (2011) Modeling and evaluation of chromium remediation from water using low cost bio-char, a green adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 188:319–333
Samsuri AW, Sadegh-Zadeh F, Seh-Bardan BJ (2013) Adsorption of As(III) and As(V) by Fe coated biochars and biochars produced from empty fruit bunch and rice husk. J Environ Chem Eng 1:981–988
Sun L, Chen D, Wan S, Yu Z (2015) Performance, kinetics, and equilibrium of methylene blue adsorption on biochar derived from eucalyptus saw dust modified with citric, tartaric, and acetic acids. Bioresour Technol 198:300–308
Tan X, Liu Y, Gu Y, Xu Y, Zeng G, Hu X, Liu S, Wang X, Liu S, Li J (2016) Biochar-based nano-composites for the decontamination of wastewater: a review. Bioresour Technol 212:318–333
Taty-Costodes VC, Fauduet H, Porte C, Delacroix A (2003) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J Hazard Mater 105:121–142
Wang SB, Ang HM, Tadé MO (2008) Novel applications of red mud as coagulant, adsorbent and catalyst for environmentally benign processes. Chemosphere 72:1621–1635
Wang S, Gao B, Zimmerman AR, Li Y, Ma L, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015a) Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour Technol 175:391–395
Wang S, Gao B, Li Y, Mosa A, Zimmerman AR, Mab LQ, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015b) Manganese oxide-modified biochars: preparation, characterization, and sorption of arsenate and lead. Bioresour Technol 181:13–17
Wang T, Zhang LY, Wang HY, Li CF, Yang WC, Chai LY, Meng YD (2015c) Synthesis of core shell magnetic Fe3O4@poly(m-phenylenediamine) particles with high chromium removal performance. Environ Sci Technol 49:5654–5662
Wang N, Xue XM, Juhasz AL, Chang ZZ, Li HB (2017) Biochar increases arsenic release from an anaerobic paddy soil due to enhanced microbial reduction of iron and arsenic. Environ Pollut 220:514–522
Wu C, Zou Q, Xue SG, Pan WS, Yue X, Hartley W, Huang L, Mo JY (2016a) Effect of silicate on arsenic fractionation in soils and its accumulation in rice plants. Chemosphere 165:478–486
Wu C, Zou Q, Xue SG, Pan WS, Huang L, Hartley W, Mo JY, Wong MH (2016b) The effect of silicon on iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation in rice genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL). Environ Pollut 212(5):27–33
Wu C, Huang L, Xue SG, Pan WS, Zou Q, Hartley W, Wong MH (2017) Oxic and anoxic conditions affect arsenic (As) accumulation and arsenite transporter expression in rice. Chemosphere 165:478–486
Xia D, Tan F, Jiang CZ, Chen XZ, Li H, Zheng Y, Li Q, Wang Y (2016) ZnCl2-activated biochar from biogas residue facilitates. Appl Surf Sci 377:361–369
Xue SG, Zhu F, Kong XF, Wu C, Huang L, Huang N, Hartley W (2016a) A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (red mud). Environ Sci Pollut R 23(2):1120–1132
Xue SG, Kong XF, Zhu F, Hartley W, Huang N, Li XF (2016b) Proposal for management and alkalinity transformation of bauxite residue in China. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(11):12822–12834
Xue SG, Shi LZ, Wu C, Wu H, Qin YY, Pan WS, Hartley W, Cui MQ (2017) Cadmium, lead, and arsenic contamination in paddy soils of a mining area and their exposure effects on human HEPG2 and keratinocyte cell-lines. Environ Res 156:23–30
Yan XL, Lin LY, Liao XY, Zhang WB, Wen Y (2013) Arsenic stabilization by zero-valent iron, bauxite residue, and zeolite at a contaminated site planting Panax notoginseng. Chemosphere 93:661–667
Yao Y, Gao B, Fang J, Zhang M, Chen H, Zhou Y, Creamer AE, Sun Y, Yang L (2014) Characterization and environmental applications of clay-biochar composites. Chem Eng J 242:136–143
Yang F, Han T, Jin XZ, Wang HQ, Yang XT, Shen ZK (2015) Effect of thermal activation on mineralogical phases and activity of red mud. Fly Ash comprehensive utilization 2:3–5
Yu ZH, Huang Y, Lian F, Xie L, Liu S, Song Z (2015) Adsorption of arsenic(III) on biochar-manganese oxide composites. J Agro-Environ Sci 1:155–161
Zhang M, Gao B, Varnoosfaderani S, Hebard A, Yao Y, Inyang M (2013) Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic biochar for arsenic removal. Bioresour Technol 130:457–462
Zhu F, Hou JT, Xue SG, Wu C, Wang QL, Hartley W (2017) Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue. Land Degrad Dev. doi:10.1002/ldr.2737
Zhu F, Liao JX, Xue SG, Hartley W, Zou Q, Wu H (2016a) Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography. Sci Total Environ 573:155–163
Zhu F, Xue SG, Hartley W, Huang L, Wu C, Li XF (2016b) Novel predictors of soil genesis following natural weathering processes of bauxite residues. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(3):2856–2863
Zhu F, Zhou JY, Xue SG, Hartley W, Wu C, Guo Y (2016c) Aging of bauxite residue in association of regeneration: a comparison of methods to determine aggregate stability & erosion resistance. Ecol Eng 92:47–54
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Project No.2016M590755) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan, China (Project No. 2015JJ3142) and Teacher’s Research Foundation of Central South University (2015JSJJ7) are gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank beamline BL14W1 (Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility) for providing the beam time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Huang, L., Xue, SG. et al. Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18168–18178 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9466-7