Abstract
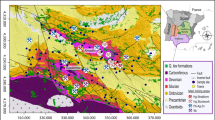
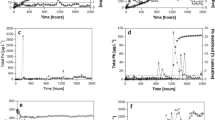
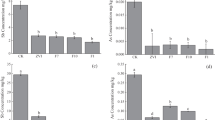
Studies have revealed that the rhizofiltration is a feasible plant-based technology for aquatic metal/metalloid removal. However, the performance of aquatic U retention via rhizofiltration has not been fully revealed yet. In this study, a field investigation was conducted in a Phragmites australis Trin ex Steud. dominated wetland to estimate the efficiency of Fe plaque (IP)-assisted U rhizofiltration, with redox-state gradient (−179 to 220 mV) and low aquatic U level (66.7 to 92.0 μg l−1). The U concentrations were determined in soil, root, and aboveground biomass of P. australis. The IP on root surface was extracted via DCB extraction procedure. The bio-concentration factor (BCF) was applied to evaluate the aquatic U transfer capacity from root to above ground biomass of P. australis. The result suggested that root of P. australis was highly effective for aquatic U uptake via rhizofiltration (BCF 1025 to 1556). It also benefited the real U accumulation in aboveground biomass of P. australis (up to 0.4 mg m−2) and related plant-water-soil U recycling. The IP and associated microbial community in rhizosphere was effective mediator for aquatic U retention on root surface (BCF 1162 to 847). The IP-assisted aquatic U rhizofiltration was significantly promoted in relatively reductive environment. It was benefited by the enhanced root uptake of Fe due to lower oxidizers (e.g., DO and NO3 −) availability. On the other hand, the competitive adsorption effect from co-existing IP-affinitive elements (e.g., As) also possibly impaired the real capacity of IP-assisted aquatic U rhizofiltration via P. australis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson TA, Kruger EL, Coats JR (1993) The potential role of rhizosphere microbial communities in bioremediation of agrochemical wastes. Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc 205:94
Banyai I, Glaser J, Micskei K, Toth I, Zekany L (1995) Kinetic behavior of carbonate ligands with different coordination modes: equilibrium dynamics for uranyl (2+) carbonato complexes in aqueous solution. A 13C and 17O NMR study. Inorg Chem 34:3785–3796
Batty LC, Baker AJM, Wheeler BD, Curtis CD (2000) The effect of pH and plaque on the uptake of Cu and Mn in Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel. Ann Bot-London 86:647–653
Bernhard G, Geipel G, Reich T, Brendler V, Amayri S, Nitsche H (2001) Uranyl (VI) carbonate complex formation: validation of the Ca2UO2(CO3) (3) (aq.) species. Radiochim Acta 89:511–518
Carvalho IG, Cidu R, Fanfani L, Pitsch H, Beaucaire C, Zuddas P (2005) Environmental impact of uranium mining and ore processing in the Lagoa Real District, Bahia, Brazil. Environ Sci Technol 39:8646–8652
Cerne M, Smodis B, Strok M (2011) Uptake of radionuclides by a common reed (Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. Ex Steud.) grown in the vicinity of the former uranium mine at Zirovski vrh. Nucl Eng Des 241:1282–1286
Chang HS, Buettner SW, Seaman JC, Jaffe PR, van Groos PGK, Li D, Peacock AD, Scheckel KG, Kaplan DI (2014) Uranium immobilization in an iron-rich rhizosphere of a native wetland plant from the Savannah river site under reducing conditions. Environ Sci Technol 48:9270–9278
Christensen KK, Sand-Jensen K (1998) Precipitated iron and manganese plaques restrict root uptake of phosphorus in Lobelia dortmanna. Canadian Journal of Botany-Revue Canadienne De Botanique 76:2158–2163
Echevarria G, Sheppard MI, Morel J (2001) Effect of pH on the sorption of uranium in soils. J Environ Radioactiv 53:257–264
Essilfie-Dughan J, Hendry MJ, Warner J, Kotzer T (2013) Arsenic and iron speciation in uranium mine tailings using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl Geochem 28:11–18
Finneran KT, Housewright ME, Lovley DR (2002) Multiple influences of nitrate on uranium solubility during bioremediation of uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. Environ Microbiol 4:510–516
Fritzsche A, Dienemann H, Dudel EG (2006) Arsenic fixation on iron-hydroxide-rich and plant litter-containing sediments in natural environments. Environ Geol 51:133–142
Gilson ER, Huang S, Jaffe PR (2015) Biological reduction of uranium coupled with oxidation of ammonium by Acidimicrobiaceae bacterium A6 under iron reducing conditions. Biodegradation 26:475–482
Hansel CM, Fendorf S, Sutton S, Newville M (2001) Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine-waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ Sci Technol 35:3863–3868
Hauck S, Benz M, Brune A, Schink B (2001) Ferrous iron oxidation by denitrifying bacteria in profundal sediments of a deep lake (Lake Constance). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:127–134
Hinsinger P, Plassard C, Tang CX, Jaillard B (2003) Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant Soil 248:43–59
Hsi CKD, Langmuir D (1985) Adsorption of uranyl onto ferric oxyhydroxides—application of the surface complexation site-binding model. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 49:1931–1941
Jakobsen ST (1994) Aerobic decomposition of organic wastes .1. Stoichiometric calculation of air change. Resour Conserv Recy 12:165–175
Kaplan DI, Kukkadapu R, Seaman JC, Arey BW, Dohnalkova AC, Buettner S, Li D, Varga T, Scheckel KG, Jaffé PR (2016) Iron mineralogy and uranium-binding environment in the rhizosphere of a wetland soil. Sci Total Environ 569-570:53–64
Khani MH, Keshtkar AR, Ghannadi M, Pahlavanzadeh H (2008) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study of the biosorption of uranium onto Cystoseria indica algae. J Hazard Mater 150:612–618
Koster van Groos PG, Kaplan DI, Chang HS, Seaman JC, Li D, Peacock AD, Scheckel KG, Jaffé PR (2016) Uranium fate in wetland mesocosms: effects of plants at two iron loadings with different pH values. Chemosphere 163:116–124
Kropfelova L, Vymazal J, Svehla J, Stichova J (2009) Removal of trace elements in three horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands in the Czech Republic. Environ Pollut 157:1186–1194
Langmuir D (1978) Uranium solution-mineral equilibria at low-temperatures with applications to sedimentary ore-deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 42:547–569
Lapham SC, Millard JB, Samet JM (1989) Health implications of radionuclide levels in cattle raised near U mining and milling facilities in Ambrosia lake, New-Mexico. Health Phys 56:327–340
Li GY, Hu N, Ding DX, Zheng JF, Liu YL, Wang YD, Nie XQ (2011) Screening of plant species for phytoremediation of uranium, thorium, barium, nickel, strontium and lead contaminated soils from a uranium mill tailings repository in south China. B Environ Contam Tox 86:646–652
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Hu Y, Zhao QL (2008) Effects of arsenic from soil and irrigation-water on as accumulation on the root surfaces and in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) Environmental Science 29:862–868
Lu L, Tian S, Zhang M, Zhang J, Yang X, Jiang H (2010) The role of Ca pathway in Cd uptake and translocation by the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 183:22–28
Massey MS, Lezama-Pacheco JS, Jones ME, Ilton ES, Cerrato JM, Bargar JR, Fendorf S (2014) Competing retention pathways of uranium upon reaction with Fe (II). Geochim Cosmochim Ac 142:166–185
Miao Z, Akyol HN, McMillan AL, Brusseau ML (2013) Transport and fate of ammonium and its impact on uranium and other trace elements at a former uranium mill tailing site. Appl Geochem 38:24–32
Nassour M, Weiske A, Schaller J, Brackhage C, Dudel EG (2015) Distribution and relationship of uranium and radium along an Allochthonously dominated wetland gradient. Arch Environ Con Tox 68:317–322
Pentrakova L, Su K, Pentrak M, Stuck JW (2013) A review of microbial redox interactions with structural Fe in clay minerals. Clay Miner 48:543–560
Petrie L, North NN, Dollhopf SL, Balkwill DL, Kostka JE (2003) Enumeration and characterization of iron (III)-reducing microbial communities from acidic subsurface sediments contaminated with uranium (VI). Appl Environ Microb 69:7467–7479
Poorter H, Niklas KJ, Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Poot P, Mommer L (2012) Biomass allocation to leaves, stems and roots: meta-analyses of interspecific variation and environmental control. New Phytol 193:30–50
Ruiz-Rueda O, Hallin S, Baneras L (2009) Structure and function of denitrifying and nitrifying bacterial communities in relation to the plant species in a constructed wetland. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:308–319
Sorrell BK, Mendelssohn IA, McKee KL, Woods RA (2000) Ecophysiology of wetland plant roots: a modelling comparison of aeration in relation to species distribution. Ann Bot-London 86:675–685
Stewart BD, Neiss J, Fendorf S (2007) Quantifying constraints imposed by calcium and iron on bacterial reduction of uranium (VI). J Environ Qual 36:363–372
Stewart BD, Nico PS, Fendorf S (2009) Stability of uranium incorporated into Fe (Hydr) oxides under fluctuating redox conditions. Environ Sci Technol 43:4922–4927
Syu CH, Lee CH, Jiang PY, Chen MK, Lee DY (2014) Comparison of As sequestration in iron plaque and uptake by different genotypes of rice plants grown in As-contaminated paddy soils. Plant Soil 374:411–422
Van Horn JD, Huang H (2006) Uranium (VI) bio-coordination chemistry from biochemical, solution and protein structural data. Coordin Chem Rev 250:765–775
Vymazal J, Svehla J, Kropfelova L, Chrastny V (2007) Trace metals in Phragmites australis and Phalaris arundinacea growing in constructed and natural wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380:154–162
Vymazal J, Brezinova T (2015) Heavy metals in plants in constructed and natural wetlands: concentration, accumulation and seasonality. Water Sci Technol 71:268–276
Weiss JV, Emerson D, Backer SM, Megonigal JP (2003) Enumeration of Fe (II)-oxidizing and Fe (III)-reducing bacteria in the root zone of wetland plants: implications for a rhizosphere iron cycle. Biogeochemistry 64:77–96
White PJ (2001) The pathways of calcium movement to the xylem. J Exp Bot 52:891–899
Wu C, Ye Z, Li H, Wu S, Deng D, Zhu Y, Wong M (2012) Do radial oxygen loss and external aeration affect iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice? J Exp Bot 63:2961–2970
Wu WM, Carley J, Green SJ, Luo J, Kelly SD, Van Nostrand J, Lowe K, Mehlhorn T, Carroll S, Boonchayanant B, Loefller FE, Watson D, Kemner KM, Zhou J, Kitanidis PK, Kostka JE, Jardine PM, Criddle CS (2010) Effects of nitrate on the stability of uranium in a bioreduced region of the subsurface. Environ Sci Technol 44:5104–5111
Xu D, Xu J, He Y, Huang PM (2009) Effect of iron plaque formation on phosphorus accumulation and availability in the rhizosphere of wetland plants. Water Air Soil Poll 200:79–87
Ye ZH, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2001) Copper uptake in Typha latifolia as affected by iron and manganese plaque on the root surface. Canadian Journal of Botany-Revue Canadienne De Botanique 79:314–320
Zimmerman JE, Bui QT, Liu HX, Bonini NM (2000) Molecular genetic analysis of Drosophila eyes absent mutants reveals an eye enhancer element. Genetics 154:237–246
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support provided by the Technical University of Dresden and China Scholarship Council for this study (Grant No. 2011671061). The authors also appreciate the assistance of the colleagues (particularly Dr. Arndt Weiske, Dipl.-Chem. Gisela Ciesielski, Yan Lu, and Carsten Brackhage) in processes of planning, sampling, analysis, and discussion of results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Gert Dudel, E. Fe plaque-related aquatic uranium retention via rhizofiltration along a redox-state gradient in a natural Phragmites australis Trin ex Steud. wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 12185–12194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8889-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8889-5