Abstract
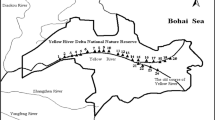
Human activity in estuarine areas has resulted in pollution of the aquatic environment, but little is known about the levels of synthetic musks (SMs) in river water and sediments in estuarine areas. This study investigated the concentrations and distribution of SMs in the Jiaozhou Bay wetland, including celestolide, phantolide, traseolide, galaxolide (HHCB), tonalide (AHTN), musk xylene and musk ketone (MK). The SMs HHCB, AHTN and MK were detected at concentrations of 10.7–208, not detected (ND)–59.2 and ND–13.6 ng/L, respectively, in surface water samples and 13.1–27.3, 3.06–14.5 and 1.33–18.8 ng/g (dry weight; dw), respectively, in sediment samples. Based on the calculated total organic carbon (TOC) concentrations, there was no significant correlation between SMs and TOC in sediment samples (p > 0.05). The hazard quotients were 0.204, 0.386 and 0.059 for AHTN, HHCB and MK, respectively, which indicated no serious environmental impact, because these values are all less than 1. The concentrations of SMs decreased as the distance to the Xiaojianxi refuse landfill increased in both surface water and sediments. Compared with previous studies, the concentration of SMs in the Jiaozhou Bay wetland was relatively high. Therefore, more attention should be paid to SMs because of their persistent impact on human health and the environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao SD (1999) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press (Bei Jing)
Bester K (2005) Polycyclic musks in the Ruhr catchment area-transport, discharges of waste water, and transformations of HHCB, AHTN and HHCB-lactone. J Environ Monit 7(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1039/B409213A
Buerge IJ, Buser HR, Mueller MD, Poiger T (2003) Behavior of the polycyclic musks HHCB and AHTN in lakes, two potential anthropogenic markers for domestic wastewater in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5636–5644. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0300721
Butte W, Schmidt S, Schmidt A (1999) Photochemical degradation of nitrated musk compounds. Chemosphere 38(6):1287–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00529-3
Che JS, Yu RP, Wang LP, Ran GX, Song QJ (2010) Investigation on content distribution of synthetic musks in Taihu Lake. Flavour Fragrance Cosmetics 6:12–16
Clara M, Gans O, Windhofer G, Krenn U, Hartl W, Braun K, Scharf S, Scheffknecht C (2010) Occurrence of polycyclic musks in wastewater and receiving water bodies and fate during wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 82(8):1116–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.041
European Commission (EC) (2003) Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) N.1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances, Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of theCouncil Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market. Part II: Environmental Risk Assessment. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Guo R, Lee IS, Kim UJ, Oh JE (2010) Occurrence of synthetic musks in Korean sewage sludges. Sci Total Environ 408(7):1634–1639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.009
HERA (Human and Environmental Risk Assessment on ingredients of household cleaning products) (2004) Polycyclic musks AHTN (CAS 1506-02-1) and HHCB (CAS 1222-05-05). Available at http://www.Heraproject.com/RiskAssessment.cfm (accessed November 10, 2014)
Heberer T (2003) Occurrence, fate, and assessment of polycyclic musk residues in the aquatic environment of urban areas-a review. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 30(5–6):227–243
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fern’andez-Alba AR, Barcel’o D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69(2006):334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Hijosa-Valsero M, Matamoros V, Pedescoll A, Martin-Villacorta J, Becares E, Garcia J, Bayona JM (2011) Evaluation of primary treatment and loading regimes in the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from urban wastewaters by subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Int J Environ Anal Chem 91(7–8):632–653. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2010.526208
Hu ZJ, Shi YL, Cai YQ (2011) Concentrations, distribution, and bioaccumulation of synthetic musks in the Haihe River of China. Chemosphere 84(11):1630–1635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.013
Hu ZJ, Shi YL, Niu HY, Cai YQ (2012) Synthetic musk fragrances and heavy metals in snow samples of Beijing urban area, China. Atmos Res 104:302–305
Kannan K, Reiner JL, Yun SH, Perrotta EE, Tao L, Johnson-Restrepo B, Rodan BD (2005) Polycyclic musk compounds in higher trophic level aquatic organisms and humans from the United States. Chemosphere 61(5):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.041
Kronimus A, Schwarzbauer J, Dsikowitzky L, Heim S, Littke R (2004) Anthropogenic organic contaminants in sediments of the Lippe river, Germany. Water Res 38(16):3473–3484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.054
Lee IS, Lee SH, Oh JE (2010) Occurrence and fate of synthetic musk compounds in water environment. Water Res 44(1):214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.049
Liu NN, Shi YL, Li WH, Xu L, Cai YQ (2014) Concentrations and distribution of synthetic musks and siloxanes in sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci Total Environ 476:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.124
Lou YH, Wang J, Wang L, Shi L, Yu Y, Zhang MY (2016) Determination of synthetic musks in sediments of Yellow River Delta wetland. China Bull Environ Contam Toxicol DOI 97(1):78–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1814-7
Luo Y, Guo W, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD, Hai FI, Zhang J, Liang S, Wang XC (2014) A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 473:619–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065
Ma L, Jing Y, Zhou J, Zeng XY, Zhang XL, Yu YX (2014) Distribution of synthetic musk in surface water and sediments from Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake. Environ Chem 33(4):630–635
Moldovan Z (2006) Occurrences of pharmaceutical and personal care products as micropollutants in rivers from Romania. Chemosphere 64(11):1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.003
Moon HB, An YR, Park KJ, Choi SG, Moon DY, Choi M, Choi HG (2011) Occurrence and accumulation features of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and synthetic musk compounds in finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides) from Korean coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 62(9):1963–1968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.031
Moon HB, Lee DH, Lee YS, Choi SG, Moon DY, Choi M, Choi HG (2012) Occurrence and accumulation patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and synthetic musk compounds in adipose tissues of Korean females. Chemosphere 86(5):485–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.10.008
Nakata H, Sasaki H, Takemura A, Yoshioka M, Tanabe S, Kannan K (2007) Bioaccumulation, temporal trend, and geographical distribution of synthetic musks in the marine environment. Environ Sci Technol 41(7):2216–2222. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0623818
Peck AM, Hornbuckle KC (2004) Synthetic musk fragrances in Lake Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 38(2):367–372. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034769y
Peck AM, Linebaugh EK, Hornbuckle KC (2006) Synthetic musk fragrances in Lake Erie and Lake Ontario sediment cores. Environ Sci Technol 40(18):5629–5635. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060134y
Quednow K, Puettmann W (2008) Organophosphates and synthetic musk fragrances in freshwater streams in Hessen/Germany. Clean-soil Air Water 36(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200700023
Reiner JL, Kannan K (2011) Polycyclic musks in water, sediment, and fishes from the upper Hudson River, New York, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut 214(1–4):335–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0427-8
Reyes-Contreras C, Hijosa-Valsero M, Sidrach-Cardona R, Bayona JM, Becares E (2012) Temporal evolution in PPCP removal from urban wastewater by constructed wetlands of different configuration: a medium-term study. Chemosphere 88(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.064
Sang WJ, Zhang YL, Zhou XF, Ma LM, Sun XJ (2012) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks in surface sediments of Liangtan River, West China. Environ Eng Sci 29(1):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2010.0241
Vera H, Ines M, Arminda A (2017) Assessing seasonal variation of synthetic musks in beach sands from Oporto coastal area: a case study. Environ Pollut 226(2017):190–197
Villa S, Assi L, Ippolito A, Bonfanti P, Finizio A (2012) First evidences of the occurrence of polycyclic synthetic musk fragrances in surface water systems in Italy: spatial and temporal trends in the Molgora River (Lombardia Region, Northern Italy). Sci Total Environ 416:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.11.027
Wang F, Zhou Y, Guo Y, Zou L, Zhang X, Zeng X (2010) Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of synthetic musk in Suzhou Creek. J. Shanghai Univ (English Edition) 14(4):306–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-010-0649-3
Wang J, Lou YH, Wang L, Zhao YY, Shi L, Zheng MG (2015) Research about the synthetic musks in intertidal sediments in the north of Jiaozhou Bay. Environ Chem 34(2):384–385
Yamauchi R, Ishibashi H, Hirano M, Mori T, Kim JW, Arizono K (2008) Effects of synthetic polycyclic musks on estrogen receptor, vitellogenin, pregnane X receptor, and cytochrome P4503A gene expression in the livers of male medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 90(4):261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.09.007
Zhang DQ, Gersberg RM, Ng WJ, Tan SK (2014) Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic plant-based systems: a review. Environ Pollut 184:620–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.009
Zhang XY, Yao Y, Zeng XY, Qian GR, Guo YW, Wu MH, Sheng GY, Fu JM (2008) Synthetic musks in the aquatic environment and personal care products in Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 72(10):1553–1558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.039
Zhou J (2016) Synthetic musk in daily chemicals. China Surfactant Detergent&Cosmetics Vol. 46 No.9 Sept.2016
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Scientific Fund for National Public Research Institutes of China (No. 2016Q07), National Key R&D Program of China (Grant 20177YFC1404504), the Open Fund of Laboratory for Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao, China (No.OF2015NO14) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21307063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Wang, L., Zheng, M. et al. Determination and environmental risk assessment of synthetic musks in the water and sediments of the Jiaozhou Bay wetland, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 4915–4923 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0811-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0811-7