Abstract
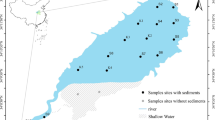
The concentrations, spatial distribution, fractionation characteristics, and potential ecological risks of trace elements (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, and Co) in the surface sediment samples collected from 32 sites in Chaohu Lake were investigated. The improved BCR sequential extraction procedure was applied to analyze the chemical forms of trace elements in sediments. The enrichment factor (EF), sediment quality guidelines (SQGs), potential ecological risk index (PERI), and risk assessment code (RAC) were employed to evaluate the pollution levels and the potential ecological risks. The results found that the concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, and Co in the surface sediments were 78.59, 36.91, 161.84, 98.87, 38.92, and 10.09 mg kg−1, respectively. The lower concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, and Ni were almost found in the middle part of the lake, while Co increased from the western toward the eastern parts of the lake. Cr, Ni, Co, and Zn predominantly existed in the residual fractions, with the average values of 76.35, 59.22, 45.60, and 44.30%, respectively. Cu and Pb were mainly combined with Fe/Mn oxides in reducible fraction, with the average values of 66.4 and 69.1%, respectively. The pollution levels were different among the selected elements. Cu had the highest potential ecological risk, while Cr had the lowest potential ecological risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci G, Guvenb DE, Ugurluc SK (2013) Assessing pollution in Izmir Bay from rivers in western Turkey: heavy metals. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 15:2252–2262
Anhui environmental state bulletin (the year of 2014 and 2015). http://www.aepb.gov.cn/pages/Aepb15_XXGKNewsList.aspx?MenuID=300304
Cao DJ, Yue YD, Huang XM, Wei M (2004) Environmental quality assessment of Pb, Cu, Fe pollution in ChaoHu Lake waters. China Environ Sci 24:509–512 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Cao XZ, Shao Y, Deng WJ, Wang H, Wang SL (2014) Spatial distribution and potential ecologic risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of the Nansi Lake in China. Environ Monit Assess 186:8845–8856
Chen SY, Lin JG (2001) Bioleaching of heavy metals from sediment: significance of pH. Chemosphere 44:1093–1102
Chen YY, Liu QQ (2015) Numerical study of hydrodynamic process in Chaohu Lake. J Hydrodyn 27:720–729
Chowdhury S, Mazumder MAJ, Al-Attas O, Husain T (2016) Heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 569-570:476–488
Díaz-de Alba M, Galindo-Riaño MD, Casanueva-Marenco MJ, García-Vargas M, Kosore CM (2011) Assessment of the metal pollution, potential toxicity and speciation of sediment from Algeciras Bay (south of Spain) using chemometric tools. J Hazard Mater 190:177–187
Fang KY (1999) Chaohu Lake. Anhui Sci Technol Publishing House, Hefei 6
Grant A, Middleton R (1990) An assessment of metal contamination of sediments in the Humber estuary, UK. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 31:71–85
Guo W, Huo SL, Xi BD, Zhang JT, Wu FC (2015) Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: distribution, bioavailability, and risk. Ecol Eng 81:243–255
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
He W, Bai ZL, Liu WX, Kong XZ, Yang B, Yang C, Jorgensen SE, Xu FL (2016) Occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in surface sediments from a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10335–10348
Ianni C, Magi E, Soggia F, Rivaro P, Frache R (2010) Trace metal speciation in coastal and off-shore sediments from Ross Sea (Antarctica). Microchem J 96:203–212
Karageorgis A, Sioulas A, Anagnostou C (2002) Use of surface sediments in Pagassitikos gulf, Greece, to detect anthropogenic influence. Geo-Marine Lett 21:200–211
Kong M, Dong ZL, Chao JY, Zhang YM, Yin HB (2015) Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu. China Environ Sci 2015:1223–1229 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Li GL, Liu GJ, Zhou CC, Kang Y, Yuan WQ, Xie FZ (2013) Mobility, binding behavior and potential risks of trace metals in the sediments of the fifth largest freshwater lake, China. Water Sci Technol 67:2503–2510
Lin Q, Liu EF, Zhang EL, Li K, Shen J (2016) Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena 145:193–203
Liu EF, Shen J (2014) A comparative study of metal pollution and potential eco-risk in the sediment of Chaohu Lake (China) based on total concentration and chemical speciation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7285–7295
Liu EF, Shen J, Yang XD, Zhang EL (2012) Spatial distribution and human contamination quantification of trace metals and phosphorus in the sediments of Chaohu Lake, a eutrophic shallow lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:2105–2118
Liu X, Jiang Y, Gao JF, Yin HB, Cai YJ (2016) Pollution characteristics of heavy metals and the risk assessment for the surface sediments from Lake Chaohu and its main tributary rivers. J Lake Sci 28:502–512 (In Chinese with English abstract)
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Malferrari D, Brigatti MF, Laurora A, Pini S (2009) Heavy metals in sediments from canals for water supplying and drainage: mobilization and control strategies. J Hazard Mater 161:723–729
Markert B, Pedrozo F, Geller W, Friese K, Korhammer S, Baffico G, Diaz M, Wolfl S (1997) A contribution to the study of the heavy-metal and nutritional element status of some lakes in the southern Andes of Patagonia (Argentina). Sci Total Environ 206:l–15
Martin CW (2000) Heavy metal trends in floodplain sediments and valley fill, river Lahn, Germany. Catena 39:53–68
Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2007) Determination of pH in soil (NY/T 1377–207). (In Chinese)
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (2016) Soil quality—determination of conductivity—electrode method (HJ 802-2016). (In Chinese)
Mucha AP, Vasconcelos MTSD, Bordalo AA (2003) Macrobenthic community in the Douro estuary: relations with trace metals and natural sediment characteristics. Environ Pollut 121:169–180
Nazeer S, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN (2014) Heavy metals distribution, risk assessment and water quality characterization by water quality index of the river Soan, Pakistan. Ecol Indic 43:262–270
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Pertsemli E, Voutsa D (2007) Distribution of heavy metals in lakes Doirani and Kerkini, northern Greece. J Hazard Mater 148:529–537
Sadiq R, Rodriguez MJ, Imran SA, Najjaran H (2007) Communicating human health risks associated with disinfection by-products in drinking water supplies: a fuzzy-based approach. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 21:341–353
Sakan SM, Dordević DS, Manojlović DD, Predrag PS (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J Environ Manag 90:3382–3390
Santos Bermejo JC, Beltrán R, Gömez Ariza JL (2003) Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel river (Southwest Spain). Environ Int 29:69–77
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Wang HK, Tang HB (2010) Study of the effect of ecological diversions for Chao Lake to improve the rivers and lakes’ exchange relations. China Water Resour 23:27–29 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang SM, Dou HS, Chen KZ, Wang XC, Jiang JH (1998) Biography of lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 230–235 (in Chinese)
Wang JQ, Sun YM, Qian JZ, Wu JG, Pan TS (2002) Simulated study on phosphorus release of Chao Lake sediment. Acta Sci Circumst 22:738–742 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YQ, Yang LY, Kong LH, Liu EF, Wang LF, Zhu JR (2015) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 125:200–205
Wang JZ, Peng SC, Chen TH, Zhang L (2016) Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:307–314
Wei CL, Bao SM, Zhu XY, Huang XM (2008) Spatio-temporal variations of the bacterioplankton community composition in Chaohu Lake, China. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 18:1115–1122
Wen SF, Shan BQ, Zhang H (2012) Metals in sediment/pore water in Chaohu Lake: distribution, trends and flux. J Environ Sci 24:2041–2050
Yang LB, Lei K, Meng W, Fu G, Yan WJ (2013) Temporal and spatial changes in nutrients and chlorophyll-a in a shallow lake, Lake Chaohu, China: an 11-year investigation. J Environ Sci 25:1117–1123
Yin HB, Deng JC, Shao SG, Gao F, Gao JF, Fan CX (2011) Distribution characteristics and toxicity assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Chaohu, China. Environ Monit Assess 179:431–442
Yu XJ, Huo SL, Zan FY, Zhao GC, Xi BD, Su J (2013) Distribution characteristics and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake, China. Chin J Environ Eng 7:430–450 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zan FY, Huo SL, Xi BD, Su J, Li X, Zhang JT, Yeager KM (2011) A 100 year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. J Environ Monit 13:2788–2797
Zhang ZY, Wang PH, Zhang CD (1999) Study on the eutrophication in Chaohu Lake and its remediation. Res Environ Sci 12:45–48 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang M, Xu J, Xie P (2007) Metals in surface sediments of large shallow eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:242–245
Zhang YN, Zhao WJ, Guo L, Ni N, Li Y (2010) Impacts of mixed bacteria on the fraction of heavy metals and their bioavailability in the surface sediment. Environ Prot Sci 36:53–57 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J, Deng HG, Wang DQ, Chen ZL, SY X (2013) Toxic heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of street dust in small towns of shanghai suburban area, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:323–332
Zhang L, Liao QJH, Shao SG, Zhang N, Shen QS, Liu C (2015) Heavy metal pollution, fractionation, and potential ecological risks in sediments from Lake Chaohu (eastern China) and the surrounding rivers. Int J Env Res Public Health 12:14115–14131
Zhu XR, Yan WX, He FZ, Liu XF, Wang DL, Wang W (1993) Water pollution and eutrophication of the northwest part of the Chaohu Lake. Oceanologia Limnologia Sinica 24:191–196 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Research Program for Environmental Protection of Anhui Province (2015-11), Key Projects of Natural Science Research of Universities in Anhui Province (KJ2015A201), and Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (grant no. KJ2013ZD07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Liu, G., Zhou, C. et al. Spatial distributions, fractionation characteristics, and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in sediments of Chaohu Lake, a large eutrophic freshwater lake in eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 588–600 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0462-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0462-8