Abstract
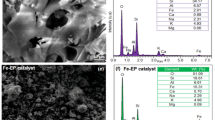
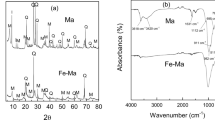
This work deals with the degradation of the azo-dye Orange II (OII) by a heterogeneous process with dark Fenton. Natural and purified ilmenites from Colombian soil were used as catalysts. The catalysts have different physicochemical properties and are basically composed of TiO2 and Fe2O3. Ilmenites (FeTiO3), raw materials highly available at low cost, were studied by means of conventional metallography (polished grain mounts), as well as BET, XRD, and XRF in order to determine their possible source area and the factors that influence their use as a catalyst for OII degradation. The pH, the ilmenite amount, the initial CH2O2, and the temperature of the reaction system were studied. Complete degradation of dye was observed within 7 h, while 90 % of OII was removed in 7 h using Cumaribo Ilmenite.

ᅟ









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfattah, N. A. (2014). Preparation of titanium dioxide anatase pigment from Rosetta ilmenite concentrate via the sulfate route. 4th International Conference on Radiation Sciences and Applications,13–17/10, Taba, Egypt
Andreozzi R, Canterino M, Caprio V, Di Sornma A, Marotta R (2008) Use of an amorphous iron oxide hydrated as catalyst for hydrogen peroxide oxidation of ferulic acid in water. J Hazard Mater 152:870–875
Bae S, Kim D, Lee W (2013) Degradation of diclofenac by pyrite catalyzed Fenton oxidation. Appl Catal B Environ 134:93–102
Bafghi MS, Zakeri A, Ghasemi Z, Adeli M (2008) Reductive dissolution of manganese ore in sulfuric acid in the presence of iron metal. Hydrometallurgy 90(2):207–212
Basińska A, Jóźwiak WK, Góralski J, Domka F (2000) The behaviour of Ru/Fe2O3 catalysts and Fe2O3 supports in the TPR and TPO conditions. Appl Catal A Gen 190(1):107–115
Cai C, Zhang Z, Liu J, Shan N, Zhang H, Dionysiou DD (2016) Visible light-assisted heterogeneous Fenton with ZnFe2O4 for the degradation of Orange II in water. Appl Catal B Environ 182:456–468
Chen Y, Lu A, Li Y, Yip HY, An T, Li G, Wong PK (2011) Photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli by natural sphalerite suspension: effect of spectrum, wavelength and intensity of visible light. Chemosphere 84:1276–1281
Costa RCC, Lelis MFF, Oliveira LCA, Fabris JD, Ardisson JD, Rios RRVA, Silva CN, Lago RM (2006) Novel active heterogeneous Fenton system based on Fe3−xMxO4 (Fe, Co, Mn, Ni): the role of M2+ species on the reactivity towards H2O2 reactions. J Hazard Mater 129:171–178
de Urzedo AP, Nascentes CC, Augusti R (2009) Degradation of the insecticides thiamethoxam and imidacloprid in aqueous solution as promoted by an innovative Fe°/Fe3O4 composite. J Braz Chem Soc 20:51–56
Garrido-Ramírez EG, Theng BKG, Mora ML (2010) Clays and oxide minerals as catalysts and nanocatalysts in Fenton-like reactions—a review. Appl Clay Sci 47:182–192
Giraldi TR, Arruda CC, Da Costa GM, Longo E, Ribeiro C (2009) Heterogeneous Fenton reactants: a study of the behavior of iron oxide nanoparticles obtained by the polymeric precursor method. Journal of Sol–Gel Science Technology 52:299–303
Hanaor DA, Sorrell CC (2011) Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J Mater Sci 46(4):855–874
Instituto Colombiano de Geología y Minería (INGEOMINAS). Bogotá D.C. Colombia.
Jeong MH, Lee DH, Bae JW (2015) Reduction and oxidation kinetics of different phases of iron oxides. Int J Hydrog Energy 40(6):2613–2620
Karunakaran C, Senthilvelan S (2006) Fe2O3-photocatalysis with sunlight and UV light: oxidation of aniline. Electrochem Commun 8:95–101
Kousha M, Daneshvar E, Sohrabi MS, Jokar M, Bhatnagar A (2012) Adsorption of acid orange II dye by raw and chemically modified brown macroalga Stoechospermum marginatum. Chem Eng J 192:67–76
Kwan WP, Voelker BM (2003) Rates of hydroxyl radical generation and organic compound oxidation in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like systems. Environ Sci Technol 37:1150–1158
Li Y, Lu A, Jin S, Wang C (2009) Photo-reductive decolorization of an azo dye by natural sphalerite: case study of a new type of visible light-sensitized photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 170:479–486
Liang X, Zhong Y, Zhu S, Zhu J, Yuan P, He H, Zhang J (2010) The decolorization of acid Orange II in non-homogeneous Fenton reaction catalyzed by natural vanadium–titanium magnetite. J Hazard Mater 181:112–120
Luo F, Yang D, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2016) One-step green synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Pd nanoparticles used to degrade Orange II. J Hazard Mater 303:145–153
Moctezuma E, Zermeño B, Zarazua E, Torres-Martínez LM, García R (2011) Photocatalytic degradation of phenol with Fe-titania catalysts. Top Catal 54:496–503
Nam S, Tratnyek PG (2000) Reduction of azo dyes with zero-valent iron. Water Res 34:1837–1845
Oliveira LCA, Gonçalves M, Guerreiro MC, Ramalho TC, Fabris JD, Pereira MC, Sapag K (2007) A new catalyst material based on niobia/iron oxide composite on the oxidation of organic contaminants in water via heterogeneous Fenton mechanisms. Appl Catal A Gen 316:117–124
Rajabi HR, Khani O, Shamsipur M, Vatanpour V (2013) High-performance pure and Fe3+−ion doped ZnS quantum dots as green nanophotocatalysts for the removal of malachite green under UV-light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 250:370–378
Rache ML, García AR, Zea HR, Silva AM, Madeira LM, Ramírez JH (2014) Azo-dye orange II degradation by the heterogeneous Fenton-like process using a zeolite Y-Fe catalyst—kinetics with a model based on the Fermi's equation. Appl Catal B Environ 146:192–200
Ramirez JH, Costa CA, Madeira LM, Mata G, Vicente MA, Rojas-Cervantes ML, Martín-Aranda RM (2007a) Fenton-like oxidation of Orange II solutions using heterogeneous catalysts based on saponite clay. Appl Catal B Environ 71(1):44–56
Ramirez JH, Maldonado-Hodar FJ, Perez-Cadenas AF, Moreno-Castilla C, Costa CA, Madeira LM (2007b) Azo-dye Orange II degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction using carbon–Fe catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 75:312–323
Ramirez JH, Zea HR, Cramer T (2014) Degradation of Chrysoidin dye by Fenton and photo-Fenton reaction using natural marmatite as catalyst. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technology 17:389–396
Schoonen MA, Xu Y, Strongin DR (1998) An introduction to geocatalysis. J Geochem Explor 62:201–215
Silva LFO, Querol X, Da Boit KM, de Vallejuelo SFO, Madariaga JM (2011) Brazilian coal mining residues and sulphide oxidation by Fenton’s reaction: an accelerated weathering procedure to evaluate possible environmental impact. J Hazard Mater 186:516–525
Tao T, Chen Y, Zhou D, Zhang H, Liu S, Amal R, Sharma N, Glushenkov AM (2013) Expanding the applications of the ilmenite mineral to the preparation of nanostructures: TiO2 nanorods and their photocatalytic properties in the degradation of oxalic acid. Chemistry–A European Journal 19:1091–1096
Tryba B, Piszcz M, Grzmil B, Pattek-Janczyk A, Morawski AW (2009) Photodecomposition of dyes on Fe-C-TiO2 photocatalysts under UV radiation supported by photo-Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 162:111–119
Xue X, Hanna K, Despas C, Wu F, Deng N (2009) Effect of chelating agent on the oxidation rate of PCP in the magnetite/H2O2 system at neutral pH. J Mol Catal A Chem 311:29–35
Yang X, Li Y, Lu A, Yan Y, Wang C, Wong PK (2011) Photocatalytic reduction of carbon tetrachloride by natural sphalerite under visible light irradiation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 95:1915–1921
Zhang L, Li P, Gong Z, Oni A (2006) Photochemical behavior of benzo[a]pyrene on soil surfaces under UV light irradiation. J Environ Sci 18:1226–1232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editro: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pataquiva-Mateus, A.Y., Zea, H.R. & Ramirez, J.H. Degradation of Orange II by Fenton reaction using ilmenite as catalyst. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 6187–6194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7263-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7263-3