Abstract
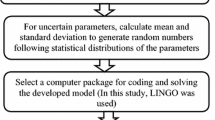
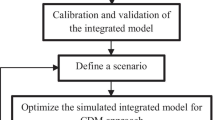
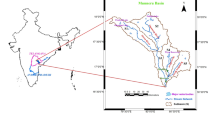
The present study proposes a waste load allocation (WLA) framework for a sustainable quality management of agricultural drainage water (ADW). Two multi-objective models, namely, abatement-performance and abatement-equity-performance, were developed through the integration of a water quality model (QAUL2Kw) and a genetic algorithm, by considering (1) the total waste load abatement, and (2) the inequity among waste dischargers. For successfully accomplishing modeling tasks, we developed a comprehensive overall performance measure (E wla ) reflecting possible violations of Egyptian standards for ADW reuse in irrigation. This methodology was applied to the Gharbia drain in the Nile Delta, Egypt, during both summer and winter seasons of 2012. Abatement-performance modeling results for a target of E wla = 100 % corresponded to the abatement ratio of the dischargers ranging from 20.7 to 75.6 % and 29.5 to 78.5 % in summer and in winter, respectively, alongside highly shifting inequity values. Abatement-equity-performance modeling results for a target of E wla = 90 % unraveled the necessity of increasing treatment efforts in three out of five dischargers during summer, and four out of five in winter. The trade-off curves obtained from WLA models proved their reliability in selecting appropriate WLA procedures as a function of budget constraints, principles of social equity, and desired overall performance level. Hence, the proposed framework of methodologies is of great importance to decision makers working toward a sustainable reuse of the ADW in irrigation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Allam A, Fliefle A, Tawfik A, Yoshimura Y, El Saadi A (2015) A simulation-based suitability index of the quality and quantity of agricultuarla drainage water for resue in irrigation. Sci Total Environ 536:79–90
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater.
Amirpoor A, Shamasai A, Niksokhan M (2010) Model for waste load allocation in rivers: a cooperative approach. American-Eurasian J Agricultral Environ Sci 8(6):626–632
Andrade N, Mauri R, Mendonça F (2012) General multiobjective model and simulated annealing algorithm for waste-load allocation. J Water Resour Plann Manage 139(3):339–344
Aras E, Togan V, Berkum M (2007) River water quality management model using genetic algorithm. Environ Fluid Mechaniccs 7:439–450
Ashtiani F, Niksokhan H, Ardestani M (2015a) Multi-objective waste load allocation in river system by MOPSO Algorithm. Int J Environ Reas 9(1):69–76
Ashtiani F, Jamshidi S, Niksokhan H, Ashtiani F (2015b) Value index, a novel decision making approach for waste load allocation. Int J Environ Chem Ecol Geol Geophys Eng 9(6):624–628
Burn D, Yulianti S (2001) Waste-load allocation using genetic algorithms. J Water Resour Plann Manage 127(2):121–129
Cho H (2013) Application of multi-objective genetic algorithm for waste load allocation in a river basin. J Environ Impact Assess 22(6):713–724
Cho H, Lee H (2014) Multi-objective waste load allocation model for optimizing waste load abatement and inequality among waste dischargers. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1892
Drainage Research Institute (DRI) (2012) Drainage water status in the Nile delta, year Book 2011/2012. Technical Report No. 82. National Water Research Center (NWRC), Egypt
EL-Gammal H, Hatem A, EL-Bahrawy A (2009) Assessment of water reuse as a non-conventional water resource in Egypt case study: Gharbia drain, Nile delta. 13th International Water Technology Conference, IWTC13, Hurghada, Egypt
Fleifle A, Saavedraina O, Yoshimura C, Elzeir M, Tawfik A (2014) Optimization of integrated water quality management for agricultural efficiency and environmental conservation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:8095–8111
Gen M, Cheng R (1997) Genetic algorithms and engineering design. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Kannel R, Lee S, Kanel R, Lee S, Ahn H (2007) Application of QUAL2Kw for water quality modeling and dissolved oxygen control in the river Bagmati. Environ Monit Assess 125(1-3):201–217
Karamouz M, Kerachian R, Mahmoodian M (2003) Seasonal waste-load allocation model for river water quality management. Proceedings of World Water and Environmental Resources Congress, Philadelphia, USA
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2005) Waste load allocation model for seasonal river water quality management application of sequential dynamic genetic algorithms. Scientia Iranica 12(2):117–130
Mostafavi S, Afshar A (2010) Waste load allocation using non-dominated archiving multi-colony ant algorithm. 2nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization, September 6-9, 2010, Lisbon, Portugal
Mujumdar P, Vemula V (2004) Fuzzy waste load allocation model: simulation–optimization approach. J Comput Civil Eng (ASCE) 120:120–131
Ng A, Perera B (2003) Selection of genetic algorithm operators for river water quality model calibration. Eng Appl Artif Intellgence 16(5-6):529–541
Rashed A, El-Sayed E (2014) Simulating agricultural drainage water reuse using QUAL2K Model: case study of the Ismailia canal catchment area, Egypt. J Irrig Drain Eng 140:501–511
ReVelle C, McGarity A (1997) Design and operation of civil and environmental engineering systems. Wiley, New York, pp 10158–0012
Saadatpour M, Afshar A (2007) Waste load allocation modeling with fuzzy goals; simulation–optimization approach. Water Resour Manag 21(7):1207–1224
Vazquez-Mendez M, Alvarez-Vazquez N, Garcia-Chan N, Martinez A (2013) Improving the environmental impact of the wastewater discharges with a specific simulation-optimization software. J Comput Appl Math 246:320–328
World Health Organization (WHO) (2002) Environmental Health Eastern Mediterranean Regional, Center for Environmental Health Activities (CEHA).
Xin-She Y (2010) Engineering optimization: an introduction with metaheuristic applications. A John Wiley & sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey
Yandamuri S, Srinivasan K, Murty Bhallamudi S (2006) Multiobjective optimal waste load allocation models for rivers using nondominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. J Water Resour Plann Manag 132(3):133–143
Acknowledgments
The first author would like to thank the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education (MoHE) for providing him the financial support (Ph.D. scholarship) for this research as well as the Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology (E-JUST) for offering the facility and tools needed to conduct this work. This study was partially supported by the Core-to-Core Program (B. Asia-Africa Science Platforms) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allam, A., Tawfik, A., Yoshimura, C. et al. Multi-objective models of waste load allocation toward a sustainable reuse of drainage water in irrigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11823–11834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6331-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6331-z