Abstract
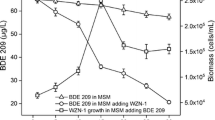
There is global concern about the effects of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) on environmental and public health. The molecular properties, biosorption, degradation, accumulation, and cellular metabolic effects of BDE209 were investigated in this study to identify the mechanisms involved in the aerobic biodegradation of BDE209. BDE209 is initially absorbed by wall teichoic acid and N-acetylglucosamine side chains in peptidoglycan, and then, BDE209 is transported and debrominated through three pathways, giving tri-, hepta-, octa-, and nona-bromodiphenyl ethers. The C–C bond energies decrease as the number of bromine atoms on the diphenyl decreases. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) inhibit protein expression or accelerate protein degradation and increase membrane permeability and the release of Cl−, Na+, NH4 +, arabinose, proteins, acetic acid, and oxalic acid. However, PBDEs increase the amounts of K+, Mg2+, PO4 3−, SO4 2−, and NO3 − assimilated. The biosorption, degradation, accumulation, and removal efficiencies when Brevibacillus brevis (1 g L−1) was exposed to BDE209 (0.5 mg L−1) for 7 days were 7.4, 69.5, 16.3, and 94.6 %, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Brar SK, Verma M, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY, Barnabé S, Valéro JR (2007) Bacillus thuringiensis proteases: production and role in growth, sporulation and synergism. Process Biochem 42:773–790
Calabrese V, Cornelius C, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Calabrese EJ, Mattson MP (2010) Cellular stress responses, the hormesis paradigm, and vitagenes: novel targets for therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxid Redox Sign 13:1763–1811
Chen DJ, Xu D, Li MS, He J, Gong YH, Wu DD, Sun M, Yu ZN (2012) Proteomic analysis of Bacillus thuringiensis ΔphaC mutant BMB171/PHB −1 reveals that the PHB synthetic pathway warrants normal carbon metabolism. J Proteomics 75:5176–5188
Chua EM, Shimeta J, Nugegoda D, Morrison PD, Clarke BO (2014) Assimilation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from microplastics by the marine amphipod, Allorchestes compressa. Environ Sci Technol 48:8127–8134
Dingemans MML, Ramakers GMJ, Gardoni F, van-Kleef GDM, Bergman A, DiLuca M, van-den-Berg M, Westerink RHS, Vijverberg HPM (2007) Neonatal exposure to brominated flame retardants BDE-47 reduces long-term potentiation and postsynaptic protein levels in mouse hippocampus. Environ Health Persp 115:865–870
Guardia MJL, Hale RC, Harvey E, Mainor TM, Ciparis S (2012) In situ accumulation of HBCD, PBDEs, and several alternative flame-retardants in the bivalve (Corbicula fluminea) and gastropod (Elimia proxima). Environ Sci Technol 46:5798–5805
He J, Robrock KR, Alvarez-Cohen L (2006) Microbial reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Environ Sci Technol 40:4429–4434
Johansson AK, Sellstrom U, Lindberg P, Bignert A, Cynthia ADW (2011) Temporal trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in Swedish peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus) eggs. Environ Int 37:678–686
Kim MN, Yoon MG (2010) Isolation of strains degrading poly(vinyl alcohol) at high temperatures and their biodegradation ability. Polym Degrad Stab 95:89–93
Kim SJ, Chang J, Singh M (2014) Peptidoglycan architecture of Gram-positive bacteria by solid-state NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:350–362
Lee LK, Ding C, Yang KL, He JZ (2011) Complete debromination of tetra- and penta-brominated diphenyl ethers by a coculture consisting of Dehalococcoides and Desulfovibrio species. Environ Sci Technol 45:8475–8482
Lim S, Marcellin E, Jacob S, Nielsen LK (2015) Global dynamics of Escherichia coli phosphoproteome in central carbon metabolism under changing culture conditions. J Proteomics 126:24–33
Lohmann R, Klanova J, Kukucka P, Yonis S, Bollinger K (2013) Concentrations, fluxes, and residence time of PBDEs across the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 47:13967–13975
Madia F, Giordano G, Fattori V, Vitalone A, Branchi I, Capone F, Costa LG (2004) Differential in vitro neurotoxicity of the flame retardant PBDE-99 and of the PCB Aroclor 1254 in human astrocytoma cells. Toxicol Lett 154:11–21
Matias PM, Pereira IAC, Soares CM, Carrondo MA (2005) Sulphate respiration from hydrogen in Desulfovibrio bacteria: a structural biology overview. Prog Biophys Mol Bio 89:292–329
McKernan MA, Rattner BA, Hatfield JS, Hale RC, Ottinger MA (2010) Absorption and biotransformation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers DE-71 and DE-79 in chicken (Gallus gallus), mallard (Anas platyrhynchos), American kestrel (Falco sparverius) and black-crowned night-heron (Nycticorax nycticorax) eggs. Chemosphere 79:100–109
Qiu MD, Chen XJ, Deng DY, Guo J, Sun GP, Mai BX, Xu MY (2012) Effects of electron donors on anaerobic microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Biodegradation 23:351–361
Rayne S, Ikonomou MG, Whale MD (2003) Anaerobic microbial and photochemical degradation of 4,4′-dibromodiphenyl ether. Water Res 37:551–560
Robrock KR, Korytar P, Alvarez-Cohen L (2008) Pathways for the anaerobic microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Sci Technol 42:2845–2852
Romani A (2007) Regulation of magnesium homeostasis and transport in mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 458:90–102
Shi GY, Yin H, Ye JS, Peng H, Li J, Luo CL (2013) Effect of cadmium ion on biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Hazard Mater 263:711–717
Sulimma L, Bullach A, Kusari S, Lamshoft M, Zuhlke S, Spiteller M (2013) Enantioselective degradation of the chiral fungicides metalaxyl and furalaxyl by Brevibacillus brevis. Chirality 25:336–340
Tang SY, Bai JQ, Yin H, Ye JS, Peng H, Liu ZH, Dang Z (2014) Tea saponin enhanced biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether by Brevibacillus brevis. Chemosphere 114:255–261
Tian M, Chen SJ, Wang J, Luo Y, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2012) Plant uptake of atmospheric brominated flame retardants at an E-waste site in southern China. Environ Sci Technol 46:2708–2714
Tokarz JA, Ahn MY, Leng J, Filley TR, Nies L (2008) Reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in anaerobic sediment and a biomimetic system. Environ Sci Technol 42:1157–1164
Upadhyay SK, Sasidhar YU (2012) Molecular simulation and docking studies of Gal1p and Gal3p proteins in the presence and absence of ligands ATP and galactose: implication for transcriptional activation of GAL genes. J Comput Aid Mol Des 26:847–864
Wisselink HW, Cipollina C, Oud B, Crimi B, Heijnen JJ, Pronk JT, van-Maris AJA (2010) Metabolome, transcriptome and metabolic flux analysis of arabinose fermentation by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 12:537–551
Xu GY, Wang JB (2014) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by white-rot fungus Phlebia lindtneri. Chemosphere 110:70–77
Ye JS, Yin H, Peng H, Bai JQ, Xie DP, Wang LL (2013a) Biosorption and biodegradation of triphenyltin by Brevibacillus brevis. Bioresource Technol 129:236–241
Ye JS, Yin H, Xie DP, Peng H, Huang J, Liang WY (2013b) Copper biosorption and ions release by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the presence of benzo[a]pyrene. Chem Eng J 219:1–9
Yen JH, Liao WC, Chen WC, Wang YS (2009) Interaction of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) with anaerobic mixed bacterial cultures isolated from river sediment. J Hazard Mater 165:518–524
Yu LH, Luo XJ, Wu JP, Liu LY, Song J, Sun QH, Zhang XL, Chen D, Mai BX (2011) Biomagnification of higher brominated PBDE congeners in an urban terrestrial food web in north China based on field observation of prey deliveries. Environ Sci Technol 45:5125–5131
Zhao Q, Ovchinnikova K, Chai BH, Yoo H, Magula J, Pollack GH (2009) Role of proton gradients in the mechanism of osmosis. J Phys Chem B 113:10708–10714
Zorbas YG, Kakuris KK, Federenko YF, Deogenov VA (2010) Utilization of magnesium during hypokinesia and magnesium supplementation in healthy subjects. Nutrition 26:1134–1138
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21377047 and 21577049), Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2014A020216013), and the University Foundation of Education Ministry of China (No. 21615459) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1.23 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Tang, L., Wang, R. et al. Biosorption and degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether by Brevibacillus brevis and the influence of decabromodiphenyl ether on cellular metabolic responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5166–5178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5762-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5762-2