Abstract
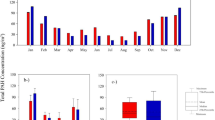
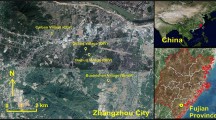
The seasonal and spatial variations, compositional profiles, and possible sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in ambient air samples in Shanghai of China were investigated by passive air samplers, and the potential inhalation risks posed by these chemicals were evaluated. The following results were obtained: (1) The World Health Organization (WHO) toxic equivalency (TEQ) values for PCDD/Fs were in the range of 10.8–259 fg m−3 (mean 63.4 fg m−3) in summer and 24.1–154 fg m−3 (mean 83.4 fg m−3) in winter. Atmospheric PCDD/F levels were in the following order: industrial areas > commercial and residential areas > rural areas. (2) 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF (24 %), 2,3,7,8-TeCDD (16 %), 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD (13 %), and 2,3,7,8-TeCDF (12 %) were the predominant contributors to the TEQ of PCDD/Fs. (3) There was a slight seasonal trend with higher TEQ values in winter than in summer, which could be related to seasonal variations in the dispersion of PCDD/Fs in ambient air. (4) The children’s daily intake was at the lower end of the range for the tolerable daily intake of PCDD/Fs recommended by WHO, which indicates that the inhalation risk of PCDD/Fs for local residents in Shanghai is relatively low.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altarawneh M, Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM, Mackie JC (2009) Mechanisms for formation, chlorination, dechlorination and destruction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs). Prog Energy Combust Sci 35:245–274
Aristizabal BH, Gonzalez CM, Morales L, Abalos M, Abad E (2011) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran in urban air of an Andean city. Chemosphere 85:170–178
Ba T, Zheng M, Zhang B, Liu W, Xiao K, Zhang L (2009) Estimation and characterization of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs from secondary copper and aluminum metallurgies in China. Chemosphere 75:1173–1178
Bruckmann P, Hiester E, Klees M, Zetzsch C (2013) Trends of PCDD/F and PCB concentrations and depositions in ambient air in Northwestern Germany. Chemosphere 93:1471–1478
Chang MB, Weng YM, Lee TY, Chen YW, Chang SH, Chi KH (2003) Sampling and analysis of ambient dioxins in northern Taiwan. Chemosphere 51:1103–1110
Chen T, Li X, Yan J, Lu S, Cen K (2011) Distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in ambient air of different regions in China. Atmos Environ 45:6567–6575
Colombo A, Benfenati E, Bugatti SG, Lodi M, Mariani A, Musmeci L, Rotella G, Senese V, Ziemacki G, Fanelli R (2013) PCDD/Fs and PCBs in ambient air in a highly industrialized city in northern Italy. Chemosphere 90:2352–2357
Cortés J, González CM, Morales L, Abalos M, Abad E, Aristizábal BH (2014) PCDD/PCDF and dl-PCB in the ambient air of a tropical Andean city: passive and active sampling measurements near industrial and vehicular pollution sources. Sci Total Environ 491–492:67–74
Ding L, Li Y, Wang P, Li X, Zhao Z, Zhang Q, Tuan T, Jiang G (2012) Seasonal trend of ambient PCDD/Fs in Tianjin City, northern China using active sampling strategy. J Environ Sci 24:1966–1971
Ding L, Li Y, Wang P, Li X, Zhao Z, Ruan T, Zhang Q (2013) Spatial concentration, congener profiles and inhalation risk assessment of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in the atmosphere of Tianjin, China. Chin Sci Bull 58:971–978
Gao L, Zhang Q, Liu L, Li C, Wang Y (2014) Spatial and seasonal distributions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and polychlorinated biphenyls around a municipal solid waste incinerator, determined using polyurethane foam passive air samplers. Chemosphere 114:317–326
Gunes G, Saral A, Celikten H, Kuzu SL, Demir S, Uygur N (2014) Investigation of temporal and spatial variations in atmospheric concentrations of PCDDs and PCDFs in Istanbul. Sci Total Environ 488–489:469–474
Hu J, Zheng M, Nie Z, Liu W, Liu G, Zhang B, Xiao K (2013) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran and polychlorinated biphenyl emissions from different smelting stages in secondary copper metallurgy. Chemosphere 90:89–94
Hutzinger O, Blumich M (1985) Sources and fate of PCDDs and PCDFs: an overview. Chemosphere 14:581–600
Japan GO (2005) Information brochure dioxins. http://www.env.go.jp/en/chemi/dioxins/brochure2005.pdf
Kadowaki S, Naitoh H (2005) Gas-particle partitioning of PCDD/Fs in Nagoya urban air, Japan. Chemosphere 59:1439–1453
Katsoyiannis A, Gioia R, Sweetman A, Jones K (2010) Continuous Monitoring of PCDD/Fs in the UK Atmosphere: 1991-2008. Environ Sci Technol 44(15):5735–5740
Lee W, Chang-Chien G, Wang L, Lee W, Tsai P, Wu K, Lin C (2004) Source identification of PCDD/Fs for various atmospheric environments in a highly industrialized city. Environ Sci Technol 38:4937–4944
Li H, Feng J, Sheng G, Lu S, Fu J, Peng P, Man R (2008a) The PCDD/F and PBDD/F pollution in the ambient atmosphere of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 70:576–583
Li Y, Jiang G, Wang Y, Cai Z, Zhang Q (2008b) Concentrations, profiles and gas–particle partitioning of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the ambient air of Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 42:2037–2047
Li X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang P, Yang H, Jiang G, Wei F (2011) Evaluation of atmospheric sources of PCDD/Fs, PCBs and PBDEs around a steel industrial complex in northeast China using passive air samplers. Chemosphere 84:957–963
Li C, Zheng M, Zhang B, Gao L, Liu L, Zhou X, Ma X, Xiao K (2012) Long-term persistence of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in air, soil and sediment around an abandoned pentachlorophenol factory in China. Environ Pollut 162:138–143
Lohmann R, Jones KC (1998) Dioxins and furans in air and deposition: a review of levels, behaviour and processes. Sci Total Environ 219:53–81
Lohmann R, Lee RGM, Abbott J, Coleman P, Jones KC (2006) Verifying emission factors and national POPs emission inventories for the UK using measurements and modelling at two rural locations. J Environ Monit 8(1):79–88
Mari M, Schuhmacher M, Feliubadaló J, Domingo JL (2008) Air concentrations of PCDD/Fs, PCBs and PCNs using active and passive air samplers. Chemosphere 70:1637–1643
Menichini E, Lacovella N, Monfredini F, Baldassarri L (2007) Atmospheric pollution by PAHs, PCDD/Fs and PCBs simultaneously collected at a regional background site in central Italy and at an urban site in Rome. Chemosphere 69:422–434
Min Y, Lee M, Kim D, Heo J (2013) Annual and seasonal variations in atmospheric PCDDs/PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs levels in satellite cities of Seoul, Korea during 2003–2009. Atmos Environ 77:222–230
Min Y, Heo J, Lee M (2014) Determination of toxic congeners of 17 PCDDs/PCDFs and 12 dl-PCBs using polyurethane foam passive air samplers in ten cities around Seoul. Sci Total Environ 491–492:17–27
Moussaoui Y, Tuduri L, Kerchich Y, Meklati BY, Eppe G (2012) Atmospheric concentrations of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs and some pesticides in northern Algeria using passive air sampling. Chemosphere 88:270–277
Nie Z, Zheng M, Liu W, Zhang B, Liu G, Su G, Lv P, Xiao K (2011) Estimation and characterization of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs, PCNs, HxCBz and PeCBz emissions from magnesium metallurgy facilities in China. Chemosphere 85:1707–1712
Nie Z, Liu G, Liu W, Zhang B, Zheng M (2012) Characterization and quantification of unintentional POP emissions from primary and secondary copper metallurgical processes in China. Atmos Environ 57:109–115
NIP CS (2007) National Implementation Plan for the Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants. http://www.pops.int/documents/implementation/nips/submissions/China_NIP_En.pdf
Pozo K, Harner T, Shoeib M, Urrutia R, Barra R, Parra O, Focardi S (2004) Passive-sampler derived air concentrations of persistent organic pollutants on a north-south transect in Chile. Environ Sci Technol 38:6529–6537
Raun LH, Correa O, Rifai H, Suarez M, Koenig L (2005) Statistical investigation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the ambient air of Houston, Texas. Chemosphere 60:973–989
Ren M, Peng PA, Zhang S, Yu L, Zhang G, Mai B, Sheng G, Fu J (2007) Atmospheric deposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in Guangzhou, China. Atmos Environ 41:592–605
Shin SK, Jin GZ, Kim WI, Kim BH, Hwang SM, Hong JP, Park JS (2011) Nationwide monitoring of atmospheric PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in South Korea. Chemosphere 83:1339–1344
Shoeib M, Harner T (2002) Characterization and comparison of three passive air samplers for persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 36:4142–4151
Sin DW-M, Choi JY-Y, Louie PK-K (2002) A study of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the atmosphere of Hong Kong. Chemosphere 47:647–653
UNEP (2001) The Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization re-evaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. ToxSci Advance Access Published 2005 WHO Re-evaluation of TEFs
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Vilavert L, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2014) Seasonal surveillance of airborne PCDD/Fs, PCBs and PCNs using passive samplers to assess human health risks. Sci Total Environ 466–467:733–740
Wagrowski DM, Hites RA (2000) Insights into the global distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 34:2952–2958
Wang C, Yang D, Zhang J, Peng C, Jiang Y, Zhou J, Huang H, He L, Zhao K (2010) Determination of Dioxins and Furans in Atmosphere of Shenzhen, China. Environmental Monitoring in China (in Chinese) 26(6):74–79
Wang L, Lee W, Tsai P, Lee W, Chang-Chien G (2003) Emissions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from stack flue gases of sinter plants. Chemosphere 50:1123–1129
WHO (1998) Assessment of the health risk of dioxins: re-evaluation of the tolerable daily intake (TDI). WHO Consultation, Geneva
Xiao H, Hung H, Harner T, Lei Y, Wania F (2008) Field testing a flow-through sampler for semivolatile organic compounds in air. Environ Sci Technol 42:2970–2975
Xu MX, Yan JH, Lu SY, Li XD, Chen T, Ni MJ, Dai HF, Wang F, Cen KF (2009) Gas/particle partitioning of atmospheric PCDD/Fs in a satellite town in Eastern China. Chemosphere 76:1540–1549
Yu L, Mai B, Meng X, Bi X, Sheng G, Fu J, Peng PA (2006) Particle-bound polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the atmosphere of Guangzhou, China. Atmos Environ 40:96–108
Zhang XL, Lu Y, Zhu MJ, Jian C, Guo ZS, Deng L, Sun J, Zhang Q, Luo CH (2014) Concentrations of PCDD/Fs in the atmosphere of Chongqing city and its seasonal variation. Environ Sci (in Chinese) 35(1):22–29
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21407137 and 51178440), the special fund for the Public Service Sector of the State Environmental Protection Agency of China (Grant No. 201209020), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2013M540122 and 2014T70105), and the State Key Laboratory of Environmental Criteria and Risk Assessment, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences (Grant No. SKLECRA2014OFP04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Constantini Samara
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Nie, Z., Tian, S. et al. Passive air sampling for determining the levels of ambient PCDD/Fs and their seasonal and spatial variations and inhalation risk in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 13243–13250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4552-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4552-1