Abstract
Purpose
PCDD/Fs, PCBs, and PAHs, ubiquitous environmental pollutants which are part of the POPs, are mainly produced by anthropogenic activities as well as by natural processes. Occurrences of these pollutants in different sites in Trieste are presented. PCDD/Fs distribution and their possible emission sources are discussed.
Methods
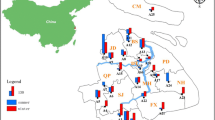
Air samples were collected in different sites near the industrial area, in the city center, and in a background area, using a high-volume sampler equipped with a quartz fiber filter and a PUF. Each sampling lasted a week.
Results
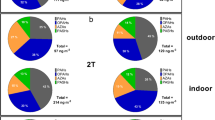
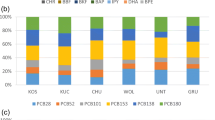
The concentrations of the organochlorinated pollutants are consistent with literature data (ΣPCDD/Fs and Σdl-PCBs were 5–38 fg TEQ/Nm3 and 4–31 fg TEQ/Nm3, respectively), and an apparent seasonal trend was found with slightly higher concentrations in the winter and lower levels in both summer campaigns. Moreover, the isomer profile of each sampling campaign was compared to the fingerprint of a sintering plant, a cement plant, and an incinerator, the main industrial activities in Trieste.
Conclusions
The organic micropollutants were detected in levels consistent with literature data. The results show that the pollutants are uniformally distributed in the atmosphere of Trieste. PCDD/F fingerprints in each site remained almost identical during summer and winter, confirming the yearly prevalence of the emissions from the nearby sintering plant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad E, Martınez K, Caixach J, Rivera J (2006) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and dioxin-like PCBs in flue gas emissions from municipal waste management plants. Chemosphere 63:570–580
Abad E, Martinez K, Gustems L, Gomez R, Guinart X, Hernandez I, Rivera J (2007) Ten years measuring PCDDs/PCDFs in ambient air in Catalonia (Spain). Chemosphere 67:709–714
Alcock RE, Sweetman AJ, Jones KC (2001) A congener-specific PCDD/F emissions inventory for the UK, do current estimates account for the measured atmospheric burden? Chemosphere 43:183–194
Arey J, Zielinska B, Atkinson R, Winer AM (1987) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and nitroarene concentrations in ambient air during wintertime high-NOx episode in the Los Angeles Basin. Atmos Environ 21(6):1437–1444
Aries E, Anderson DR, Ordsmith N, Hall K, Fisher R (2004) Development and validation of a method for analysis of “dioxin-like” PCBs in environmental samples from the steel industry. Chemosphere 54:23–31
Aries E, Anderson DR, Fisher R, Fray TAT, Hemfrey D (2006) PCDD/F and “dioxin-like” PCB emissions from iron ore sintering plants in the UK. Chemosphere 65:1470–1480
Chang MB, Huang HC, Tsai SS, Chi KH, Chang-Chien GP (2006) Evaluation of the emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs from electric arc furnaces. Chemosphere 62:1761–1773
Chi KH, Lin C-Y, Yang C-FO, Wang JL, Lin NH, Sheu GR, Lee CT (2010) PCDD/F measurement at a high-altitude station in Central Taiwan: evaluation of long-range transport of PCDD/Fs during the Southeast Asia biomass burning event. Environ Sci Technol 44:2954–2960
Choi MPK, Ho SKM, So BKL, Cai Z, Lau AKH, Wong MH (2008) PCDD/F and dioxin-like PCB in Hong Kong air in relation to their regional transport in the Pearl River Delta region. Chemosphere 71(2):211–218
Cleverly D, Ferrario J, Byrne C, Riggs K, Joseph D, Hartford P (2007) A general indication of the contemporary background levels of PCDDs, PCDFs, and coplanar PCBs in the ambient air over rural and remote areas of the United States. Environ Sci Technol 41:1537–1544
Conesa JA, Galvez A, Mateos F, Martin-Gullon I, Font R (2008) Organic and inorganic pollutants from cement kiln stack feeding alternative fuels. J Hazard Mater 158(2–3):585–592
de Assunção JV, Pesquero CR, Bruns RE, Carvalho LRF (2005) Dioxins and furans in the atmosphere of São Paulo City, Brazil. Chemosphere 58:1391–1398
Everaert K, Baeyens J (2002) The formation and emission of dioxins in large scale thermal processes. Chemosphere 46:439–448
Guerriero E, Bianchini M, Gigliucci PF, Guarnieri A, Mosca S, Rossetti G, Vardè M, Rotatori M (2009a) Influence of process changes on PCDD/Fs produced in an iron ore sintering plant. Environ Eng Sci 26:71–80
Guerriero E, Guarnieri A, Mosca S, Rossetti G, Rotatori M (2009b) PCDD/Fs removal efficiency by electrostatic precipitator and wetfine scrubber in an iron ore sintering plant. J Hazard Mater 172:1498–1504
Halsall CJ, Lee RGM, Coleman PJ, Burnett V, Harding-Jones P, Jones KC (1995) PCBs in UK urban air. Environ Sci Technol 29:2368–2376
Hovmand MF, Vikelsøe J, Andersen HV (2007) Atmospheric bulk deposition of dioxin and furans to Danish background areas. Atmos Environ 41:2400–2411
IARC (1987) Overall evaluations of carcinogenicity: an updating of IARC monographs vols. 1 to 42. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, Suppl. 7
IARC (1997) Polychlorinated Dibenzo-para-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, vol. 69
Katsoyiannis A, Gioia R, Sweetman AJ, Jones KC (2010) Continuous monitoring of PCDD/Fs in the UK Atmosphere: 1991–2008. Environ Sci Technol 44:5735–5740
Kouimtzis TH, Samara C, Voutsa D, Balafoutis CH, Muller L (2002) PCDD/Fs and PCBs in air borne particulate matter of the greater Thessaloniki area, N. Greece. Chemosphere 47:193–205
Lee RGM, Green NJL, Lohmann R, Jones KC (1999) Seasonal, anthropogenic, air mass, and meteorological influences on the atmospheric concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs): evidence for the importance of diffuse combustion sources. Environ Sci Technol 33(17):2864–2871
Lee RGM, Coleman P, Jones JL, Jones KC, Lohmann R (2005) Emission factors and importance of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PCNs, PAHs and PM10 from the domestic burning of coal and wood in the U.K. Environ Sci Technol 39(6):1436–1447
Li Y, Wang P, Ding L, Li X, Wang T, Zhang Q, Yang H, Jiang G, Wei F (2010) Atmospheric distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls around a steel plant Area, Northeast China. Chemosphere 79(3):253–258
Liu GR, Zheng MH, Liu WB, Wang CZ, Zhang B, Gao LR, Su G, Xiao K, Lv P (2009) Atmospheric emission of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, hexachlorobenzene, and pentachlorobenzene from the coking industry. Environ Sci Technol 43:9196–9201
Lohmann R, Jones KC (1998) Dioxins and furans in air and deposition: a review of levels, behaviour and processes. Sci Total Environ 219(1):53–81
Lohmann R, Nelson E, Eisenreich SJ, Jones KC (2000) Evidence for a dynamic air-water exchange of PCDD/Fs: a study in the Raritan Bay/Hudson River Estuary. Environ Sci Technol 34(15):3086–3093
Luthardt P, Mayer J, Fuchs J (2002) Total TEQ emissions (PCDD/F and PCB) from industrial sources. Chemosphere 46:1303–1308
Mandalakis M, Tsapakis M, Tsoga A, Stephanou EG (2002) Gas–particle concentrations and distribution of aliphatic hydrocarbons, PAHs, PCBs and PCDD/Fs in the atmosphere of Athens (Greece). Atmos Environ 36(25):4023–4035
Mari M, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2008) Monitoring PCDD/Fs, PCBs and metals in the ambient air of an industrial area of Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 73(6):990–998
Martinez K, Austrui JR, Jover E, Ábalos M, Rivera J, Abad E (2010) Assessment of the emission of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs from an industrial area over a nearby town using a selective wind direction sampling device. Environ Pollut 158:764–769
Menichini E, Iacovella N, Monfredini F, Turrio-Baldassarri L (2007) Atmospheric pollution by PAHs, PCDD/Fs and PCBs simultaneously collected at a regional background site in central Italy and at an urban site in Rome. Chemosphere 69:422–434
Mosca S, Torelli GN, Guerriero E, Tramontana G, Pomponio S, Rossetti G, Rotatori M (2010) Evaluation of a simultaneous sampling method of PAHs, PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs in ambient air. J Environ Monit 12(5):1092–1099
Nakano M, Hosotani Y, Kasai E (2005) Observation of behaviors of dioxins and some relating elements in iron ore sintering bed by quenching pot test. ISIJ Int 45(4):609–617
Oehme M, Larssen S, Brevik EM (1991) Emission factors of PCDD and PCDF for road vehicles obtained by tunnel experiment. Chemosphere 23(11–12):1699–1708
Ogura I, Masunaga S, Nakanishi J (2004) Quantitative source identification of dioxin-like PCBs in Yokohama, Japan, by temperature dependence of their atmospheric concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 38(12):3279–3285
Quaß U, Fermann M, Breoker G (2004) The european dioxin air emission inventory project - final results. Chemosphere 54:1319–1327
Rossetti G, Rotatori M, Guerriero E, Guarnieri A, Mosca S, Manni A (2009) GPC/alumina automated clean-up method for PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs in flue gas emissions. Organohalogen Compd 71:2278–2281
Shih ML, Lee WJ, Shih TS, Huang SL, Chang-Chien GP, Wang LC, Tsai PJ (2006) Characterization of dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in the atmosphere of a sinter of different workplaces plant. Sci Total Environ 366:197–205
Smith RM, O’Keefe PW, Aldous KM, Valente H, Connor SP, Donnelly RJ (1990) Chlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxins in atmospheric samples from cities in New York. Environ Sci Technol 24(10):1502–1506
Stockholm Convention (2001) Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants
Tysklind M, Faengmark I, Marklund S, Lindskog A, Thaning L, Rappe C (1993) Atmospheric transport and transformation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 27(10):2190–2197
US EPA (1999a) Method TO-4A – Determination of pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in ambient air using high volume Polyurethane Foam (PUF) sampling followed by Gas Chromatographic/Multi-Detector Detection (GC/MD)
US EPA (1999b) Method TO-9A—determination of polychlorinated, polybrominated and brominated/chorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofuran in ambient air
US EPA (1999c) Method TO-13A—determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in ambient air using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS)
Venier M, Ferrario J, Hites RA (2009) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p- dioxins and dibenzofurans in the atmosphere around the great lakes. Environ Sci Technol 43:1036–1041
Wagrowski DM, Hites RA (2000) Insights into the global distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 34(14):2952–2958
Wang L-C, Lee W-J, Tsai P-J, Lee W-S, Chang-Chien G-P (2003a) Emissions of polychlorinated dibenzo dioxin and dibenzofurans from stack flue gases of sinter plants. Chemosphere 50:1123–1129
Wang T, Anderson D, Thompson D, Clench M, Fisher R (2003b) Studies into the formation of dioxins in the sintering process used in the iron and steel industry. 1. Characterisation of isomer profiles in particulate and gaseous emissions. Chemosphere 51:585–594
Wang JB, Hung C-H, Hung C-H, Chang-Chien GP (2009) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran emissions from an industrial park clustered with metallurgical industries. J Hazard Mater 161:800–807
WHO (2000) Air quality guidelines for Europe, WHO Regional Publications, Eur. Series No. 91. World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, 2nd edn
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosca, S., Torelli, G.N., Tramontana, G. et al. Concentration of organic micropollutants in the atmosphere of Trieste, Italy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 1927–1935 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0696-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0696-9