Abstract
Introduction
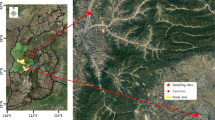
Two hundred twenty-five precipitation samples were collected at high- (summit, 1,534 m ASL) and low-elevation (base, 218 m ASL) sites between 2005 and 2008 in eastern China. The present work focused on the roles of long-range transport and under-cloud/boundary layer scavenging on chemical composition of precipitation collected at the two sites.
Methods
Ionic and trace species were analyzed in 225 precipitation samples. A total of 72 precipitation events occurring simultaneously at the summit and base sites were further examined. Positive matrix factorization (PMF) and backward air mass trajectories were used to identify the sources of precipitation pollutants.
Results
Low pH and high concentrations of ionic and trace species were measured at both sites. Inter-correlations for the simultaneous samples at the two sites were poor for trace elements (−0.07~0.47). A several fold increase in major ion (122~546%) and trace element (261~3,302%) concentrations occurred as the rain fell. Approximately 89% of the air masses responsible for the summit precipitation events were of distance origin. Marine salt, crustal material, fossil fuel burning plus secondary products, and metallic-industry-related factors were identified by PMF, contributing 9.7%, 22.8%, 41.8%, and 25.6%, respectively, to the precipitation pollutants at the summit and 13.3%, 31.9%, 39.6%, and 15.2%, respectively, at the base.
Conclusions
Long-range atmospheric transport primarily influenced the high and the low site precipitation was strongly influenced by the under-cloud scavenging process of local boundary layer pollutants. Crustal material and fossil fuel burning plus secondary products were the predominant pollution sources in this region.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aas W, Shao M, Jin L, Larssen T, Zhao D, Xiang R, Zhang J, Xiao J, Duan L (2007) Air concentrations and wet deposition of major inorganic ions at five non-urban sites in China, 2001–2003. Atmos Environ 41:1706–1716
Aleksic N, Roy K, Sistla G, Dukett J, Houck N, Casson P (2009) Analysis of cloud and precipitation chemistry at Whiteface Mountain, NY. Atmos Environ 43:2709–2716
Al-Momani IF (2003) Trace elements in atmospheric precipitation at Northern Jordan measured by ICP-MS: acidity and possible sources. Atmos Environ 37:4507–4515
Anderson JB, Baumgardner RE, Grenville SE (2006) Trends in cloud water sulfate and nitrate as measured at two mountain sites in the Eastern United States: regional contributions and temporal changes compared with regional changes in emissions, 1986–1999. Atmos Environ 40:4423–4437
Anttila P, Paatero P, Tapper U, Järvinen O (1995) Source identification of bulk wet deposition in Finland by positive matrix factorization. Atmos Environ 29:1705–1718
Bacardit M, Camarero L (2010) Atmospherically deposited major and trace elements in the winter snowpack along a gradient of altitude in the Central Pyrenees: the seasonal record of long-range fluxes over SW Europe. Atmos Environ 44:582–595
Battarbee RW, Thompson R, Catalan J, Grytnes JA, Birks HJB (2002) Climate variability and ecosystem dynamics of remote alpine and arctic lakes: the MOLAR project. J Paleolimnol 28:1–6
Bhanuprasad SG, Venkataraman C, Bhushan M (2008) Positive matrix factorization and trajectory modelling for source identification: a new look at Indian Ocean experiment ship observations. Atmos Environ 42:4836–4852
Draxler RR, Rolph GD (2003) HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website/http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.htmlS. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD
EANET (2008) Available at: http://www.eanet.cc/product/index.html. Accessed June 2010
EMEP (2007) Available at: http://tarantula.nilu.no/projects/ccc/emepdata.html. Accessed June 2010
Galloway JN, Diawu Z, Jiling X, Likens GE (1987) Acid rain: China, United States and a remote area. Science 236:1559–1562
Hou H, Takamastsu T, Koshikawa MK, Hosomi M (2005) Trace metals in buld precipitation and throughfall in a suburban area of Japan. Atmos Environ 39:3583–3595
Huang X, Olmez I, Aras NK (1994) Emissions of trace elements from motor vehicles: potential marker elements and source composition profile. Atmos Environ 28(8):1385–1391
Huo M-Q, Sun Q, Xie P, Bai Y-H, Liu Z-R, Li J-L (2009) Relationship between atmospheric particles and rain water chemistry character. Environ Sci 30(11):3160–3166 (in Chinese)
Juntto S, Paatero P (1994) Analysis of daily precipitation data by positive matrix factorization. Environmetrics 5:127–144
Kang S, Zhang Q, Kaspari S, Qin D, Cong Z, Ren J, Mayewski PA (2007) Spatial and seasonal variations of elemental composition in Mt. Everest (Qomolangma) snow/firn. Atmos Environ 41:7208–7218
Kitayama K, Murao N, Hara H (2010) PMF analysis of impacts of SO2 from Miyakejima and Asian Continent on precipitation sulfate in Japan. Atmos Environ 44:95–105
Klimont Z, Cofala J, Schöpp W, Amann M, Streets DG, Ichikawa Y, Fujita S (2001) Projections of SO2, NOx, NH3 and VOC emissions in East Asia up to 2030. Water Air Soil Pollut 130:193–198
Lei HC, Tanner PA, Huang MY (1997) The acidification process under the cloud in southwest China: observation results and simulation. Atmos Environ 31(6):851–861
Li Y, Yu XL, Chen HB, Lin WL, Tang J, Wang SF (2010) Chemical characteristics of precipitation at three Chinese regional background stations from 2006 to 2007. Atmos Res 96:173–183
Liu XH, Wang Y, Wang WX, Sun MH (2010a) Characteristics of heavy metals in wet deposition at Mt. Tai, China,4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, June 18–20; doi:10.1109/ICBBE.2010.5516029
Liu Y, Yang D, Chen W, Zhang H (2010b) Measurements of Asian dust optical properties over the Yellow Sea of China by shipboard and ground-based photometers, along with satellite remote sensing: a case study of the passage of a frontal system during April 2006. J Geophys Res 115:D00K04. doi:10.1029/2009JD012684
Melaku S, Morris V, Raghavan D, Hosten C (2008) Seasonal variation of heavy metals in ambient air and precipitation at a single site in Washington, DC. Environ Pollut 155:88–98
Moody JL, Samson PJ (1989) The influence of atmospheric transport on precipitation chemistry at two sites in the midwestern United States. Atmos Environ 23:2117–2132
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2007) China Statistical Yearbook on Environment 2007. National Bureau of Statistics of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2009) China Statistical Yearbook 2007. National Bureau of Statistics of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Paatero P, Tapper U (1994) Positive matrix factorization: a non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 5:111–126
Reff A, Eberly SI, Bhave PV (2007) Receptor modeling of ambient particulate matter data using positive matrix factorization: review of existing methods. J Air Waster Manage 57:146–154
Ren Y, Ding AJ, Wang T, Shen XH et al (2009) Measurement of gas-phase total peroxides at the summit of Mount Tai in China. Atmos Environ 43:1702–1711
Safai PD, Rao PSP, Momin GA, Ali K, Chate DM, Praveen PS (2004) Chemical composition of precipitation during 1984–2002 at Pune, India. Atmos Environ 38:1705–1714
Seto S, Hara H (2006) Precipitation chemistry in western Japan: its relationship to meteorological parameters. Atmos Environ 40:1538–1549
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2009) China Environmental Statement of 2008. State Environmental Protection Administration of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Stortini AM, Freda A, Cesari D, Cairns WRL, Contini D, Barbante C, Prodi F, Cescon P, Gambaro A (2009) An evaluation of the PM2.5 trace elemental composition in the Venice Lagoon area and an analysis of the possible sources. Atmos Environ 43:6296–6304
Tanner PA, Lei HC, Huang MY (1997) Acid rain and below-cloud scavenging in South-Western China. J Atmos Chem 27(1):71–78
Tasic M, Mijic Z, Rajsic S, Stojic A, Radenkovic M, Joksic J (2009) Source apportionment of atmospheric bulk deposition in the Belgrade urban area using Positive Matrix Factorization. Journal of Physics: conference Series 162. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/162/1/012018
Wang Y, Wai KM, Gao J, Liu X, Wang T, Wang W (2008) The impacts of anthropogenic emissions on the precipitation chemistry at an elevated site in North-eastern China. Atmos Environ 42:2959–2970
Wang Y, Guo J, Wang T, Ding A, Gao J, Zhou Y Jr, Collett JL, Wang W (2011) Influence of regional pollution and sandstorms on the chemical composition of cloud/fog at the summit of Mt. Taishan in northern China. Atmos Res 99:434–442
Zheng M, Guo ZG, Fang M, Rahn AK, Kester RD (2005) Dry and wet deposition of elements in Hong Kong. Mar Chem 97:124–139
Zhou Y, Wang T, Gao X, Xue L et al (2009) Continuous observations of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at Mount Tai (1534 m a.s.l.) in central-eastern China. J Atmos Chem 64:107–127
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Mt. Tai Meteorological Station for support of the field study and for providing meteorological data and to the Shandong Province Environmental Monitoring Center for chemical analysis of samples. We express our sincere thanks to Dr. Pentti Paatero for sharing information on the PMF program and to the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for providing the HYSPLIT model. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2005CB422203) and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41075092). Thank to Dr. Eric Codner from Write Science Right, CSO and Dr. Edward C. Mignot, Shandong University, for linguistic advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Ding, A. et al. Impact of long-range transport and under-cloud scavenging on precipitation chemistry in East China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18, 1544–1554 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0516-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0516-2