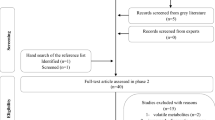
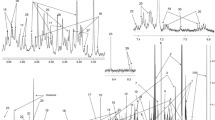
Abstract
Introduction
Despite the rise of metabolomics over the past years, and particularly salivary metabolomics, little research on Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) biomarkers has focused on the salivary metabolome.
Objectives
This study aims to identify metabolites that could be used as biomarkers for SS.
Methods
Using the software called XCMS online, the salivary metabolic profiles obtained with liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry for 18 female SS patients were compared to those obtained for 22 age-matched female healthy controls.
Results and conclusion
A total of 91 metabolites showed differential expression in SS patients. A putative identification was proposed with the use of a database for 37 of these metabolites and, of these, 16 identifications were confirmed. Given the identified metabolites, some important metabolic pathways, such as amino acid metabolism, purine metabolism, or even the citric acid cycle seem to be affected. Through the analyses of the ROC (receiver operating characteristic) curves, three metabolites, namely alanine, isovaleric acid, and succinic acid, showed both good sensitivity (respectively 1.000, 1.000, and 0.750) and specificity (respectively 0.692, 0.615, and 0.692) for identifying SS and could then be interesting biomarkers for a potential salivary diagnosis test.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials are stored in the Laboratory of Bioanalytical Sciences and Miniaturization (LSABM), UMR CBI 8231, ESPCI Paris, CNRS, PSL University, Paris, France. The data are not publicly available due to ethical concerns.
References
Aqrawi, L. A., Galtung, H. K., Vestad, B., Øvstebø, R., Thiede, B., Rusthen, S., et al. (2017). Identification of potential saliva and tear biomarkers in primary Sjögren’s syndrome, utilising the extraction of extracellular vesicles and proteomics analysis. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 19(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1228-x.
Asai, Y., Itoi, T., Sugimoto, M., Sofuni, A., Tsuchiya, T., Tanaka, R., et al. (2018). Elevated polyamines in saliva of pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 10(2), E43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043.
Baldini, C., Ferro, F., & Bombardieri, S. (2017). Classification criteria in Sjögren’s syndrome. Annals of Translational Medicine, 5(15), 313. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2017.05.07.
Bonne, N. J., & Wong, D. T. (2012). Salivary biomarker development using genomic, proteomic and metabolomic approaches. Genome Medicine, 4(10), 82. https://doi.org/10.1186/gm383.
Bosman, P., Pichon, V., Acevedo, A. C., Chardin, H., & Combes, A. (2022a). Development of analytical methods to study the salivary metabolome: Impact of the sampling. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04255-5.
Bosman, P., Pichon, V., Acevedo, A. C., Le Pottier, L., Pers, J. O., Chardin, H., & Combès, A. (2022b). Untargeted Metabolomic Approach to study the impact of aging on salivary metabolome in women. Metabolites, 12(10), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100986.
Cuevas-Córdoba, B., & Santiago-García, J. (2014). Saliva: A fluid of study for OMICS. Omics: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 18(2), 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2013.0064.
Florkowski, C. M. (2008). Sensitivity, specificity, receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) Curves and Likelihood Ratios: Communicating the performance of diagnostic tests. The Clinical Biochemist Reviews, 29(Suppl 1), S83–S87.
Fox, P. C. (2007). Autoimmune Diseases and Sjögren’s syndrome. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1098(1), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1384.003.
Garreto, L., Charneau, S., Mandacaru, S. C., Nóbrega, O. T., Motta, F. N., de Araújo, C. N., et al. (2021). Mapping salivary proteases in Sjögren’s syndrome patients reveals overexpression of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4/CD26. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 686480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.686480.
Goksuluk, D., Korkmaz, S., Zararsiz, G., & Karaagaoglu, A. E. (2016). easyROC: An interactive web-tool for ROC curve analysis using R Language Environment. The R Journal, 8(2), 213–230.
Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V., Martínez-Martínez, E., & del Bosque-Plata, L. (2022). The potential of Metabolomics in Biomedical Applications. Metabolites, 12(2), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020194.
Grimaldi, M., Palisi, A., Rossi, G., Stillitano, I., Faiella, F., Montoro, P., et al. (2018). Saliva of patients affected by salivary gland tumour: An NMR metabolomics analysis. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis, 160, 436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.08.015.
Hyvärinen, E., Savolainen, M., Mikkonen, J. J. W., & Kullaa, A. M. (2021). Salivary metabolomics for diagnosis and monitoring Diseases: Challenges and possibilities. Metabolites, 11(9), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090587.
Ishikawa, S., Sugimoto, M., Kitabatake, K., Sugano, A., Nakamura, M., Kaneko, M., et al. (2016). Identification of salivary metabolomic biomarkers for oral cancer screening. Scientific Reports, 6, 31520. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31520.
Jinno, H., Murata, T., Sunamura, M., & Sugimoto, M. (2015). Investigation of potential salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 33(28_suppl), 145–145. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2015.33.28_suppl.145.
Jung, J. Y., Kim, J. W., Kim, H. A., & Suh, C. H. (2021). Salivary biomarkers in patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome—A systematic review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312903.
Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K. E., Carreras-Presas, M., Aro, C., Tu, K., Garcia-Godoy, M., F., & Wong, D. T. (2017). Saliva diagnostics – current views and directions. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 242(5), 459–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370216681550.
Kageyama, G., Saegusa, J., Irino, Y., Tanaka, S., Tsuda, K., Takahashi, S., et al. (2015). Metabolomics analysis of saliva from patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Salivary metabolomics among Sjögren’s syndrome. Clinical & Experimental Immunology, 182(2), 149–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12683.
Kuboniwa, M., Sakanaka, A., Hashino, E., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Amano, A. (2016). Prediction of Periodontal inflammation via metabolic profiling of Saliva. Journal of Dental Research, 95(12), 1381–1386. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034516661142.
Laine, M., Porola, P., Udby, L., Kjeldsen, L., Cowland, J. B., Borregaard, N., et al. (2007). Low salivary dehydroepiandrosterone and androgen-regulated cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 levels in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 56(8), 2575–2584. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22828.
Lau, H. C., Lee, I. K., Ko, P. W., Lee, H. W., Huh, J. S., Cho, W. J., & Lim, J. O. (2015). Non-invasive screening for Alzheimer’s disease by sensing salivary sugar using Drosophila cells expressing gustatory receptor (Gr5a) immobilized on an extended gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (EG-ISFET) biosensor. PloS One, 10(2), e0117810. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117810.
Liang, Q., Liu, H., Zhang, T., Jiang, Y., Xing, H., & Zhang, A. (2015). Metabolomics-based screening of salivary biomarkers for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. RSC Advances, 5(116), 96074–96079. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA19094K.
Mikkonen, J. J., Herrala, M., Soininen, P., Lappalainen, R., Tjäderhane, L., Seitsalo, H., et al. (2013). Metabolic profiling of saliva in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Metabolomics, 3(3), 7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2153-0769.1000128.
Montenegro-Burke, J. R., Guijas, C., & Siuzdak, G. (2020). METLIN: A Tandem Mass Spectral Library of Standards. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton N J), 2104, 149–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_9.
Nijakowski, K., Gruszczyński, D., Kopała, D., & Surdacka, A. (2022). Salivary metabolomics for oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis: A systematic review. Metabolites, 12(4), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040294.
Nijakowski, K., Zdrojewski, J., Nowak, M., Gruszczyński, D., Knoll, F., & Surdacka, A. (2023). Salivary metabolomics for systemic Cancer diagnosis: A systematic review. Metabolites, 13(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010028.
Ohshima, M., Sugahara, K., Kasahara, K., & Katakura, A. (2017). Metabolomic analysis of the saliva of japanese patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology Reports, 37(5), 2727–2734. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5561.
Peri, Y., Agmon-Levin, N., Theodor, E., & Shoenfeld, Y. (2012). Sjögren’s syndrome, the old and the new. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology, 26(1), 105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2012.01.012.
Proctor, G. B., & Carpenter, G. H. (2014). Salivary secretion: mechanism and neural regulation. Monographs in oral science, 24. https://doi.org/10.1159/000358781.
Roblegg, E., Coughran, A., & Sirjani, D. (2019). Saliva: An all-rounder of our body. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 142, 133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.06.016.
Romano, F., Meoni, G., Manavella, V., Baima, G., Tenori, L., Cacciatore, S., & Aimetti, M. (2018). Analysis of salivary phenotypes of generalized aggressive and chronic periodontitis through nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics. Journal of Periodontology, 89(12), 1452–1460. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.18-0097.
Sakanaka, A., Kuboniwa, M., Hashino, E., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Amano, A. (2017). Distinct signatures of dental plaque metabolic byproducts dictated by periodontal inflammatory status. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 42818. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42818.
Setti, G., Righi, V., Mucci, A., Panari, L., Bernardelli, G., Tarentini, E., et al. (2023). Metabolic Profile of whole unstimulated saliva in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Metabolites, 13(3), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030348.
Slomiany, B. L., Kosmala, M., Nadziejko, C., Murty, V. L. N., Gwozdzinski, K., Slomiany, A., & Mandel, I. D. (1986). Lipid composition and viscosity of parotid saliva in Sjögren syndrome in man. Archives of Oral Biology, 31(10), 699–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9969(86)90100-7.
Sridharan, G., Ramani, P., Patankar, S., & Vijayaraghavan, R. (2019). Evaluation of salivary metabolomics in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine: Official Publication of the International Association of Oral Pathologists and the American Academy of Oral Pathology, 48(4), 299–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12835.
Stefanski, A. L., Tomiak, C., Pleyer, U., Dietrich, T., Burmester, G. R., & Dörner, T. (2017). The diagnosis and treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome. Deutsches Arzteblatt International, 114(20), 354–361. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0354.
Sugimoto, M., Wong, D. T., Hirayama, A., Soga, T., & Tomita, M. (2009). Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics: Official Journal of the Metabolomic Society, 6(1), 78–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0178-y.
Takayama, T., Tsutsui, H., Shimizu, I., Toyama, T., Yoshimoto, N., Endo, Y., et al. (2016). Diagnostic approach to breast cancer patients based on target metabolomics in saliva by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 452, 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.10.032.
Tautenhahn, R., Patti, G. J., Rinehart, D., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). XCMS Online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Analytical Chemistry, 84(11), 5035–5039. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300698c.
Vitali, C., Bombardieri, S., Jonsson, R., Moutsopoulos, H. M., Alexander, E. L., Carsons, S. E., et al. (2002). Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: A revised version of the european criteria proposed by the american-european Consensus Group. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 61(6), 554–558. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.61.6.554.
Wang, Q., Gao, P., Cheng, F., Wang, X., & Duan, Y. (2014). Measurement of salivary metabolite biomarkers for early monitoring of oral cancer with ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta, 119, 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.008.
Wei, J., Xie, G., Zhou, Z., Shi, P., Qiu, Y., Zheng, X., et al. (2011). Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia. International Journal of Cancer, 129(9), 2207–2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25881.
Zhong, L., Cheng, F., Lu, X., Duan, Y., & Wang, X. (2016). Untargeted saliva metabonomics study of breast cancer based on ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with HILIC and RPLC separations. Talanta, 158, 351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.049.
Funding
This work was supported by the “Plateforme d’expertise pour le suivi de toxines à l’état de traces en milieu réel” project from DIM analytics from the Ile de France region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: P.B., A.C.A., H.C. and A.C; methodology: H.C. and A.C; formal analysis: P.B., H.C. and A.C.; investigation: P.B., A.C.A., H.C. and A.C.; resources: P.B., J.O.P., L.L.P., F.M.B.M., L.M.P. and A.C.A; writing—original draft preparation: P.B. and A.C.; writing—review and editing: P.B., A.C.A., H.C., J.O.P., L.L.P., F.M.B.M., L.M.P. V.P. and A.C; supervision: A.C.A., H.C. and A.C.; funding acquisition: V.P., H.C. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee (Hospital Center Regional University Morvan De Brest, CHRU Brest, CCPP Ouest VI, BB-0033-00037) in 2015. The Brest Biological Resources Center (CRB Santé du CHRU de Brest) provided the saliva samples for this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bosman, P., Pichon, V., Acevedo, A.C. et al. Identification of potential salivary biomarkers for Sjögren’s syndrome with an untargeted metabolomic approach. Metabolomics 19, 76 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02040-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02040-8