Abstract
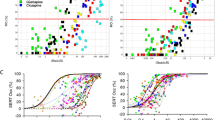
The A3 adenosine receptor (AR) is emerging as an attractive drug target. Antagonists are proposed for the potential treatment of glaucoma and asthma. However, currently available A3AR antagonists are potent in human and some large animals, but weak or inactive in mouse and rat. In this study, we re-synthesized a previously reported A3AR antagonist, DPTN, and evaluated its affinity and selectivity at human, mouse, and rat ARs. We showed that DPTN, indeed, is a potent A3AR antagonist for all three species tested, albeit a little less selective for mouse and rat A3AR in comparison to the human A3AR. DPTN’s Ki values at respective A1, A2A, A2B, and A3 receptors were (nM) 162, 121, 230, and 1.65 (human); 411, 830, 189, and 9.61 (mouse); and 333, 1147, 163, and 8.53 (rat). Its antagonist activity at both human and mouse A3ARs was confirmed in a cyclic AMP functional assay. Considering controversial use of currently commercially available A3AR antagonists in rats and mice, we also re-examined other commonly used and selective A3AR antagonists under the same experimental conditions. The Ki values of MRS1523 were shown to be 43.9, 349, and 216 nM at human, mouse, and rat A3ARs, respectively. MRS1191 and MRS1334 showed incomplete inhibition of [125I]I-AB-MECA binding to mouse and rat A3ARs, while potent human A3AR antagonists, MRS1220, MRE3008F20, PSB10, PSB-11, and VUF5574 were largely inactive. Thus, we demonstrated that DPTN and MRS1523 are among the only validated A3AR antagonists that can be possibly used (at an appropriate concentration) in mouse or rat to confirm an A3AR-related mechanism or function.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original data from this study will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Cvicek V, Goddard WA III, Abrol R (2016) Structure-based sequence alignment of the transmembrane domains of all human GPCRs: phylogenetic, structural and functional implications. PLoS Comput Biol 12(3):e1004805. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004805
Zhou QY, Li C, Olah ME, Johnson RA, Stiles GL, Civelli O (1992) Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(16):7432–7326
Salvatore CA, Jacobson MA, Taylor HE, Linden J, Johnson RG (1993) Molecular cloning and characterization of the human A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(21):10365–10369
Salvatore CA, Tilley SL, Latour AM, Fletcher DS, Koller BH, Jacobson MA (2000) Disruption of the A3 adenosine receptor gene in mice and its effect on stimulated inflammatory cells. J Biol Chem 275(6):4429–4434
Garcia-Garcia L, Olle L, Martin M, Roca-Ferrer J, Muñoz-Cano R (2021) Adenosine signaling in mast cells and allergic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 22(10):5203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105203
Ramkumar V, Stiles GL, Beaven MA, Ali H (1993) The A3 adenosine receptor is the unique adenosine receptor which facilitates release of allergic mediators in mast cells. J Biol Chem 268(23):16887–16990
Zhong Y, Yang Z, Huang WC (1830) Luo X (2013) Adenosine, adenosine receptors and glaucoma: an updated overview. Biochim Biophys Acta 4:2882–2890
Gao ZG, Jacobson KA (2017) Purinergic signaling in mast cell degranulation and asthma. Front Pharmacol 8:947. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00947
Jacobson KA, Civan MM (2016) Ocular purine receptors as drug targets in the eye. J Ocular Pharmacol Therap 32:534–547
van Galen PJ, van Bergen AH, Gallo-Rodriguez C, Melman N, Olah ME, IJzerman AP, Stiles GL, Jacobson KA (1994) A binding site model and structure-activity relationships for the rat A3 adenosine receptor. Mol Pharmacol 45(6):1101–1111
Gao ZG, Blaustein JB, Gross AS, Melman N, Jacobson KA (2003) N6-Substituted adenosine derivatives: selectivity, efficacy, and species differences at A3 adenosine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 65(10):1675–1684
Alnouri MW, Jepards S, Casari A, Schiedel AC, Hinz S, Muller CE (2015) Selectivity is species-dependent: characterization of standard agonists and antagonists at human, rat, and mouse adenosine receptors. Purinergic Signal 11(3):389–407
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Linden J, Müller CE (2011) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors–an update. Pharmacol Rev 63:1–34
Yamano K, Inoue M, Masaki S, Saki M, Ichimura M, Satoh M (2006) Generation of adenosine A3 receptor functionally humanized mice for the evaluation of the human antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 71(3):294–306
Yamano K, Inoue M, Masaki S, Saki M, Ichimura M, Satoh M (2005) Human adenosine A3 receptor activation leads to intracellular Ca2+ mobilization but is insufficient to activate the signaling pathway via phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 70(10):1487–1496
Jacobson KA, Park KS, Jiang JL, Kim YC, Olah ME, Stiles GL, Ji XD (1997) Pharmacological characterization of novel A3 adenosine receptor-selective antagonists. Neuropharmacology 36:1157–1165
Kreckler LM, Wan TC, Ge ZD, Auchampach JA (2006) Adenosine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from mouse peritoneal macrophages via A2A and A2B but not the A3 adenosine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317(1):172–180
Kim YC, Ji XD, Jacobson KA (1996) Derivatives of the triazoloquinazoline adenosine antagonist (CGS15943) are selective for the human A3 receptor subtype. J Med Chem 39(21):4142–4148
Yoon MH, Bae HB, Choi JI, Kim SJ, Chung ST, Kim CM (2006) Roles of adenosine receptor subtypes in the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal adenosine in a rat formalin test. Pharmacology 78(1):21–26
Bar-Yehuda S, Rath-Wolfson L, Del Valle L, Ochaion A, Cohen S, Patoka R, Zozulya G, Barer F, Atar E, Pina-Oviedo S, Perez-Liz G, Castel D, Fishman P (2009) Induction of an anti-inflammatory effect and prevention of cartilage damage in rat knee osteoarthritis by CF101 treatment. Arthritis Rheum 60(10):3061–3071
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Madi L, Rath-Wolfson L, Ochaion A, Cohen S (2006) Baharav E (2006) The PI3K-NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway is involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effect of IB-MECA in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(1):R33
Yoshikawa N, Yamada S, Takeuchi C, Kagota S, Shinozuka K, Kunitomo M, Nakamura K (2008) Cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine) inhibits the growth of B16-BL6 mouse melanoma cells through the stimulation of adenosine A3 receptor followed by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activation and cyclin D1 suppression. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 377(4–6):591–595
Li AH, Moro S, Melman N, Ji XD, Jacobson KA (1998) Structure-activity relationships and molecular modeling of 3, 5-diacyl-2,4-dialkylpyridine derivatives as selective A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 41(17):3186–3201
Gao Z, Li BS, Day YJ, Linden J (2001) A3 adenosine receptor activation triggers phosphorylation of protein kinase B and protects rat basophilic leukemia 2H3 mast cells from apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol 59(1):76–82
Miwatashi S, Arikawa Y, Matsumoto T, Uga K, Kanzaki N, Imai YN, Ohkawa S (2008) Synthesis and biological activities of 4-phenyl-5-pyridyl-1,3-thiazole derivatives as selective adenosine A3 antagonists. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 56(8):1126–1137. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.56.1126
Asano T, Noda Y, Tanaka KI, Yamakawa N, Wada M, Mashimo T, Fukunishi Y, Mizushima T, Takenaga M (2020) A2B adenosine receptor inhibition by the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker nifedipine involves colonic fluid secretion. Sci Rep 10:3555
Cheng Y-C, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Carlin JL, Jain S, Gizewski E, Wan TC, Tosh DK, Xiao C, Auchampach JA, Jacobson KA, Gavrilova O, Reitman ML (2017) Hypothermia in mouse is caused by adenosine A1 and A3 receptor agonists and AMP via three distinct mechanisms. Neuropharmacol 114:101–113
Jiang JL, van Rhee AM, Melman N, Ji XD, Jacobson KA (1996) 6-Phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives as potent and selective A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 39(23):4667–4675
Baraldi PG, Cacciari B, Romagnoli R, Spalluto G, Klotz KN, Leung E, Varani K, Gessi S, Merighi S, Borea PA (1999) Pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine derivatives as highly potent and selective human A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 42:4473–4478
Ozola V, Thorand M, Diekmann M, Qurishi R, Schumacher B, Jacobson KA, Müller CE (2003) 2-Phenylimidazo[2,1–i]purin-5-ones: structure-activity relationships and characterization of potent and selective inverse agonists at human A3 adenosine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem 11(3):347–356
van Muijlwijk-Koezen JE, Timmerman H, van der Goot H, Menge WM, Von Drabbe F, Künzel J, de Groote M, IJzerman AP, (2000) Isoquinoline and quinazoline urea analogues as antagonists for the human adenosine A3 receptor. J Med Chem 43(11):2227–2238
Besnard J, Ruda GF, Setola V, Abecassis K, Rodriguiz RM, Huang XP, Norval S, Sassano MF, Shin AI, Webster LA, Simeons FRC, Stojanovski L, Prat A, Seidah NG, Constam DB, Bickerton GR, Read KD, Wetsel WC, Gilbert IH, Roth BL, Hopkins AL (2012) Automated design of ligands to polypharmacological profiles. Nature 492:215–220
Tosh DK, Salmaso V, Rao H, Bitant A, Fisher CL, Lieberman DI, Vorbrüggen H, Reitman ML, Gavrilova O, Gao ZG, Auchampach JA, Jacobson KA (2020) Truncated (N)-methanocarba nucleosides as partial agonists at mouse and human A3 adenosine receptors: Affinity enhancement by N6-(2-phenylethyl) substitution. J Med Chem 63(8):4334–4348
Francis JE, Cash WD, Psychoyos S, Ghai G, Wenk P, Friedmann RC, Atkins C, Warren V, Furness P, Hyun JL, Stone GA, Desai M, Williams C (1988) Structure-activity profile of a series of novel triazoloquinazoline adenosine antagonists. J Med Chem 31(5):1014–1020
Di Angelantonio S, Bertollini C, Piccinin S, Rosito M, Trettel F, Pagani F, Limatola C, Ragozzino D (2015) Basal adenosine modulates the functional properties of AMPA receptors in mouse hippocampal neurons through the activation of A1R A2AR and A3R. Front Cell Neurosci 9:409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00409
Gao ZG, Kim SK, Biadatti T, Chen W, Lee K, Barak D, Kim SG, Johnson CR, Jacobson KA (2002) Structural determinants of A3 adenosine receptor activation: nucleoside ligands at the agonist/antagonist boundary. J Med Chem 45(20):4471–4484
Jeong LS, Pal S, Choe SA, Choi WJ, Jacobson KA, Gao ZG, Klutz AM, Hou X, Kim HO, Lee HW, Lee SK, Tosh DK, Moon HR (2008) Structure-activity relationships of truncated D- and l-4’-thioadenosine derivatives as species-independent A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 51(20):6609–6613
Gao ZG, Jacobson KA (2008) Translocation of arrestin induced by human A3 adenosine receptor ligands in an engineered cell line: comparison with G protein-dependent pathways. Pharmacol Res 57(4):303–311
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from Astrocyte Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. We thank Ryan Campbell and Harsha Rao (NIDDK, NIH) for technical assistance. We thank Dr. Bryan L. Roth (Univ. North Carolina at Chapel Hill) and National Institute of Mental Health’s Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (Contract # HHSN-271-2008-00025-C) for screening data.
Funding
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Intramural Research Program (grant no. ZIADK031117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable; no animal studies are included.
Informed consent
Not applicable; no patient studies are included.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, ZG., Suresh, R.R. & Jacobson, K.A. Pharmacological characterization of DPTN and other selective A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. Purinergic Signalling 17, 737–746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09823-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09823-5