Abstract
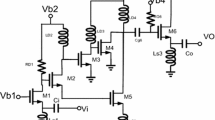
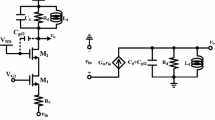
In this paper, we present a 0.9 V, 4.57 mW UWB LNA with improved gain and low power consumption for 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wide band applications. In its input stage, a common gate amplifier is used to achieve approximately \(50\,\Omega\) input resistance across the entire band, instead of using a common source stage. However, the current reused technique is used to save power consumption by using the same DC current path for both transistors in the designed circuit instead of utilizing two stage cascade configuration. The output matching is achieved by tuning the total parasitic capacitance with the inductor \(\hbox {L}_{d1}\) at the output node. In its inter stage, inter stage matching technique is used to make the flat gain response and to extend the bandwidth, simultaneously. From simulation results, the designed LNA shows an average power gain \(\hbox {S}_{21}\) of 15.8 dB with the gain variation of \(\pm 0.97 \hbox { dB}\), an input return loss \(\hbox {S}_{11}\) of −30 to −10 dB, a high reverse isolation \(\hbox {S}_{12}\) of −59 to −43 dB, output return loss \(\hbox {S}_{22}\) of −16 to −10 dB, and a small group-delay variation of \(\pm 34\) ps across the entire band. It also shows minimum achievable noise figure below 3.2 dB, and a power consumption of 4.57 mW from a supply voltage of 0.9 V. When a two tone test is performed at 8 GHz with 10 MHz spacing, the linearity of the designed LNA such as 1-dB compression point and third order input intercept point are −22.5 and −9 dBm, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rastegar, H., Saryazdi, S., & Hakimi, A. (2012). Wideband and multiband CMOS LNAs: State-of-the-art and future prospects. Microelectronics Journal, 44(9), 774–786.
Rastegar, H., Saryazdi, S., & Hakimi, A. (2013). A low power and high linearity UWB low noise amplifier (LNA) for 3.1–10.6 GHz wireless applications in \(0.13\,\upmu\)m CMOS process. Microelectronics Journal, 44(3), 201–209.
Nakhlestani, A., Hakimi, A., & Movahhedi, M. (2012). A novel configuration for UWB LNA suitable for low-power and low-voltage applications. Microelectronics Journal, 43(7), 444–451.
Shim, J., Yang, T., & Jeong, J. (2013). Design of low power CMOS ultra wide band low noise amplifier using noise canceling technique. Microelectronics Journal, 44(9), 821–826.
Slimane, A., Trabelsi, M., & Belaroussi, M. T. (2011). A 0.9 V, 7 mW UWB LNA for 3.1–10.6 GHz wireless applications in \(0.18\,\mu \text{ m }\) CMOS technology. Microelectronics Journal, 42(11), 1263–1268.
Pandey, S., & Singh, J. (2015). A 0.6 V, low-power and high-gain ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier with forward-body-bias technique for low-voltage operations. IET Microwaves Antennas & Propagation, 9(8), 728–734.
Hsieh, J.-Y., Wang, T., & Lu, S.-S. (2009). Wideband low-noise amplifier by LC load-reusing technique. Electronics Letters, 45(25), 1280–1281.
Chang, C.-H., Wang, T., & Jou, C. F. (2012). Dual cross-coupling LNA with forward body bias technique. Electronics Letters, 48(18), 280–281.
Wang, Y.-H., Lin, K.-T., Wang, T., Chiu, H.-W., Chen, H.-C., & Lu, S.-S. (2010). A 2.1–6 GHz tunnable-band LNA with adaptive frequency responses by transisitor size scaling. IEEE Mirocwave and Wireless Components Letters, 20(6), 346–348.
Wang, T., Chen, H.-C., Chiu, H.-W., Lin, Y.-S., Huang, G.-W., & Shey-Shi, L. (2006). Micromachined CMOS LNA and VCO by CMOS-compatible ICP deep trench technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(2), 580–588.
Meng-Ting, H., Yi-Cheng, C., & Yu-Zhang, H. (2013). Design of low power UWB LNA based on common source topology with current-reused technique. Microelectronics Journal, 44(12), 1223–1230.
Sapone, G., & Palmisano, G. (2011). A 3–10 GHz low-power CMOS low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband communication. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(3), 678–686.
Hsieh, H. -H., Wu, P.-Y., Jou, C.-P., Hsueh, F.-L., & Huang, G.-W. (2011). 60 GHz high gain low noise amplifiers with a common-gate inductive feedback in 65 nm CMOS. In RFIC symposium (pp. 1–4).
Lu, Y., Yeo, K. S., Cabuk, A., Ma, J., Do, M. A., & Lu, Z. (2006). A novel CMOS low noise amplifier design for 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wideband wireless receiver. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 53(8), 1683–1692.
Weng, R.-M., Liu, C.-Y., & Lin, P.-C. (2010). A low-power full-band low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(8), 2077–2083.
Wan, Q., Wang, Q., & Zheng, Z. (2015). Design and analysis of a 3.1–10.6 GHz UWB low noise amplifier with forward body bias technique. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 69(1), 119–125.
Shim, Y., Kim, C.-W., Lee, J., & Lee, S.-G. (2007). Design of full band UWB common-gate LNA. The IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 17(10), 721–723.
Chen, C. C., & Wang, Y. C. (2013). 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wideband LNA design using dual-resonant broadband matching technique. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 67(6), 500–503.
Sarkar, A., Das, A. K., De, S., & Sarkar, C. K. (2012). Effect of gate engineering in double-gate MOSFETs for analog/RF applications. Microelectronic Journal, 43(11), 873–882.
Wan, Q., Wang, Q., & Zheng, Z. (2010). Low-power current-reused RF front-end based on optimized transformers topology. Elsevier Integration, the VLSI Journal, 43, 230–236.
Brederlow, R., et al. (2001). A mixed-signal design roadmap. IEEE Design & Test of Computers, 18(6), 34–36.
Yang, H. Y., Lin, Y. S., & Chen, C. C. (2008). 2.5 dB NF 3.1–10.6 GHz CMOS UWB LNA with small group-delay variation. Electronics Letters, 44(8), 528–529.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Gawande, T. & Kondekar, P.N. A 0.9 V, 4.57 mW UWB LNA with Improved Gain and Low Power Consumption for 3.1–10.6 GHz Ultra-Wide Band Applications. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 583–597 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4185-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4185-4