Abstract
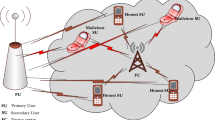
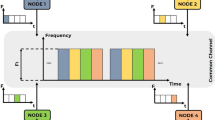
Cognitive radio (CR) is a novel and promising spectrum management technique, which aims to cope with the spectrum scarcity problem occurring in unlicensed bands and alleviate the inefficient spectrum utilization of licensed bands. To ensure that the operation of licensed users will not be adversely affected and that the licensed bands can be efficiently utilized by unlicensed users, this paper proposes a cognitive radio MAC protocol called SMC-CR-MAC. When any primary user is detected, the proposed SMC-CR-MAC protocol applies Contiguous Channel Switching and Sender-Receiver Channel Swap rules to cope with the rendezvous, packet collision, and channel congestion problems. Simulation results show that the proposed SMC-CR-MAC protocol can significantly improve the network performance in terms of utilization of licensed bands, standard deviation of traffic load on each channel, and probability of successful rendezvous.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
“Federal Communications Commission Spectrum Policy Task Force,” the Spectrum Efficiency Working Group, FCC, Nov. 2002.
Domenico, A. D., Strinati, E. C., & Benedetto, M. D. (2012). A survey on MAC strategies for cognitive. IEEE Communication Survey & Tutorials, 14(1), 21–44. First Quarter.
Liang, Y.-C., Chen, K.-C., Li, G. Y., & Mähönen, P. (2011). Cognitive radio networking and communications: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(7), 3386–3407.
Thomas, R. W., Friend, D. H., Dasilva, L. A., & Mackenzie, A. B. (2006). Cognitive networks: Adaptation and learning to achieve end-to-end performance objectives. IEEE Communications Magazine, 44(12), 51–57.
IEEE 802.22 Working Group in Wireless Regional Area Networks, http://www.ieee802.org/22/.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W.-Y., & Chowdhury, K. R. (2009). CRAHNs: Cognitive radio ad hoc networks. ACM Journal of Ad Hoc Networks, 7(5), 810–836.
Tan, L. T., & Le, L. B. (2011). Distributed MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks: Design, analysis, and optimization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(8), 3990–4003.
Jeon, W. S., Han, J. A., & Jeong, D. G. (2012). A novel MAC scheme for multichannel cognitive radio ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 11(6), 922–937.
Tan, L. T., & Le, L. B. (2012). Channel assignment with access contention resolution for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(6), 2808–2823.
Jia, J., Zhang, Q., & Shen, X. (2008). HC-MAC: A hardware-constrained cognitive MAC for efficient spectrum management. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication, 26(1), 106–117.
Su, H., & Zhang, X. (2007). Opportunistic MAC protocols for cognitive radio based wireless networks. IEEE CISS, USA.
Jeon, W. S., Han, J. A., & Jeong, D. G. (2012). A novel MAC scheme for multi-channel cognitive radio Ad Hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 11(6), 922–934.
Lau, L. C., Lin, C. C., & Wang, S. Y. (2012). An IEEE 802.11 cognitive radio MAC protocol with dynamic bandwidth allocation capabilities. IEEE WCNC.
Ma, L., Han, X., & Shen, C.-C. (2005). Dynamic open spectrum sharing MAC protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE DySPAN, pp. 203–213.
Kamruzzaman, S. M. (2010). CR-MAC: A multichannel MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. IEEE International Journal of Computer Networks and Communications, 2(5), 1–14.
Kamruzzaman, S. M. (2010). An energy efficient multichannel MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security, 2(2), 112–119.
Hung, L. L., Chang, C. Y., Wang, T. L., & Hsiao, C. Y. (2012) Cooperative MAC protocol for multi-channel wireless networks. IEEE HPCC.
So, H.-S. W., Nguyen, G., & Walrand, J. (2006). Practical synchronization techniques for multi-channel MAC. MobiCom '06 proceedings of the 12th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking (pp. 134–145). New York: ACM.
VINT Group, “UCB/LBNL/VINT Network Simulator ns (version 2),” available: http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns.
MW-Node path for ns2 to support multiple interfaces & multiple channels, available: http://www.q2s.ntnu.no/~paquerea/ns.php.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, CY., Wang, TL. & Lin, CY. A MAC protocol by applying staggered channel model for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Netw 20, 1873–1888 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0713-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0713-2