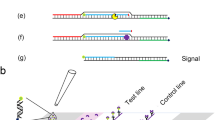
Abstract
Vibrio alginolyticus (V. alginolyticus) is a common pathogen in the ocean. In addition to causing serious economic losses in aquaculture, it can also infect humans. The rapid detection of nucleic acids of V. alginolyticus with high sensitivity and specificity in the field is very important for the diagnosis and treatment of infection caused by V. alginolyticus. Here, we established a simple, fast and effective molecular method for the identification of V. alginolyticus that does not rely on expensive instruments and professionals. The method integrates recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) technology with CRISPR system in a single PCR tube. Using this method, the results can be visualized by lateral flow dipstick (LFD) in less than 50 min, we named this method RPA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD. The method was confirmed to achieve high specificity for the detection of V. alginolyticus with no cross-reactivity with similar Vibrio and common clinical pathogens. This diagnostic method shows high sensitivity; the detection limit of the RPA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD is 10 copies/µL. We successfully identified 35 V. alginolyticus strains from a total of 55 different bacterial isolates and confirmed their identity by (Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, MALDI-TOF MS). We also applied this method on infected mice blood, and the results were both easily and rapidly obtained. In conclusion, RPA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD offers great potential as a useful tool for reliable and rapid diagnosis of V. alginolyticus infection, especially in limited conditions.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abudayyeh OO, Gootenberg JS, Konermann S et al (2016) C2c2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector. Science (1979) 353:aaf5573. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf5573
Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD, Alam M et al (2018) Vibrio spp. infections. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0005-8
Baron EJ, Miller JM, Weinstein MP et al (2013) A guide to utilization of the microbiology laboratory for diagnosis of infectious diseases: 2013 recommendations by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society for Microbiology (ASM)(a). Clin Infect Dis 57:e22–e121. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit278
Bonney LC, Watson RJ, Slack GS et al (2020) A flexible format LAMP assay for rapid detection of Ebola virus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14:e0008496. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008496
Brehm TT, Berneking L, Sena Martins M et al (2021) Heatwave-associated Vibrio infections in Germany, 2018 and 2019. Euro Surveill 26:2002041. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.41.2002041
Chen Z, Mao S, Zhang W et al (2021) Rapid visual detection method for barley yellow mosaic virus using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Plant Dis 105:2658–2663. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-20-1216-RE
Fu K, Li J, Wang Y et al (2016) An innovative method for rapid identification and detection of Vibrio alginolyticus in different infection models. Front Microbiol 7:651. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00651
Gong Q, Yang D, Jiang M et al (2020a) l-Aspartic acid promotes fish survival against Vibrio alginolyticus infection through nitric oxide-induced phagocytosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.12.061
Gong QY, Yang MJ, Yang LF et al (2020b) Metabolic modulation of redox state confounds fish survival against Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Microb Biotechnol 13:796–812. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13553
Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Lee JW et al (2017) Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2. Science (1979) 356:438–442. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam9321
Hu F, Liu Y, Zhao S et al (2022) A one-pot CRISPR/Cas13a-based contamination-free biosensor for low-cost and rapid nucleic acid diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 202:113994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113994
Jacobs Slifka KM, Newton AE, Mahon BE (2017) Vibrio alginolyticus infections in the USA, 1988–2012. Epidemiol Infect 145:1491–1499. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268817000140
Kersting S, Rausch V, Bier FF, Von Nickisch-Rosenegk M (2014) Rapid detection of Plasmodium falciparum with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow analysis. Malar J 13:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-13-99
Li J, Macdonald J, Von Stetten F (2019) Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 144:31–67
Li M, Gao Q, Yu T (2023) Kappa statistic considerations in evaluating inter-rater reliability between two raters: which, when and context matters. BMC Cancer 23(1):799
Liu XF, Zhang H, Liu X et al (2014) Pathogenic analysis of Vibrio alginolyticus infection in a mouse model. Folia Microbiol (praha) 59(2):167–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0279-x
Liu Y, Pei T, Yi S et al (2021) Phylogenomic analysis substantiates the gyrB gene as a powerful molecular marker to efficiently differentiate the most closely related genera Myxococcus, Corallococcus, and Pyxidicoccus. Front Microbiol 12:763359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.763359
Rosser A, Rollinson D, Forrest M, Webster BL (2015) Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection. Parasit Vectors 8:446. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1055-3
Safiabadi Tali SH, LeBlanc JJ, Sadiq Z et al (2021) Tools and techniques for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 detection. Clin Microbiol Rev 34(3):e00228-e320. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00228-20
Sheahan M, Gould CA, Neumann JE et al (2022) Examining the relationship between climate change and vibriosis in the United States: projected health and economic impacts for the 21st century. Environ Health Perspect 130:87007. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP9999a
Sun Y, Yu L, Liu C et al (2021) One-tube SARS-CoV-2 detection platform based on RT-RPA and CRISPR/Cas12a. J Transl Med 19:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-02741-5
Tian Z, Yang L, Qi X et al (2022) Visual LAMP method for the detection of Vibrio vulnificus in aquatic products and environmental water. BMC Microbiol 22(1):256. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-022-02656-1
Vuddhakul V, Nakai T, Matsumoto C et al (2000) Analysis of gyrB and toxR gene sequences of Vibrio hollisae and development of gyrB- and toxR-targeted PCR methods for isolation of V. hollisae from the environment and its identification. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(8):3506–3514. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.8.3506-3514.2000
Wang J, Ding Q, Yang Q et al (2021a) Vibrio alginolyticus triggers inflammatory response in mouse peritoneal macrophages via activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:769777. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.769777
Wang R, Qian C, Pang Y et al (2021b) opvCRISPR: one-pot visual RT-LAMP-CRISPR platform for SARS-cov-2 detection. Biosens Bioelectron 172:112766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112766
Wang Y, Li J, Li S et al (2021c) LAMP-CRISPR-Cas12-based diagnostic platform for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex using real-time fluorescence or lateral flow test. Mikrochim Acta 188:347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04985-w
Weis KE, Hammond RM, Hutchinson R, Blackmore CG (2011) Vibrio illness in Florida, 1998–2007. Epidemiol Infect 139:591–598. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268810001354
Wu Z, Wu Y, Gao H et al (2022) Identification and whole-genome sequencing analysis of Vibrio vulnificus strains causing pearl gentian grouper disease in China. BMC Microbiol 22(1):200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-022-02610-1
Yin D, Yin L, Wang J et al (2022a) Visual detection of duck tembusu virus with CRISPR/Cas13: a sensitive and specific point-of-care detection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:848365. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.848365
Yin Y, Yin Y, Yang H et al (2022b) Vibrio alginolyticus survives from ofloxacin stress by metabolic adjustment. Front Microbiol 13:818923. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.818923
Zhang W, Jiao Y, Ding C et al (2021) Rapid detection of tomato spotted wilt virus with Cas13a in tomato and Frankliniella occidentalis. Front Microbiol 12:745173. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.745173
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No.81401311].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experimental protocol designed was performed by YW. Animal experiments was completed by YW, YH and XL. Experimental procedure was optimized by YH and XL. Environmental Vibrio alginolyticus strains identified were by NL and YD. Nucleic acid extracted from environmental Vibrio alginolyticus strains were by FL, WX and YZ. WX, JC, and CC supervised the project. YW wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hou, Y., Liu, X. et al. Rapid visual nucleic acid detection of Vibrio alginolyticus by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with CRISPR/Cas13a. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 51 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03847-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03847-2