Abstract
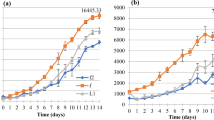
Several Pleurotus species (oyster mushrooms) are commercially cultivated in India owing to the favorable tropical agro-climatic conditions. However, there are only a few studies on the microbiome of mushrooms, especially oyster mushrooms. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of endobacteria on mycelial growth, spawning, sporophore development, and proximate composition of P. pulmonarius. We isolated several bacterial strains from the sporophores of P. pulmonarius and assessed the in vitro production of indole acetic acid, ammonia, and siderophores. The selected bacteria were individually supplemented with spawn, substrate, or both for sporophore production. Three of 130 isolates were selected as mycelial growth-promoting bacteria in both solid and submerged fermentation. These bacterial isolates were identified through Gram staining, biochemical characterization, and 16S rRNA sequencing. Isolate PP showed 99.24% similarity with Priestia paraflexa, whereas isolates PJ1 and PJ2 showed 99.78% and 99.65% similarities, respectively, with Rossellomorea marisflavi. The bacterial supplementation with spawn, substrate, or both, increased the biological efficiency (BE) and nutrient content of the mushrooms. The bacterial supplementation with substrate augmented BE by 64.84%, 13.73%, and 27.13% using PJ2, PP, and PJ1, respectively; under similar conditions of spawn supplementation, BE was increased by 15.24%, 47.30%, 48.10%, respectively. Overall, the supplementation of endobacteria to improve oyster mushroom cultivation may open a new avenue for sustainable agricultural practices in the mushroom industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are preserved with the corresponding author and can be procured on request.
References
Ali S, Charles TC, Glick BR (2017) Endophytic phytohormones and their role in plant growth promotion. In: Doty SL (ed) Functional importance of the plant microbiome: implications for agriculture, forestry and bioenergy. Springer, Chamberlain, pp 89–105
Ancheeva E, Daletos G, Proksch P (2020) Bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytic fungi. Curr Med Chem 27:1836–1854. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867326666190916144709
Antony-Babu S, Deveau A, Van Nostrand JD, Zhou J, Le Tacon F, Robin C, Frey-Klett P, Uroz S (2014) Black truffle-associated bacterial communities during the development and maturation of Tuber melanosporum ascocarps and putative functional roles. Environ Microbiol 16:2831–2847. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12294
Aslani MA, Harighi B, Abdollahzadeh J (2018) Screening of endofungal bacteria isolated from wild growing mushrooms as potential biological control agents against brown blotch and internal stipe necrosis diseases of Agaricus bisporus. Biol Control 119:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2018.01.006
Braat N, Koster MC, Wösten HAB (2022) Beneficial interactions between bacteria and edible mushrooms. Fungal Biol Rev 39:60–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2021.12.001
Carrasco J, Preston GM (2020) Growing edible mushrooms: a conversation between bacteria and fungi. Environ Microbiol 22:858–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14765
Carrasco J, Zied DC, Pardo JE, Preston GM, Pardo-Giménez A (2018) Supplementation in mushroom crops and its impact on yield and quality. AMB Express 8:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0678-0
Chen L, Yan M, Qian X, Yang Z, Xu Y, Wang T, Cao J, Sun S (2022a) Bacterial community composition in the growth process of Pleurotus eryngii and growth-promoting abilities of isolated bacteria. Front Microbiol 13:787628. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.787628
Chen Z, Oh WD, Yap PS (2022b) Recent advances in the utilization of immobilized laccase for the degradation of phenolic compounds in aqueous solutions: a review. Chemosphere 307:135824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135824
Cho YS, Kim JS, Crowley DE, Cho BG (2003) Growth promotion of the edible fungus Pleurotus ostreatus by fluorescent pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Lett 218:271–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(02)01144-8
Cunha D, Savoie J-M, Pardo-Gimenez A (2011) Soybean the main nitrogen source in cultivation substrates of edible and medicinal mushrooms. In: El-Shemy H (ed) Soybean and nutrition. In Tech Open, London, pp 433–452
Das N, Mukherjee M (2007) Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus on weed plants. Bioresour Technol 98:2723–2726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.061
Das N, Sengupta S, Mukherjee M (1997) Importance of laccase in vegetative growth of Pleurotus florida. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4120–4122. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.63.10.4120-4122.1997
Das N, Naskar S, Chowdhury P, Pasman B, Adhikari D (2011) Experimental evidence for presence of a growth regulating extracellular laccase in some Pleurotus species. Res J Microbiol 6:496–502. https://doi.org/10.3923/jm.2011.496.502
Das N, Mishra S, Biswas L, Karmakar NC (2015) Comparative study of five Pleurotus species cultivated in warm temperature on non-sterilized rice straw. Emir J Food Agric 27:749–755. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.2015.04.107
Deveau A, Bonito G, Uehling J, Paoletti M, Becker M, Bindschedler S, Hacquard S, Hervé V, Labbé J, Lastovetsky OA, Mieszkin S, Millet LJ, Vajna B, Junier P, Bonfante P, Krom BP, Olsson S, van Elsas JD, Wick LY (2018) Bacterial-fungal interactions: ecology, mechanisms and challenges. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42:335–352. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuy008
Dubey RC, Maheswari DK (2006) Practical microbiology. S. Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi
Eyini M, Parani K, Pothiraj C, Rajapandy V (2005) Effect of ‘Azotobacter’ bioinoculant on the growth and substrate utilization potential of Pleurotus eous seed spawn. Mycobiology 33:19–22. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2005.33.1.019
Febriansyah E, Saskiawan I, Mangunwardoyo W, Sulistiyani TR, Widhiya EW (2018) Potency of growth promoting bacteria on mycelial growth of edible mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus and its identification based on 16S rDNA analysis. AIP Conf Proc. https://doi.org/10.1063/15050119
Gautam CK, Madhav M, Sinha A, Jabez Osborne W (2016) VIT-CMJ2: endophyte of Agaricus bisporus in production of bioactive compounds. Iran J Biotechnol 14:19–24. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijb.1287
Gregori A, Svagelj M, Pohleven J (2007) Cultivation techniques and medicinal properties of Pleurotus spp. Food Technol Biotechnol 45:236–247
Kertesz MA, Thai M (2018) Compost bacteria and fungi that influence growth and development of Agaricus bisporus and other commercial mushrooms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:1639–1650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8777-z
Kües U, Liu Y (2000) Fruiting body production in basidiomycetes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000396
Kumari S, Naraian R (2021) Enhanced growth and yield of oyster mushroom by growth promoting bacteria Glutamicibacter arilaitensis MRC119. J Basic Microbiol 61:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202000379
Lata SAK (2003) Characterization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. In: Saxena AK (ed) Training manual on biofertilizer technology. IARI, Delhi, pp 24–25
Lee CK, Haque MA, Choi BR, Lee HY, Hwang CE, Ahn MJ, Cho KM (2015) Molecular diversity of endobacterial communities in edible part of king oyster mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) based on 16S rRNA 6. Kor J Microbiol 51:148–155. https://doi.org/10.7845/kjm.2015.4086
Li Q, Li X, Chen C, Li S, Huang W, Xiong C, Jin X, Zheng L (2016) Analysis of bacterial diversity and communities associated with Tricholoma matsutake fruiting bodies by barcoded pyrosequencing in Sichuan Province, southwest China. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:89–98. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1505.05008
Li H, Zhang Z, Li M, Li X, Sun Z (2017) Yield, size, nutritional value, and antioxidant activity of oyster mushrooms grown on perilla stalks. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.10.001
Lim Y, Ryu JS, Shi S, Noh W, Kim E, Le QV, Lee HS, Ro HS (2008) Isolation of bacteria associated with the king oyster mushroom, Pleurotus eryngii. Mycobiology 36:13–18. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2008.36.1.013
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Matsuda R, Handayani ML, Sasaki H, Takechi K, Takano H, Takio S (2018) Production of indoleacetic acid by strains of the epiphytic bacteria Neptunomonas spp. isolated from the red alga Pyropia yezoensis and the seagrass Zostera marina. Arch Microbiol 200:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1439-1
Milagres AMF, Machuca A, Napoleão D (1999) Detection of siderophore production from several fungi and bacteria by a modification of chrome azurol S (CAS) agar plate assay. J Microbiol Methods 37:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-7012(99)00028-7
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Method 65(1–2):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Mukhopadhyay R, Chatterjee S, Chatterjee BP, Guha AK (2005) Enhancement of biomass production of edible mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju grown in whey by plant growth hormones. Process Biochem 40:1241–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.05.006
Noble R, Dobrovin-Pennington A, Hobbs PJ, Pederby J, Rodger A (2009) Volatile C8 compounds and pseudomonads influence primordium formation of Agaricus bisporus. Mycologia 101:583–591. https://doi.org/10.3852/07-194
Oh SY, Kim M, Eimes JA, Lim YW (2018) Effect of fruiting body bacteria on the growth of Tricholoma matsutake and its related molds. PLoS ONE 13:e0190948. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190948
Pardo-Giménez A, Pardo JE, Zied DC (2017) Casing materials and techniques in Agaricus bisporus cultivation. In: Zied DC, Pardo-Giménez A (eds) Edible and medicinal mushrooms: technology and applications. Wiley, Chichester, pp 149–174
Poonga PRJ, Kaviyarasan V (2015) Basidiome initiation in medicinal mushroom Hypsizygus ulmarius by free living nitrogen fixing Azotobacter sp. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 31:85–88
Pramoj NA, Ayudhya S, Riffiani R, Ozaki Y, Onda Y, Nakano S, Aimi T, Simomura N (2019) Isolation of bacteria from fruiting bodies of Rhizopogon roseolus and their effect on mycelial growth of host. Page 13/21 mushroom. Mush Sci Biotechnol 27:134–139
Proctor LM (2011) The human microbiome project in 2011 and beyond. Cell Host Microbe 10:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2011.10.001
Rossouw W, Korsten L (2017) Cultivable microbiome of fresh white button mushrooms. Lett Appl Microbiol 64:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12698
Roy T, Bandopadhyay A, Sonawane PJ, Majumdar S, Mahapatra NR, Alam S, Das N (2018) Bio-effective disease control and plant growth promotion in lentil by two pesticide degrading strains of Bacillus sp. Biol Control 127:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2018.08.018
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sánchez C (2010) Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus and other edible mushrooms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1321–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2343-7
Schulz B, Römmert AK, Dammann U, Aust HJ, Strack D (1999) The endophyte-host interaction: a balanced antagonism? Mycol Res 103:1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756299008540
Silva CF, Azevedo RS, Braga C, da Silva R, Dias ES, Schwan RF (2009) Microbial diversity in a bagasse-based compost prepared for the production of Agaricus brasiliensis. Braz J Microbiol 40:590–600. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838220090003000023
Suarez C, Ratering S, Weigel V, Sacharow J, Bienhaus J, Ebert J, Hirz A, Rühl M, Schnell S (2019) Isolation of bacteria at different points of Pleurotus ostreatus cultivation and their influence in mycelial growth. Microbiol Res 234:126393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2019.126393
Sun SJ, Liu JZ, Hu KH, Zhu HX (2011) The level of secreted laccase activity in the edible fungi and their growing cycles are closely related. Curr Microbiol 62:871–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9794-z
Suwannarach N, Kumla J, Zhao Y, Kakumyan P (2022) Impact of cultivation substrate and microbial community on improving mushroom productivity: a review. Biology (basel) 11:569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040569
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tiryaki D, Gulmez O (2021) Determination of the effect of indole acetic acid (IAA) produced from edible mushroom on plant growth and development. Anatol J Biol 2:17–20
Tsivileva O, Shaternikov A, Ponomareva E (2022) Edible mushrooms could take advantage of the growth-promoting and biocontrol potential of Azospirillum. Proc Latv Acad Sci B 76:211–217. https://doi.org/10.2478/prolas-2022-0032
Vahdatzadeh M, Deveau A, Splivallo R (2015) The role of the microbiome of truffles in aroma formation: a meta-analysis approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:6946–6952. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01098-15
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991
Wu L, Thompson DK, Li G, Hurt RA, Tiedje JM, Zhou J (2001) Development and evaluation of functional gene arrays for detection of selected genes in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5780–5790. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.12.5780-5790.2001
Zhang WR, Liu SR, Kuang YB, Zheng SZ (2019) Development of a novel spawn (block spawn) of an edible mushroom, Pleurotus ostreatus, in liquid culture and its cultivation evaluation. Mycobiology 47:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/12298093.2018.1552648
Zhao Y (2010) Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112308
Zhou Q, Tang X, Huang Z, Song P, Zhou J (2010) Novel method for cultivating Agaricus blazei. Acta Edulis Fungi 17:39–42
Zhu B, Li Y, Hu T, Zhang Y (2019) The hepatoprotective effect of polysaccharides from Pleurotus ostreatus on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury rats. Int J Biol Macromol 131:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.043
Acknowledgements
CP acknowledges the financial support of West Bengal Government for sponsoring Swami Vivekananda Merit-cum-Means Scholarship (G.O. No. 52-Edn (B)/5B-15/2017). We are very much thankful to Dr. Shariful Alam, Professor, Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, Pin-711103, India, Dr. Sukhendu Mandal, Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology, University of Calcutta, Pin-700019, India and Mr. Santosh Kumar Jana, Research Scholar, Department of Microbiology, University of Calcutta, Pin-700019, India for their assistances during preparation of revised manuscript.
Funding
The West Bengal Government sponsored Swami Vivekananda Merit-cum-Means Scholarship (G.O. No. 52-Edn(B)/5B-15/2017) to CP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CP performed most of the laboratory investigations. TR performed some laboratory experiments and data curation. KS contributed to data curation and interpretation. MM designed the experiments and participated in data interpretation. ND conceptualized the study, designed the experiments, interpreted the results, wrote the manuscript, and supervised the work. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, C., Roy, T., Singh, K. et al. Study of growth-improving and sporophore-inducing endobacteria isolated from Pleurotus pulmonarius. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 349 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03776-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03776-0