Abstract
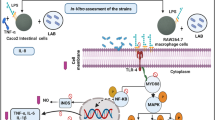
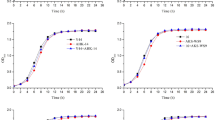
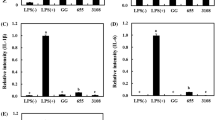
Our previous study indicated that ethanol-induced intracellular extracts (E-IEs) of Lactococcus lactis subsp. Lactis IL1403 (L. lactis IL1403) alleviated hangovers more effectively in mice than untreated intracellular extracts (U-IEs), but the material basis was unclear. Considering that stress-related proteins might play a significant role, the effects of ethanol induction on probiotic properties of L. lactis IL1403 and the associated stress response mechanism were initially explored in this study. E-IEs of L. lactis IL1403 showed better biological activities, significantly increased bacteria survival rates in oxidative stress environments, increased ADH activity, and enhanced proliferation in RAW264.7 and AML-12 cells. Proteomic analyses revealed that 414 proteins were significantly changed in response to ethanol induction. The expression of proteins involved in the universal stress response, DNA repair, oxidative stress response, and ethanol metabolism was rapidly upregulated under ethanol stress, and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) results were consistent with proteomic data. KEGG pathway analysis indicated that citrate metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, and pyruvate metabolism were significantly enriched during ethanol stress to increase energy requirements and survival rates of stressed cells. Based on this observation, the active induction is an effective strategy for increasing the biological activity of L. lactis IL1403. Exploring the molecular mechanism and material basis of their functions in vivo can help us understand the adaptive regulatory mechanism of microorganisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Hall FG, Urbizo-Reyes UC, Garcia HS, Vallejo-Cordoba B, González-Córdova AF, Hernández-Mendoza A, Liceaga AM (2019a) In Silico prediction and in vitro assessment of multifunctional properties of postbiotics obtained from two probiotic bacteria. Probiotics Antimicro 2020(12):608–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09568-z
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Astiazarán-García H, Estrada-Montoya MC, Garcia HS, Vallejo-Cordoba B, González-Córdova AF, Hernández-Mendoza A (2019b) Modulatory effect of the intracellular content of Lactobacillus casei CRL 431 against the aflatoxin B (1)-induced oxidative stress in rats. Probiotics Antimicro 11(2):470–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9433-8
Amaretti A, Nunzio M, Pompei A, Raimondi S, Rossi M, Bordoni A (2013) Antioxidant properties of potentially probiotic bacteria: in vitro and in vivo activities. Appl Microbiol Biot 97(2):809–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4241-7
An J, Yang C, Li Z, Finn PW, Perkins DL, Sun J, Bai Z, Gao L, Zhang M, Ren D (2019) In vitro antioxidant activities of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and protective effect on Caco-2 cell line model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(2):917–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9497-0
Arnér E, Holmgren A (2000) Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. FEBS J 267(20):6102–6109. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01701.x
Bertsch J, Siemund AL, Kremp F, Microbiology V (2016) A novel route for ethanol oxidation in the acetogenic bacterium Acetobacterium woodii: the acetaldehyde/ethanol dehydrogenase pathway. Environ Microbiol 18(9):2913–2922. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13082
Chen S, Jia S, Suo K, Kang Q, Hao L, Lu L, Liu X, Huang J, Lu J (2022) Positive effect of ethanol-induced Lactococcus lactis on alcohol metabolism in mice. Food Sci Hum Well 11(5):1183–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.04.016
Chiang SS, Liu CF, Tseng KC, Mau JL, Pan TM (2012) Immunomodulatory effects of dead Lactobacillus on murine splenocytes and macrophages. Food Agr Immunol 23(2):183–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2011.609246
Das D, Goyarl A (2015) Antioxidant activity and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing ability of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum DM5 isolated from Marcha of Sikkim. Lwt-Food Sci Technol 61(1):263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.11.013
Devi MC, Meera NS, Theja PC, Gopal DVRS (2011) Production and optimization of β-galactosidase enzyme from probiotic Lactobacillus sps. BioTechnol Indian J 5(3):153–159
Gan Y, Tong J, Zhou XR, Long XY, Pan YN, Liu WW, Zhao X (2021) Hepatoprotective effect of Lactobacillus plantarum HFY09 on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice. Front Nutr 8:684588. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.684588
Herawati I, Hilmi D, Fauziah PNJ (2014) Effect of lactic acid filtrate and bacteriocins of lactobacillus acidophillus on phagocytosis activity of macrophages cell againts enteropathogen Escherichia coli (EPEC). Microbio Indonesia 8(4):183–190. https://doi.org/10.5454/mi.8.4.6
Higuchi M, Yamamoto Y, Kamio Y (2000) Molecular biology of oxygen tolerance in lactic acid bacteria: functions of nadh oxidases and Dpr in oxidative stress. J Biosci Bioeng 90(5):484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80028-1
Kitazawa H, Shahid M, Rajoka R, Teame T, Zhou Z (2020) Citation: paraprobiotics and postbiotics of probiotic lactobacilli, their positive effects on the host and action mechanisms: a review. Front Nutr 7:570344. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.570344
Kullisaar T, Zilmer M, Mikelsaar M, Vihalemm T, Annuk H, Kairane C, Kilk A (2002) Two antioxidative lactobacilli strains as promising probiotics. Int J Food Microbiol 72(3):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(01)00674-2
Larsen R, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2005) Interaction between ArgR and AhrC controls regulation of arginine metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem 280(19):19319–19330. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413983200
Li Y, Hugenholtz J, Abee T, Molenaar D (2003) Glutathione protects Lactococcus lactis against oxidative stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(10):5739–5745. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.10.5739-5745.2003
Li H, Shi J, Zhao L, Guan J, Liu F, Huo G, Li B (2021) Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0344 and Lactobacillus acidophilus KLDS1.0901 mixture prevents chronic alcoholic liver injury in mice by protecting the intestinal barrier and regulating gut microbiota and liver-related pathways. J Agr Food Chem 69(1):183–197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06346
Lorena D, Ana S, Rocío F, Miriam G, Cenmen T, Oscar K, Fernada R (2017) Transcriptome analysis shows activation of the arginine deiminase pathway in Lactococcus lactis as a response to ethanol stress. Int J Food Microbiol 257:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.05.017
Mbye M, Baig MA, Abuqamar SF, El-Tarabily KA, Ayyash MM (2020) Updates on understanding of probiotic lactic acid bacteria responses to environmental stresses and highlights on proteomic analyses. Compr Rev Food Sci F 19(3):1110–1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12554
Olguin N, Champomier-Verges M, Anglade P, Baraige F, Cordero-Otero R, Bordons A, Zagorec M, Reguant C (2015) Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of Oenococcus oeni PSU-1 response to ethanol shock. Food Microbiol 51(10):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2015.05.005
Power O, Jakeman P, FitzGerald RJ (2013) Antioxidative peptides: enzymatic production, in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity and potential applications of milk-derived antioxidative peptides. Amino Acids 44(3):797–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1393-9
Rivas-Sendra A, Landete JM, Alcántara C, Microbiology M (2011) Response of Lactobacillus casei BL23 to phenolic compounds. J Appl Microbiol 111(6):1473–1481. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05160.x
Sheng Y, Yang X, Lian YY, Zhang BY, He XY, Xu WT, Huang KL (2016) Characterization of a cadmium resistance Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain by antioxidant assays and proteome profiles methods. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 46:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.08.008
Shi J, Zhou X, Zhao Y, Tang X, Feng L, Wang B, Chen J (2021) The three-spot seahorse-derived peptide PAGPRGPA attenuates ethanol-induced oxidative stress in LO2 cells through MAPKs, the Keap1/Nrf2 signalling pathway and amino acid metabolism. Food Funct 12(4):1672–1687. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02457k
Shigwedha N, Sichel L, Li J, Zhang L (2014) Probiotical cell fragments (PCFs) as “novel nutraceutical ingredients.” J Biosciences 2(3):43–55. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2014.23007
Songyang L, Qiaozhen K, Dan P, Xin L, Laizheng L, Limin H, Jike L (2019) Identification of lyoprotectants released from gradient-freezing pretreated entocyte in Lactococcus lactis Subsp lactis IL1403. Curr Top Nutraceut R 17(2):122–134. https://doi.org/10.37290/ctnr2641-452X
Suo K, Chen S, Li X, Liu X, Yi J, Zhu J, Lu L, Hao L, Kang Q, Lu J (2021) Radioprotective effect of radiation-induced Lactococcus lactis cell-free extract against (60) Coγ injury in mice. J Dairy Sci 104(9):9532–9542. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2021-20291
Taverniti V, Guglielmetti SJG, Nutrition (2011) The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: proposal of paraprobiotic concept). Genes Nutr 6:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-011-0218-x
Van B, Abee T, Tempelaars M, Bron PA, Kleerebezem M, Marco ML (2011) Short- and long-term adaptation to ethanol stress and its cross-protective consequences in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(15):5247–5256. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00515-11
Vidal R (2017) Alcohol dehydrogenase AdhA plays a role in ethanol tolerance in model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(8):3473–3482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8138-3
Xue H, Han J, He B, Yi M, Liu X, Song H, Li J (2021) Bioactive peptide release and the absorption tracking of casein in the gastrointestinal digestion of rats. Food Funct 12(11):5157–5170. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo00356a
Yan F, Liu L, Dempsey PJ, Tsai YH, Raines EW, Wilson CL, Cao H, Cao Z, Liu L, Polk DB (2013) A Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-derived soluble protein, p40, stimulates ligand release from intestinal epithelial cells to transactivate epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 288(42):30742–30751. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.492397
Yang X, Teng K, Zhang J, Wang F, Zhang T, Ai G, Han P, Bai F, Zhong J (2017) Transcriptome responses of Lactobacillus acetotolerans F28 to a short and long term ethanol stress. Sci Rep 7(1):2650. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02975-8
Yang X, Teng K, Li L, Su R, Zhong J (2019) Transcriptional regulator acrR increases ethanol tolerance through regulation of fatty acid synthesis in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 85(22):e01690-e1719. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01690-19
Yang K, Liu M, Yang J, Wei X, Zhang G (2020) Physiological and proteomic responses of freeze-dried Oenococcus oeni SD-2a with ethanol-acclimations. J Sci Food Agric 129:109425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109425
Yao S, Zhou R, Jin Y, Huang J, Qin J, Wu C (2022) Formation of biofilm changed the responses of Tetragenococcus halophilus to ethanol stress revealed by transcriptomic and proteomic analyses. Food Res Int 161:111817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111817
Yu GC, Li JT, He H, Huang WH, Zhang WJ (2013) Ultrafiltration preparation of potent bioactive corn peptide as alcohol metabolism stimulator in vivo and study on its mechanism of action. J Food Biochem 37(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4514.2011.00613.x
Zhang J, Fu RY, Hugenholtz J, Li Y, Chen J (2007) Glutathione protects Lactococcus lactis against acid stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5268–5275. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02787-06
Zhang X, Zhang S, Xie B, Sun Z (2021) Influence of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of Chickpea yam milk. J Food Quality 2021(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5523356
Zhao RJ, Huo CY, Qian Y, Ren DF, Lu J (2017) Ultra-high-pressure processing improves proteolysis and release of bioactive peptides with activation activities on alcohol metabolic enzymes in vitro from mushroom foot protein. Food Chem 231:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.03.058
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900296 and 32172211), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFF1103300), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province for Outstanding Youth (202300410365), the Program for Science &Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (22HASTIT037) and the Technology Development (Cooperation) project of Zhengzhou University (20210442A, 20210327A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC, JY and KS designed the study and wrote the manuscript. QK, LL and JL collected and analyzed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Yi, J., Suo, K. et al. Probiotic properties and proteomics analysis of ethanol-induced Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis IL1403. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03627-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03627-y