Abstract
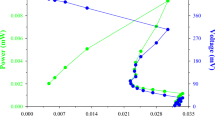
Metabolomic study of electrogenic bacteria is a necessity to understand the extent of complex organic matter degradation and to invent new co-culture techniques to achieve complete degradation. In this study, we have subjected Alkanivorax xenomutans (KCTC 23751T; NBRC 108843T), a bacterium capable for biodegradation of complex hydrocarbons, to oxic and anoxic conditions in a three chambered microbial fuel cell. In an attempt to understand the molecular mechanisms during the electrogenic processes of A. xenomutans, intra cellular (endo metabolome or the fingerprint) and exo metabolome (extracellular metabolome or the foot print) were analyzed under oxic and anoxic conditions, using FTIR and GC–MS. Interpretation of the data revealed higher number of metabolites in the anoxic fraction as compared to oxic fraction. In addition, expression of putative metabolites that influence electron transfer like flavins, fumarate and quinones were found to be predominant in the organisms when grown in anoxic conditions. Hence, the presence of anoxic conditions governed the electrogenic bacteria to produce enhanced power output by modulating differential metabolomic profiling, compared to the culture grown in oxic conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas RM, Hazen TC (2011) Oil biodegradation and bioremediation: a tale of the two worst spills in U.S. history. Environ Sci Technol 45:6709–6715. doi:10.1021/es2013227
Bruns A, Berthe-Corti L (1999) Fundibacter jadensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new slightly halophilic bacterium, isolated from intertidal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:441–448. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-2-441
Butler J, Young N, Lovley D (2010) Evolution of electron transfer out of the cell: comparative genomics of six Geobacter genomes. BMC Genom 11:40
Du Z, Li H, Gu T (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: a promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotech Adv 25:464–482. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.05.004
Gargouri B, Mhiri N, Karray F, Aloui F, Sayadi S (2015) Isolation and characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading yeast strains from petroleum contaminated industrial wastewater. BioMed Res Int 2015:11. doi:10.1155/2015/929424
Gil G-C, Chang I-S, Kim BH, Kim M, Jang J-K, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Operational parameters affecting the performannce of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 18:327–334. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00110-0
Kim B-C, Postier BL, DiDonato RJ, Chaudhuri SK, Nevin KP, Lovley DR (2008) Insights into genes involved in electricity generation in Geobacter sulfurreducens via whole genome microarray analysis of the OmcF-deficient mutant. Bioelectrochemistry 73:70–75. doi:10.1016/j.bioelechem.2008.04.023
Lai Q et al (2011) Alcanivorax pacificus sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea pyrene-degrading consortium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1370–1374. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.022368-0
Lai Q, Wang J, Gu L, Zheng T, Shao Z (2013) Alcanivorax marinus sp. nov. isolated from deep-sea water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4428–4432. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.049957-0
Liu C, Shao Z (2005) Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov. a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1181–1186. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63443-0
Lodha TD, Srinivas A, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (2015) Hopanoid inventory of Rhodoplanes spp. Arch Microbiol 197:861–867. doi:10.1007/s00203-015-1112-5
Logan BE (2008) Introduction. In: Microbial fuel cells. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1–11. doi:10.1002/9780470258590.ch1
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Microbial fuel cells: challenges and applications. Environ Sci Technol 40:5172–5180. doi:10.1021/es0627592
Lovley DR (2006) Bug juice: harvesting electricity with microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:1526–1740. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1442
Lovley DR (2012) Electromicrobiology. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:391–409. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150104
Mahidhara G, Chintalapati VR (2015) Eco-physiological and interdisciplinary approaches for empowering biobatteries. Ann Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s13213-015-1148-4
Mahidhara G, Kanwar RK, Roy K, Kanwar JR (2015) Oral administration of iron-saturated bovine lactoferrin-loaded ceramic nanocapsules for breast cancer therapy and influence on iron and calcium metabolism. Int J Nanomed 10:4081–4098 doi:10.2147/ijn.s75877
Manzella MP, Reguera G, Kashefi K (2013) Extracellular electron transfer to Fe(III) oxides by the hyperthermophilic archaeon geoglobus ahangari via a direct contact mechanism. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4694–4700. doi:10.1128/AEM.01566-13
Miller LG, Oremland RS (2008) Electricity generation by anaerobic bacteria and anoxic sediments from hypersaline soda lakes. Extremophiles 12:837–848. doi:10.1007/s00792-008-0191-5
Nevin KP et al (2009) Anode biofilm transcriptomics reveals outer surface components essential for high density current production in Geobacter sulfurreducens fuel cells. PLoS ONE 4:e5628. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005628
Núñez C et al (2006) DNA microarray and proteomic analyses of the RpoS regulon in Geobacter sulfurreducens. J Bacteriol 188:2792–2800. doi:10.1128/jb.188.8.2792-2800.2006
Park DH, Zeikus JG (2000) Electricity generation in microbial fuel cells using neutral red as an electronophore. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1292–1297. doi:10.1128/aem.66.4.1292-1297.2000
Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol 23:291–298. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.04.008
Rahul K, Sasikala C, Tushar L, Debadrita R, Ramana CV (2014) Alcanivorax xenomutans sp. nov., a hydrocarbonoclastic bacterium isolated from a shrimp cultivation pond. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3553–3558. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.061168-0
Rismani-Yazdi H, Carver SM, Christy AD, Tuovinen OH (2008) Cathodic limitations in microbial fuel cells: an overview. J Power Sour 180:683–694 doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.02.074
Rivas R, García-Fraile P, Peix A, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2007) Alcanivorax balearicus sp. nov., isolated from Lake Martel. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1331–1335. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64912-0
Ryerson TB et al (2012) Chemical data quantify deepwater horizon hydrocarbon flow rate and environmental distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:20246–20253. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110564109
Sevda S, Sreekrishnan TR (2012) Effect of salt concentration and mediators in salt bridge microbial fuel cell for electricity generation from synthetic wastewater. J Environ Sci Health A 47:878–886 doi:10.1080/10934529.2012.665004
Thauer RK, Jungermann K, Decker K (1977) Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41 100–180
Wang H, Hollywood K, Jarvis RM, Lloyd JR, Goodacre R (2010) Phenotypic characterization of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6266–6276. doi:10.1128/aem.00912-10
Wang H, Correa E, Dunn W, Winder C, Goodacre R, Lloyd J (2013) Metabolomic analyses show that electron donor and acceptor ratios control anaerobic electron transfer pathways in Shewanella oneidensis. Metabolomics 9:642–656. doi:10.1007/s11306-012-0488-3
Wu Y, Lai Q, Zhou Z, Qiao N, Liu C, Shao Z (2009) Alcanivorax hongdengensis sp. nov., an alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from surface seawater of the straits of Malacca and Singapore, producing a lipopeptide as its biosurfactant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1474–1479. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.001552-0
Xia J, Sinelnikov IV, Han B, Wishart DS (2015) MetaboAnalyst 3.0: making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W251–W257. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv380
Yakimov MM, Golyshin PN, Lang S, Moore ERB, Abraham W-R, Lünsdorf H, Timmis KN (1998) Alcanivorax borkumensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, hydrocarbon-degrading and surfactant-producing marine bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 48:339–348. doi:10.1099/00207713-48-2-339
Yang TH, Coppi M, Lovley D, Sun J (2010) Metabolic response of Geobacter sulfurreducens towards electron donor/acceptor variation. Microb Cell Fact 9:90
Yi H, Nevin KP, Kim B-C, Franks AE, Klimes A, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2009) Selection of a variant of Geobacter sulfurreducens with enhanced capacity for current production in microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3498–3503. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.05.004
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi under Dr. D. S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship Scheme [Grant No. F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/BL/13-14/0283]. We acknowledge Dr. K. Rahul and Mrs. M. Azmatunnisa Begum for providing the pure cultures of Alkanivorax xenomutans. We acknowledge Dr. Rasika Samarasinghe for proof reading the manuscript and her valuable inputs during the course of revision. We also thank Mr. Devender and Dr. E.V.V. Ramprasad for their help with GC–MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahidhara, G., Ch., S. & Ch., V. Comparative metabolomic studies of Alkanivorax xenomutans showing differential power output in a three chambered microbial fuel cell. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 102 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2268-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2268-8