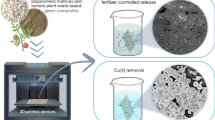
Abstract
Circular economy has renewed its focus; a novel eco-friendly semi-interpenetrating network (semi-IPN) device was prepared from functionally modified natural backbone (Colocasia esculenta) for controlled release of fertilizers. The method encompasses the usage of natural non-toxic materials with addition of fortifying nutrients. Naturally procured starch moieties converted into acetylated starch, coded as Acy CE. This was further cross-linked with polyacrylamide (PAAm) in the presence of N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide and ammonium persulfate as a crosslinker-initiater system. The chemical, physical, and thermal properties of the synthesized semi-IPN coded as Acy CE-cl-PAAm were also presented through various characterization techniques. The Acy CE-cl-PAAm was assessed for its fertilizer release mechanism in water media studied on three pH values. The release kinetics of all the fertilizers followed Korsmeyer-Peppas Model (Fickian diffusion), unveiling its excellent potential as controlled agrochemical release device. The macromolecular relaxation of the given network matrix was found to be comparable to the diffusion rate of urea indicated by Fickian (n = 0.4) diffusion mechanism. The initial diffusion coefficients of DI = 8.03*10−7, DI = 7.9*10−7, DI = 9.8*10−7, DI = 1.7 * 10−7 were found to be greater than the lateral diffusion co-efficients of DL = 1.4*10−7, DL = 1.3*10−7, DL = 3.9*10−7, DL = 3.9*10−7 in the case of urea, ammonium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and bio-fertilizer, released at pH = 7.0, respectively. Also, it was found to get degraded up to 76% by weight with 1.1% rate of degradation per day within 70 days in vermi-compost method. The results indicated that this is an effective approach for controlled agrochemical release with great potential applications in sustained agriculture.
Highlights
• Biodegradable hydrogel was synthesized from acetylated derivative of Colocasia esculenta (CE) based backbone under the influence of microwave irradiations.
• The synthesized device showed highest swelling of 1375%.
• Hence, used for comparative analysis of urea, ammonium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and biofertilizer-controlled release in water media.
• The semi-IPN was found eco-friendly and biodegradable in nature.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- Acy:
-
Acetylated
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- APS:
-
Ammonium persulfate
- CE :
-
Colocasia esculenta
- DA :
-
Average diffusion co-efficient
- DI :
-
Initial diffusion co-efficient
- DL :
-
Lateral diffusion co-efficient
- Ds :
-
Degradation swelling percentage
- df:
-
Degree of freedom
- DTG:
-
Differential thermogravimetric
- EDX:
-
Energy dispersive X-ray analysis
- FDT:
-
Final decomposition temperature
- FE-SEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscope
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- F-value:
-
Fisher–Snedecor distribution
- IDT:
-
Initial decomposition temperature
- MBA:
-
N, N’- methylene bis-acrylamide
- MPD:
-
Multipurpose diffraction
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- OFAT:
-
One factor at a time
- PAAm:
-
Polyacrylamide
- P-value:
-
Probability value
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- UV-Vis:
-
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Ahmed, E. M. (2015). Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. Journal of Advanced Research, 6, 105–121.
Aouada, F. A., Moura, M. R., Menezes, E. A., Nogueira, A. R. A., & Capparelli Mattoso, L. H. (2008). Hydrogel synthesis and kinetics of ammonium and potassium release. Revista Brasileira De Ciencia Do Solo, 32(4), 1643–1649.
Awual, R. (2016). Solid phase sensitive palladium (II) ions detection and recovery using ligand based efficient conjugate nanomaterials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 300, 264–272.
Awual, R., Hasan, M., Islam, A., Rahman, M. M., Asiri, A. M., Khaleque, A., & Sheikh, C. (2019a). Offering an innovative composited material for effective lead (II) monitoring and removal from polluted water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 231, 214–223.
Awual, R., Islam, A., Hasan, M., Rahman, M. M., Asiri, A. M., Khaleque, A., & Sheikh, C. (2019b). Introducing an alternate conjugated material for enhanced lead (II) capturing from wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 224, 920–929.
Bastani, D., Esmaeili, N., & Asadollahi, M. (2013). Polymeric mixed matrix membranes containing zeolites as a filler for gas separation applications: A review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 19(2), 375–393.
Bora, A., & Karak, N. (2022). Starch and itaconic acid-based superabsorbent hydrogels for agricultural application. European Polymer Journal, 176, 111430.
Chang, L., Xu, L., Liu, Y., & Qiu, D. (2021). Superabsorbent polymers used for agricultural water retention. Polymer Testing, 94, 107021.
Cheng, B., Pei, B., Wang, Z., & Hu, Q. (2017). Advances in chitosan-based superabsorbent hydrogels. RSC Advances, 7, 42036–42046.
Cuenca, P., Ferrero, S., & Albani, O. (2020). Preparation of cassava starch acetate with high substitution degree. Food Hydrocolloids, 100, 105430.
Dispat, N., Poompradub, S., & Kiatkamjornwong, S. (2020). Synthesis of ZnO/SiO2-modified starch-graft-polyacrylate superabsorbent polymer for agricultural application. Carbohydrate Polymers, 249, 116862.
Essawy, H. A., Ghazy, M. B. M., El-Hai, F. A., & Mohamed, M. F. (2016). Superabsorbent hydrogels via graft polymerization of acrylic acid from chitosan-cellulose hybrid and their potential in controlled release of soil nutrients. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 89, 144–151.
Guo, L., Wang, Y., Wang, M., Shaghaleh, H., Hamoud, Y. A., Xu, X., & Liu, H. (2021a). Synthesis of bio-based MIL-100(Fe)@CNF-SA composite hydrogel and its application in slow-release N-fertilizer. Journal of Cleaner Production, 324, 129274.
Guo, T., Wangxia, W., Song, J., Jin, Y., & Xiao, H. (2021b). Dual-responsive carboxymethyl cellulose/dopamine/cystamine hydrogels driven by dynamic metal-ligand and redox linkages for controllable release of agrochemical. Carbohydrate Polymers, 253, 117188.
Gupta, P., & Nayak, K. K. (2016). Optimization of keratin/alginate scaffold using RSM and its characterization for tissue engineering. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 85, 141–149.
Hasija, V., Sharma, K., Kumar, V., Sharma, S., & Sharma, V. (2018). Green synthesis of agar/gum Arabic based superabsorbent as an alternative for irrigation in agriculture. Vacuum, 157, 458–464.
Hennick, W. E., & Nostrum, C. F. (2012). Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64, 223–236.
Hua, S., & Wang, A. (2009). Synthesis, characterization and swelling behaviors of sodium-alginate-g-poly(acrylic acid)/sodium humate superabsorbent. Carbohydrate Polymers, 75, 79–84.
Huttermann, A., Orikiriza, L. J., & Agaba, H. (2009). Application of superabsorbent polymers for improving the ecological chemistry of degraded or polluted lands. CLEAN-Soil, Air Water, 37, 517–526.
Islam, A., Teo, S. H., Taufiq-Yap, Y. H., Ng, C. H., Vo, D. V. N., Ibrahim, M. L., Hasan, M., Khan, M. A. R., Nur, A. S. M., & Awual, M. R. (2021). Step towards the sustainable toxic dyes removal and recycling from aqueous solution- A comprehensive review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 175, 105849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105849
Jamnongkan, T., & Kaewpirom, S. (2010). Potassium release kinetics and water retention of controlled-release fertilizers based on chitosan hydrogels. Journal of Polymers and Environment, 18, 413–421.
Jindal, R., Mittal, H., Kaith, B. S., & Sharma, R. (2011). Biodegradable composites from black gram and resorcinol-formaldehyde-Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of physical properties. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2(2), 19–27.
Kaith, B. S., Saruchi, Jindal, R., & Bhatti, M. S. (2012). Screening and RSM optimization for synthesis of a Gum tragacanth–acrylic acid based device for in situ controlled cetirizine dihydrochloride release. Soft Matter, 8(7), 2286–2293.
Kalita, N. K., Hazarika, D., Kalamdhad, A., & Katiyar, V. (2021). Biodegradation of biopolymeric composites and blends under different environmental conditions: Approach towards end-of-life panacea for crop sustainability. Bioresource Technology Reports, 15, 100705.
Kumar, K., Kaith, B. S., & Mittal, H. (2010). Utilization of acrylamide and natural polysaccharide based polymeric networks in pH controlled release of 5-amino salicylic acid. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 55(4), 522–526.
Laftah, W. A., Hashim, S., & Ibrahim, A. N. (2011). Polymer hydrogels: A review. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering, 50, 1475–1486.
Li, J., Kong, X., & Ai, Y. (2022). Modification of granular waxy, normal and high-amylose maize starches by maltogenic alpha-amylase to improve functionality. Carbohydrate Polymers, 290, 119503.
Liu, M., Ni, B., Lu, S., Xie, L., & Wang, Y. (2010). Multifunctional slow-release organic-inorganic compound fertilizer. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(23), 12373–12378.
Mikkelsen, R. L., Behel, A. N. D., & Williams, H. M. (1993). Addition of gel-forming hydrophilic polymers to nitrogen fertilizer solutions. Fertilizer Research, 36, 55–61.
Mishra, B., Upadhyay, M., Reddy, A. S. K., Vasant, B. G., & Muthu, M. S. (2017). Hydrogels: An introduction to a controlled drug delivery device, synthesis and application in drug delivery and tissue engineering, Austin. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 4, 1037.
Mohammadi-Khoo, S., Moghadam, P. N., Fareghi, A. R., & Movagharnezhad, N. (2016). Synthesis of a cellulose-based hydrogel network: Characterization and study of urea fertilizer slow release. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 133, 42935.
Montesano, F. F., Parente, A., Santamaria, P., Sannino, A., & Serio, F. (2015). Biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogel increases water retention properties of growing media and plant growth. Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia, 4, 451–458.
Ni, B., Liu, M., & Lu, S. (2009). Multifunctional slow-release urea fertilizer from ethyl-cellulose and superabsorbent coated formulations. Chemical Engineering Journal, 155(3), 892–898.
Pan, S., & Ragauskas, A. S. (2011). Preparation of superabsorbent cellulosic hydrogels. Carbohydrate Polymers, 87, 1410–1418.
Pourjavadi, A., Harzandi, A. M., & Hosseinzadeh, H. (2004). Modified carrageenan 3. Synthesis of a novel polysaccharide-based superabsorbent hydrogel via graft copolymerization of acrylic acid onto kappa-carrageenan in air. European Polymer Journal, 40(7), 1363–1370.
Priya, Sharma, A. K., Kaith, B. S., Tanvar, V., Bhatia, J. K., Sharma, N., Bajaj, S., & Panchal, S. (2019). RSM-CCD optimized sodium alginate/gelatin based ZnS-nanocomposite hydrogel for the effective removal of biebrich scarlet and crystal violet dyes. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 129(214), 226.
Ritger, P. L., & Peppas, N. A. (1987). A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. Journal of Controlled Release, 5(1), 23–36.
Rizwan, M., Gilani, S. R., Durani, A. I., & Naseem, S. (2021). Materials diversity of hydrogel: Synthesis, polymerization process and soil conditioning properties in agricultural field. Journal of Advanced Research, 33, 15–40.
Sabbagh, F., Muhamad, I. I., Nazari, Z., Mobini, P., & Taraghdari, S. B. (2018). From formulation of acrylamide-based hydrogels to their optimization for drug release using response surface methodology. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 92, 20–25.
Saeed, A. M. (2013). Temperature effect on swelling properties of commercial polyacrylic acid hydrogel beads. International Journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research, 1(12), 1614–1627.
Saha, A., Sekharan, S., & Manna, U. (2020). Superabsorbent hydrogel (SAH) as a soil amendment for drought management: A review. Soil and Tillage Research, 204, 104736.
Sartore, L., Vox, G., & Schettini, E. (2013). Preparation and performance of novel biodegradable polymeric materials based on hydrolysed proteins for agricultural application. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 21(3), 718–725.
Saruchi, V., Kumar, H. M., et al. (2019). Biodegradable hydrogels of tragacanth gum polysaccharide to improve water retention capacity of soil and environment-friendly controlled release of agrochemicals. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 132, 1252–1261.
Selvakumaran, S., Muhamad, I. I., & Razak, S. I. (2016). Evaluation of kappa carrageenan as potential carrier for floating drug delivery system: Effect of pore forming agents. Carbohydrate Polymers, 135, 207–214.
Shah, A., Masoodi, F. A., Gani, Adil, & Ashwar, B. A. (2017). Physiochemical, rheological and structural characterization of acetylated oat starches. LWT – Food Science and Technology, 80, 19–26.
Sharma, P., Mittal, H., Jindal, R., Jindal, D., & Alhassan, S. M. (2019). Sustained delivery of atenolol drug using gum dammar crosslinked polyacrylamide and zirconium based biodegradable hydrogel composites. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 562, 136–145.
Singh, B., Sharma, N., & Chauhan, N. (2007). Synthesis, characterization and swelling studies of pH responsive psyllium and methacrylamide based hydrogels for the use in colon specific drug delivery. Carbohydrate Polymers, 69, 631–643.
Song, Y., Qu, X., Guo, M., Hu, Q., Mu, Y., Hao, N., Wei, Y., Wang, Q., & Mackay, C. R. (2023). Indole acetylated high-amylose maize starch: Synthesis, characterization and application for amelioration of colitis. Carbohydrate Polymers, 302, 120425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120425
Thombare, N., Mishra, S., Siddiqui, M. Z., Jha, U., Singh, D., & Mahajan, G. R. (2018). Design and development of guar gum based novel, superabsorbent and moisture retaining hydrogels for agricultural applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 185, 169–178.
Tiwari, K. R., Krishnamoorthi, S., & Kumar, K. (2019). Synthesis of cross-linker devoid novel hydrogels: Swelling behaviour and controlled urea release studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(4), 103162.
Ulery, B. D., Nair, L. S., & Laurencin, C. T. (2011). Biomedical applications of biodegradable polymers. Journal of Polymer Science Part B - Polymer Physics, 49(12), 832–864.
Yang, J., Xu, S., Wang, W., Ran, X., et al. (2023). Preparation and characterization of bioplastics from silylated cassava starch and epoxidized soybean oils. Carbohydrate Polymers, 300, 120253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120253
Zhang, L., Xie, W., Zhao, X., Liu, Y., & Gao, W. (2009). Study on the morphology, crystalline structure and thermal properties of yellow ginger starch acetates with different degrees of substitution. Thermochimica Acta, 495, 57–62.
Acknowledgements
Author is extremely thankful to MHRD, for giving financial assistantship to carry out this research work. Author is also thankful to Saif IIT Bombay, MNIT Jaipur and NIT Jalandhar for characterization of the samples. The author is also thankful to DAV University Jalandhar, for UV –Vis spectrophotometer analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Kaith, B.S., Sud, D. et al. Fabrication of Smart Hydrogel Based on Functionally Modified Colocasia esculenta as Potential Nutrient Carrier and Soil Conditioner. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 402 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06399-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06399-1