Abstract
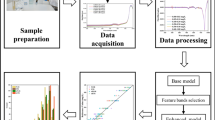
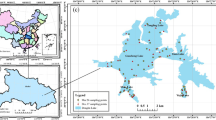
Phosphorus (P) is widely known as a limiting nutrient of water eutrophication for inland freshwater ecosystems. Owing to the complexity of P chemistry, remote sensing detection of total phosphorus (TP) concentrations currently remains limited especially for optically complex turbid inland waters. To address this need, a new TP remote sensing algorithm is developed based on prior water optical classification and the use of support vector regression (SVR) machine. The in situ observed datasets, used in this study, were collected at specific times during 2009 ~ 2011, covering a total of 232 stations from eight cruises in Lakes Taihu, Chaohu, Dianchi, and Three Gorges reservoir of China. Three types of waters were first classified by using a recently developed NTD675 (Normalized Trough Depth of spectral reflectance at 675 nm) water classification method. Then, spectral regions sensitive specifically to each water type were explored and expressed via several band ratios and used for retrieval algorithm development. The established type-specific SVR algorithms yield relatively high predictive accuracies. Specifically, the mean absolute percentage errors (MAPE) produced with the independent validation samples were achieved at 32.7, 23.2, and 14.1 % for type 1, type 2, and type 3 waters, respectively. Such water type-specific SVR algorithms are more accurate for the classified waters than an aggregated SVR algorithm for the nonclassified water and also superior to commonly used statistical algorithms. Moreover, application of the developed algorithms with HJ1A/HSI image data demonstrates that the algorithms have a large potential for remote sensing estimation of TP concentrations in optically complex turbid inland waters.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binding, C. E., Bowers, D. G., & Mitchelson-Jacob, E. G. (2005). Estimating suspended sediment concentrations from ocean colour measurements in moderately turbid waters; the impact of variable particle scattering properties. Remote Sensing of Environment, 94, 373–383.
Bricker, S. B., Clement, C. G., Pirhalle, D. E., Orlando, S. P., & Farrow, D. R. G. (1999). National estuarine eutrophication assessment. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries (p. 71). Silver Spring: NOAA.
Busse, L. B., Simpson, J. C., & Cooper, S. D. (2006). Relationships among nutrients, algae, and land use in urbanized southern California streams. Canadian Journal of Aquatic Science, 63, 2621–2638.
Camps-Valls, G., Gómez-Chova, L., Muñoz-Marí, J., Vila-Francés, J., Amorós-López, J., & Calpe-Maravilla, J. (2006). Retrieval of oceanic chlorophyll concentration with relevance vector machines. Remote Sensing of Environment, 105, 23–33.
Camps-Valls, G., Muñoz-Marí, J., Gómez-Chova, L., Richter, K., & Calpe-Maravilla, J. (2009). Biophysical parameter estimation with a semisupervised support vector machine. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 6, 248–252.
Cannizzaro, J. P., & Carder, K. L. (2006). Estimating chlorophyll a concentrations from remote-sensing reflectance in optically shallow waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 101, 13–24.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22, 361–369.
Chang, C. C., & Lin, C. J. (2002). Training nu-support vector regression: theory and algorithms. Neural Computation, 14(8), 1959–1977.
Chang, N. B., Xuan, Z., & Yang, Y. J. (2013). Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of phosphorus concentrations in a coastal bay with MODIS images and machine learning models. Remote Sensing of Environment, 134, 100–110.
Chapra, S. C., & Canale, R. P. (1991). Long-term phenomenological model of phosphorus and oxygen for stratified lakes. Water Research, 25, 707–715.
Chen, J., & Quan, W. (2012). Using Landsat/TM imagery to estimate nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 5(1), 273–280.
Chen, Y. W., Chen, K. N., & Hu, Y. H. (2006). Discussion on possible error for phytoplankton chlorophyll-a concentration analysis using hot-ethanol extraction method. Journal of Lake Science, 18(5), 550–552.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., et al. (2009). Controlling eutrophication by reducing both nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323, 1015–1016.
Dafner, E. V., Mallin, M. A., Souza, J. J., Wells, H. A., & Parsons, D. C. (2007). Nitrogen and phosphorus species in the coastal and shelf waters of Southeastern North Carolina, Mid-Atlantic U.S. coast. Marine Chemistry, 103, 289–303.
Dai, Y. N., Li, S. J., & Wang, X. J. (2008). Measurement of analysis on the apparent optical properties of water in Chaohu Lake. China Environmental Science, 28(11), 979–983.
Dekker, A. G., Malthus, T. J., & Seyhan, E. (1991). Quantitative modeling of inland water quality for high resolution MSS system. IEEE Transactions Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 29, 89–95.
Diaz, R. J., & Rosenberg, R. (2008). Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science, 321, 926–928.
Dillon, P. J., & Rigler, F. H. (1974). The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 19, 767–773.
Domagalski, J., Lin, C., Luo, Y., Kang, J., Wang, S. M., Brown, L. R., et al. (2007). Eutrophication study at the Panjiakou-Daheiting Reservoir system, northern Hebei Province, People’s Republic of China: chlorophyll-a model and sources of phosphorus and nitrogen. Agricultural Water Management, 94, 43–53.
Duan, H. T., Zhang, B., Song, K. S., Wang, Z. M., & Zhang, S. Q. (2006). Hyperspectral remote sensing of chlorophyll a in the Chagan Lake, China. Environmental Science, 27(3), 503–507.
Ebina, J., Tsutsui, T., & Shirai, T. (1983). Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Water Research, 17, 1721–1726.
Edmondson, W. T. (1970). Phosphorus, nitrogen and algae in Lake Washington after diversion of sewage. Science, 169, 690–691.
Edwards, V., Icely, J., Newton, A., & Webster, R. (2005). The yield of chlorophyll from nitrogen: a comparison between the shallow Ria Formosa lagoon and the deep oceanic conditions at Sagres along the southern coast of Portugal. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 62, 391–403.
Feng, H., Campbell, J. W., Dowell, M. D., & Moore, T. S. (2005). Modeling spectral reflectance of optically complex waters using bio-optical measurements from Tokyo Bay. Remote Sensing of Environment, 99, 232–243.
Feng, N., Mao, F., Li, X. Y., & Zhang, A. D. (2010). Research on ecological security assessment of Dian Lake. Environmental Science, 31(2), 282–286.
Gons, H. J. (1999). Optical teledetection of chlorophyll a in turbid inland waters. Environment Science Technology, 33(7), 1127–1132.
González Vilas, L., Spyrakos, E., & Torres Palenzuela, J. M. (2011). Neural network estimation of chlorophyll a from MERIS full resolution data for the coastal waters of Galician rias (NW Spain). Remote Sensing of Environment, 2, 524–535.
Guildford, S. J., & Hecky, R. E. (2000). Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: is there a common relationship? Limnology and Oceanography, 45, 1213–1223.
Gulati, R. D., & van Donk, E. (2002). Lakes in the Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: state-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia, 478, 73–106.
Guo, L. (2007). Doing battle with the green monster of Lake Taihu. Science, 317, 1166.
Hanson, C. E., Waite, A. M., Thompson, P. A., & Pattiaratchi, C. B. (2007). Phytoplankton community structure and nitrogen nutrition in Leeuwin Current and coastal waters of the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. Deep-Sea Research II, 54, 902–924.
Hecky, R. E., & Kilham, P. (1988). Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 33, 796–822.
Heiskary, S., & Wilson, B. (2005). Minnesota Lake water quality: Developing nutrient criteria (3rd ed.). St Paul: Minnesota Pollution Control Agency.
Hood, R. R., Subramaniam, A., May, L. R., Carpenter, E. J., & Capone, D. G. (2002). Remote estimate of nitrogen fixation by Trichodesmium. Deep-Sea Research II, 49, 123–147.
Howarth, R., & Paerl, H. W. (2008). Coastal marine eutrophication: control of both nitrogen and phosphorus in necessary. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(49), E103. doi:10.1073/pnas.0807266106.
Hsu, C. W., Chang, C. C., & Lin, C. J. (2003). A practical guide to support vector classification technical report department of computer science and information engineering. Taipei: National Taiwan University.
Huang, X. (1999). Eco-investigation, observation and analysis of lakes (pp. 77–99). Beijing: Standard Press of China.
Huisman, J., Matthijs, H. C. P., & Visser, P. M. (2005). Harmful cyanobacteria (Springer aquatic ecology series 3). Dordrecht: Springer.
Jiao, H. B., Zha, Y., Gao, J., Li, Y. M., Wei, Y. C., & Huang, J. Z. (2006). Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in Lake Tai, China using in situ hyperspectral data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(19), 4267–4276.
Jorgensen, S. E., Kamp-nielsen, L., Christensen, T., Windolf-nielsen, J., & Westergaard, B. (1986). Validation of a prognosis based upon a eutrophication model. Ecological Modelling, 32, 165–182.
Kishino, M., Tanaka, A., & Ishizaka, J. (2005). Retrieval of chlorophyll a, suspended solids, and colored dissolved organic matter in Tokyo Bay using ASTER data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 99, 66–74.
Koza, J. R. (1992). Genetic programming: On the programming of computers by means of natural selection. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Kutser, T., Arst, H., Miller, T., Käärmann, L., & Milius, A. (1995). Telespectrometrical estimation of water transparency, chlorophyll-a and total phosphorus concentration of Lake Peipsi. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 16, 3069–3085.
Le, C. F., Li, Y. M., Zha, Y., Sun, D. Y., Huang, C. C., & Lu, H. (2009). A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: the case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113, 1175–1182.
Le, C. F., Li, Y., Zha, Y., Sun, D., Huang, C., & Zhang, H. (2011). Remote estimation of chlorophyll a in optically complex waters based on optical classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115, 725–737.
Leondes, C. T. (1998). Neural network systems techniques and applications. New York: Academic Press.
Li, S. J., Wu, Q., Wang, X. J., Piao, X. Y., & Dai, Y. N. (2002). Correlations between reflectance spectra and contents of chlorophyll-a in Chaohu Lake. Journal of Lakes Sciences, 14(3), 228–234.
Lin, S. L., & Liu, Z. (2007). Parameter selection in SVM with RBF kernel function. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 35(2), 163–167.
Lorenzen, C. J. (1967). Determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnology and Oceanography, 12, 343–346.
Ma, R. H., & Dai, J. F. (2005). Chlorophyll-a concentration estimation with field spectra of water body near Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake. Journal of Remote Sensing, 9(1), 78–86.
Malmaeus, J. M., & Hakanson, L. (2004). Development of a lake eutrophication model. Ecological Modelling, 171, 35–63.
Mobley, C. D. (1999). Estimation on the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Applied Optics, 38(36), 7442–7455.
Moore, T. S., Campbell, J. W., & Feng, H. (2001). A fuzzy logic classification scheme for selecting and blending satellite ocean color algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 39, 1764–1776.
Mueller, J. L., Morel, A., Frouin, R., Davis, C., Arnone, R., Carder, K., et al. (2003). Ocean optics protocols for satellite ocean color sensor validation, revision 4, volume III: Radiometric measurements and data analysis protocols. Maryland: Greenbelt.
Nixon, S. W. (1995). Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia, 41, 199–219.
Poor, N. D. (2010). Effect of lake management efforts on the trophic state of a subtropical shallow lake in Lakeland, Florida, USA. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 207, 333–347.
Pulliainen, J., Kallio, K., Eloheimo, K., Koponen, S., Servomaa, H., Hannonen, T., et al. (2001). A semioperative approach to lake water quality retrieval from remote sensing data. The Science of the Total Environment, 268, 79–93.
Qin, B. Q., Hu, W. P., & Chen, W. M. (2004). The process and mechanism of water environment evolvement in Taihu Lake. Beijing: Science Press.
Ryther, J. H., & Dunstan, W. M. (1971). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science, 171, 1008–1013.
Schindler, D. W. (1977). The evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science, 195, 260–266.
Schindler, D. W., Hecky, R. E., Findlay, D. L., Stainton, M. P., Parker, B. R., Paterson, M. J., et al. (2008). Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37 year whole ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 11254–11258.
Schölkopf, B., Bartlett, P., Smola, A., & Williamson, R. (1998). Support vector regression with automatic accuracy control. In L. Niklasson et al. (Ed.), Proc. Int. Conf. Artif. Neural Netw., Perspectives Neural Comput (pp. 111–116).
Smith, V. H. (2003). Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: a global problem. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 10, 126–139.
Song, K., Li, L., Li, S., Lenore, T., Bob, H., & Li, L. (2012). Hyperspectral remote sensing of total phosphorus (TP) in three central Indiana water supply reservoirs. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(4), 1481–1502.
Sun, D. Y., Li, Y. M., & Wang, Q. (2009). A unified model for remotely estimating chlorophyll a in Lake Taihu, China based on SVM and in situ hyperspectral data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47, 2957–2965.
Sun, D. Y., Li, Y. M., Wang, Q., Le, C. F., Lv, H., Huang, C. C., et al. (2012a). Specific inherent optical quantities of complex turbid inland waters, from the perspective of water classification. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 11, 1299–1312.
Sun, D. Y., Li, Y. M., Wang, Q., Lv, H., Le, C. F., & Huang, C. C. (2012b). A novel SVR model for estimating C-PC concentrations in inland turbid waters using in situ hyperspectral measurements. Hydrobiologia, 680, 199–217.
Sun, D. Y., Li, Y. M., Le, C. F., Shi, K., Huang, C. C., Gong, S. Q., et al. (2013). A semi-analytical approach for detecting suspended particulate composition in complex turbid inland waters (China). Remote Sensing of Environment, 134, 92–99.
Tang, J. W., Tian, G. L., Wang, X. Y., Wang, X. M., & Song, Q. J. (2004). Methods of water spectra measurement and analysis I: above water method. Journal of Remote Sensing, 8(1), 37–44.
Tassan, S. (1994). Local algorithm using SeaWiFS data for the retrieval of phytoplankton pigments, suspended sediment, and yellow substance in coastal waters. Applied Optics, 33(12), 2369–2378.
Tyrrell, T. (1999). The relative influences of nitrogen and phosphorus on oceanic primary production. Nature, 400, 525–531.
Usitalo, R., Yli-Halla, M., & Turtola, E. (2000). Suspended soil as a source of potentially bioavailable phosphorus in surface runoff waters from clay soils. Water Research, 34(9), 2477–2482.
Vapnik, V. N. (1995). The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Spring-Verlag.
Wang, Q., Wu, C. Q., & Li, Q. (2010). Environment satellite 1 and its application in environmental monitoring. Journal of Remote Sensing, 14, 104–121.
Wu, C., Wu, J., Qi, J., Zhang, L., Huang, H., Lou, L., et al. (2010). Empirical estimation of total phosphorus concentration in the mainstream of the Qiantang River in China using Landsat TM data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(9), 2309–2324.
Xu, H., Paerl, H. W., Qin, B., Zhu, G., & Gao, G. (2010). Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(1), 420–432.
Yang, Y., Li, Y. M., Wang, Q., Wang, Y. F., Jin, X., Yin, B., et al. (2010). Retrieval of chlorophyll a concentration by three-band model in Lake Chaohu. Journal of Lake Science, 22(4), 495–503.
Zhan, H. G., Shi, P., & Chen, C. Q. (2003). Retrieval of oceanic chlorophyll concentration using support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41, 2947–2951.
Zhang, T., Fell, F., Liu, Z.-S., Preusker, R., Fisher, J., & He, M. X. (2003). Evaluating the performance of artificial neural network techniques for pigment retrieval from ocean color in case I. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, 3286–3298.
Zhang, B., Li, J. S., Shen, Q., & Chen, D. (2008). A bio-optical model based method of estimating total suspended matter of Lake Taihu from near-infrared remote sensing reflectance. Environment Monitoring and Assessment, 145, 339–347.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a National Natural Science Foundation for Young Scholars (No. 41101340) of China; a Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201005030); an Open Research Fund (No. (11)key04) of the State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing; an Open Research Fund (No. 2011LDE009) of the Key Laboratory of Digital Earth, Center for Earth Observation and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences; a Major Project of University Natural Science (No. 11KJA170003) funded by the Ministry of Education, Jiangsu Province; and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). We show our deep thanks to two anonymous reviewers providing valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Qiu, Z., Li, Y. et al. Detection of Total Phosphorus Concentrations of Turbid Inland Waters Using a Remote Sensing Method. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1953 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1953-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1953-6