Abstract
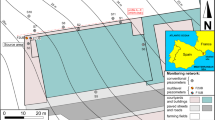
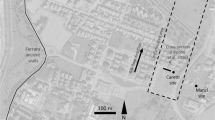
The variability of hydrogeochemical conditions can affect groundwater microbial communities and the natural attenuation of organic chemicals in contaminated aquifers. It is suspected that in situ biodegradation in anoxic plumes of chloroethenes depends on the spatial location of the contaminants and the electron donors and acceptors, as well as the patchiness of bacterial populations capable of reductive dechlorination. However, knowledge about the spatial variability of bacterial communities and in situ biodegradation of chloroethenes in aquifers is limited. Here, we show that changes of the bacterial communities, the distribution of putative dechlorinating bacteria and in situ biodegradation at the border of a chloroethenes plume (Bitterfeld, Germany) are related to local hydrogeochemical conditions. Biotic reductive dechlorination occurred along a 50 m vertical gradient, although significant changes of the hydrogeochemistry and contaminant concentrations, bacterial communities and distribution of putative dechlorinating bacteria (Dehalobacter spp., Desulfitobacterium spp., Dehalococcoides spp., and Geobacter spp.) were observed. The occurrence and variability of in situ biodegradation of chloroethenes were revealed by shifts in the isotope compositions of the chloroethenes along the vertical gradient (δ13C ranging from −14.4‰ to −4.4‰). Our results indicate that habitat characteristics were compartmentalized along the vertical gradient and in situ biodegradation occurred with specific reaction conditions at discrete depth. The polyphasic approach that combined geochemical and biomolecular methods with compound-specific analysis enabled to characterize the spatial variability of hydrochemistry, bacterial communities and in situ biodegradation of chloroethenes in a heterogeneous aquifer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulencia, C. B., Wyborski, D. L., Garcia, J. A., Podar, M., Chen, W. Q., Chang, S. H., et al. (2006). Environmental whole-genome amplification to access microbial populations in contaminated sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(5), 3291–3301.
Becue-Bertaut, M., & Pages, J. (2008). Multiple factor analysis and clustering of a mixture of quantitative, categorical and frequency data. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 52(6), 3255–3268.
Boyd, E. S., Cummings, D. E., & Geesey, G. G. (2007). Mineralogy influences structure and diversity of ba communities associated with geological substrata in a pristine aquifer. Microbial Ecology, 54(1), 170–182.
Bradley, P. M., & Chapelle, F. H. (1996). Anaerobic mineralization of vinyl chloride in Fe(III)-reducing, aquifer sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(6), 2084–2086.
Bradley, P. M., & Chapelle, F. H. (1998). Microbial mineralization of VC and DCE under different terminal electron accepting conditions. Anaerobe, 4, 81–87.
Butler, E. C., & Hayes, K. F. (1999). Kinetics of the transformation of trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylene by iron sulfide. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(12), 2021–2027.
Carreon-Diazconti, C., Santamaria, J., Berkompas, J., Field, J. A., & Brusseau, M. L. (2009). Assessment of in situ reductive dechlorination using compound-specific stable isotopes, functional gene PCR, and geochemical data. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(12), 4301–4307.
Chapelle, F., Zelibor, J. Jr, Grimes, D., Knobel, L. (1987). Bacteria in deep coastal plain sediments of Maryland: a possible source of CO2 to groundwater. Water Resources Research, 23, 1625–1632.
Chartrand, M. M. G., Waller, A., Mattes, T. E., Elsner, M., Lacrampe-Couloume, G., Gossett, J. M., et al. (2005). Carbon isotopic fractionation during aerobic vinyl chloride degradation. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(4), 1064–1070.
Chu, K. H., Mahendra, S., Song, D. L., Conrad, M. E., & Alvarez-Cohen, L. (2004). Stable carbon isotope fractionation during aerobic biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(11), 3126–3130.
Cole, J. R., Chai, B., Marsh, T. L., Farris, R. J., Wang, Q., Kulam, S. A., et al. (2003). The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Research, 31(1), 442–443.
Connon, S. A., Tovanabootr, A., Dolan, M., Vergin, K., Giovannoni, S. J., & Semprini, L. (2005). Bacterial community composition determined by culture-independent and -dependent methods during propane-stimulated bioremediation in trichloroethene-contaminated groundwater. Environmental Microbiology, 7(2), 165–178.
Coplen, T. B., Brand, W. A., Gehre, M., Groning, M., Meijer, H. A. J., Toman, B., et al. (2006). New guidelines for delta C-13 measurements. Analytical Chemistry, 78(7), 2439–2441.
Cunningham, J. A., & Fadel, Z. J. (2007). Contaminant degradation in physically and chemically heterogeneous aquifers. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 94(3–4), 293–304.
Duhamel, M., & Edwards, E. A. (2006). Microbial composition of chlorinated ethene-degrading cultures dominated by Dehalococcoides. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 58(3), 538–549.
Eaddy, E.A. (2008). Scale-up and characterization of an enrichment culture for bioaugmentation of the P-area chlorinated ethene plume at the Savannah river site. M.S. thesis, Clemson University, Clemson
Escofier, B., & Pages, J. (1994). Multiple factor-analysis (Afmult Package). Computational statistics and data analysis, 18(1), 121–140.
Eyers, L., George, I., Schuler, L., Stenuit, B., Agathos, S., & El Fantroussi, S. (2004). Environmental genomics: exploring the unmined richness of microbes to degrade xenobiotics. Applied Microbiology and Technology, 66(2), 123–130.
Fagervold, S. K., May, H. D., & Sowers, K. R. (2007). Microbial reductive dechlorination of aroclor 1260 in Baltimore Harbor sediment microcosms is catalyzed by three phylotypes within the phylum Chloroflexi. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(9), 3009–3018.
Feris, K., Hristova, K., Gebreyesus, B., Mackay, D., & Scow, K. (2004). A shallow BTEX and MTBE contaminated aquifer supports a diverse microbial community. Microbial Ecology, 48(4), 589–600.
Goldscheider, N., Hunkeler, D., & Rossi, P. (2006). Review: Microbial biocenoses in pristine aquifers and an assessment of investigative methods. Hydrogeology Journal, 14(6), 926–941.
Grossmann, J., Poetke, D., Nitschke, F., Drangmeister, J., Oelmann, D., Hirsch, D., Dommaschk, K., & Naue, F. (2009). Fortschreibung Sanierungsrahmenkonzept Landesanstalt für Altlasten Freistellung, Bitterfeld-Wolfen. Fortschreibung Sanierungsrahmenkonzept SRK8, Internal reports, Ökologisches Grossprojekt Bitterfeld-Wolfen.Grossman Ingenieur Consult GmbH, Dresden, Germany.
Haack, S. K., & Bekins, B. A. (2000). Microbial populations in contaminant plumes. Hydrogeology Journal, 8(1), 63–76.
Heidrich, S., Weiss, H., & Kaschl, A. (2004). Attenuation reactions in a multiple contaminated aquifer in Bitterfeld (Germany). Environmental Pollution, 129, 277–288.
Hendrickson, E., Payne, J., Young, R., Starr, M., Perry, M., Fahnestock, S., et al. (2002). Molecular analysis of Dehalococcoides 16S ribosomal DNA from chloroethene-contaminated sites throughout north America and Europe. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(2), 485–495.
Heuer, H., Krsek, M., Baker, P., Smalla, K., & Wellington, E. M. H. (1997). Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63(8), 3233–3241.
Huang, L., Sturchio, N. C., Abrajano, T., Heraty, L. J., & Holt, B. D. (1999). Carbon and chlorine isotope fractionation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons by evaporation. Organic Geochemistry, 30((8A), 777–785.
Hunkeler, D., Aravena, R., & Butler, B. (1999). Monitoring microbial dechlorination of tetrachloroethene (PCE) in groundwater using compound-specific stable carbon isotope ratios: Microcosm and field studies. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(16), 2733–2738.
Imfeld, G., Estop, C., Fetzer, I., Mészáros, E., Zeiger, S., Nijenhuis, I., et al. (2010). Characterization of microbial communities in the aqueous phase of a constructed model wetland treating 1, 2-dichloroethene-contaminated groundwater. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 72, 74–88.
Imfeld, G., Nijenhuis, I., Nikolausz, M., Zeiger, S., Paschke, H., Drangmeister, J., et al. (2008). Assessment of in situ degradation of chlorinated ethenes and bacterial community structure in a complex contaminated groundwater system. Water Research, 42, 871–882.
Jeong, H. Y., & Hayes, K. F. (2007). Reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene by mackinawite (FeS) in the presence of metals: Reaction rates. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(18), 6390–6396.
Kleikemper, J., Schroth, M. H., Sigler, W. V., Schmucki, M., Bernasconi, S. M., & Zeyer, J. (2002). Activity and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(4), 1516–1523.
Lane, D. J. (1991). 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In E. Stackebrandt & M. Goodfellow (Eds.), Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. New York: Wiley.
Lehman, R. M. (2007). Understanding of aquifer microbiology is tightly linked to sampling approaches. Geomicrobiology Journal, 24(3–4), 331–341.
Lehman, R. M., & O'Connell, S. P. (2002). Comparison of extracellular enzyme activities and community composition of attached and free-living bacteria in porous medium columns. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(4), 1569–1575.
Löffler, F. E., Sun, Q., Li, J. R., & Tiedje, J. M. (2000). 16S rRNA gene-based detection of tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating Desulfuromonas and Dehalococcoides species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(4), 1369–1374.
Maymo-Gatell, X., Chien, Y. T., Gossett, J. M., & Zinder, S. H. (1997). Isolation of a bacterium that reductivley dechlorinates tetrachloroethene to ethane. Science, 276(5318), 1568–1571.
McCarty, P., & Semperini, L. (1994). Groundwater treatment for chlorinated solvents. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Meckenstock, R., Morasch, B., Griebler, C., & Richnow, H. (2004). Stable isotope fractionation analysis as a tool to monitor biodegradation in contaminated acquifers. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 75(3–4), 215–255.
Morrill, P. L., Sleep, B. E., Slater, G. F., Edwards, E. A., & Lollar, B. S. (2006). Evaluation of isotopic enrichment factors for the biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes using a parameter estimation model: Toward an improved quantification of biodegradation. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(12), 3886–3892.
Mouser, P. J., Rizzo, D. M., Röling, W. F. M., & Van Breukelen, B. M. (2005). A multivariate statistical approach to spatial representation of groundwater contamination using hydrochemistry and microbial community profiles. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(19), 7551–7559.
Nijenhuis, I., Nikolausz, M., Koth, A., Felfolfi, T., Weiss, H., Drangmeister, J., et al. (2007). Assessment of the natural attenuation of chlorinated ethenes in an anaerobic contaminated aquifer in the Bitterfeld/Wolfen area using stable isotope techniques, microcosm studies and molecular biomarkers. Chemosphere, 67(2), 300–311.
Nocker, A., Burr, M., & Camper, A. K. (2007). Genotypic microbial community profiling: A critical technical review. Microbial Ecology, 54(2), 276–289.
Nubel, U., Engelen, B., Felske, A., Snaidr, J., Wieshuber, A., Amann, R. I., et al. (1996). Sequence heterogeneities of genes encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa detected by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. Journal of Bacteriology, 178(19), 5636–5643.
Oksanen, J., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., O’Hara, R., Simpson, G., Solymos, P., Stevens, M., & Wagner, H. (2008). Vegan: community ecology package version 1.15-1. Available at: http://cran.r-project.org.
Poulson, S. R., & Drever, J. I. (1999). Stable isotope (C, Cl, and H) fractionation during vaporization of trichloroethylene. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(20), 3689–3694.
Röling, W. F. M., van Breukelen, B. M., Braster, M., Lin, B., & van Verseveld, H. W. (2001). Relationships between microbial community structure and hydrochemistry in a landfill leachate-polluted aquifer. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(10), 4619–4629.
Rossi, P., Gillet, F., Rohrbach, E., Diaby, N., & Holliger, C. (2009). Statistical assessment of variability of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis applied to complex microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(22), 7268–7270.
Schlotelburg, C., von Wintzingerode, C., Hauck, R., von Wintzingerode, F., Hegemann, W., & Gobel, U. (2002). Microbial structure of an anaerobic bioreactor population that continuously dechlorinates 1, 2-dichloropropane. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 39(3), 229–237.
Schüth, C., Taubald, H., Bolano, N., & Maciejczyk, K. (2003). Carbon and hydrogen isotope effects during sorption of organic contaminants on carbonaceous materials. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 64(3–4), 269–281.
Seshadri, R., Adrian, L., Fouts, D., Eisen, J., Phillippy, A., Methe, B., et al. (2005). Genome sequence of the PCE-dechlorinating bacterium Dehalococcoides ethenogenes. Science, 307(5706), 105–108.
Sherwood Lollar, B. S., Slater, G. F., Witt, M. B., Klecka, G. M., Harkness, M. R., & Spivack, J. (2001). Stable carbon isotope evidance for intrinsic bioremediation of tetrachloroethene and trichloroethene at Area 6, Dover Air Force Base. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 261–269.
Smalla, K., Oros-Sichler, M., Milling, A., Heuer, H., Baumgarte, S., Becker, R., et al. (2007). Bacterial diversity of soils assessed by DGGE, T-RFLP and SSCP fingerprints of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments: Do the different methods provide similar results? Journal of Microbiological Methods, 69(3), 470–479.
Stelzer, N., Imfeld, G., Thullner, M., Lehmann, J., Poser, A., Richnow, H. H., et al. (2009). Integrative approach to delineate natural attenuation of chlorinated benzenes in anoxic aquifers. Environmental Pollution, 157(6), 1800–1806.
Sung, Y., Fletcher, K. F., Ritalaliti, K. M., Apkarian, R. P., Ramos-Hernandez, N., Sanford, R. A., et al. (2006). Geobacter lovleyi sp nov strain SZ, a novel metal-reducing and tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating bacterium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(4), 2775–2782.
Sung, Y., Ritalahti, K. M., Sanford, R. A., Urbance, J. W., Flynn, S. J., Tiedje, J. M., et al. (2003). Characterization of two tetrachloroethene-reducing, acetate-oxidizing anaerobic bacteria and their description as Desulfuromonas michiganensis sp nov. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(5), 2964–2974.
Ulrich, G., Martino, D., Burger, K., Routh, J., Grossman, E., Ammerman, J., et al. (1998). Sulfur cycling in the terrestrial subsurface: commensal interactions, spatial scales, and microbial heterogeneity. Microbial Ecology, 36, 141–151.
Vainberg, S., Condee, C. W., & Steffa, R. J. (2009). Large-scale production of bacterial consortia for remediation of chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Technology, 36(9), 1189–1197.
Vogel, T. M. (1994). Natural bioremediation of chlorinated solvents. In R. D. Norris, R. E. Hinchee, R. Brown, P. L. McCarty, L. Semprini, D. H. Wilson, M. Kampbell, E. G. Reinhard, R. Bouwer, C. Borden, T. M. Vogel, J. M. Thomas, & C. H. Ward (Eds.), Handbook of bioremediation (pp. 201–225). Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Watts, J. E. M., Fagervold, S. K., May, H. D., & Sowers, K. R. (2005). A PCR-based specific assay reveals a population of bacteria within the Chloroflexi associated with the reductive dehalogenation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Microbiology-SGM, 151, 2039–2046.
Weiss, J. V., & Cozzarelli, I. M. (2008). Biodegradation in contaminated aquifers: incorporating microbial/molecular methods. Ground Water, 46(2), 305–322.
Wilson, R. D., Thornton, S. F., & Mackay, D. M. (2004). Challenges in monitoring the natural attenuation of spatially variable plumes. Biodegradation, 15(6), 359–369.
Wycisk, P., Weiss, H., Kaschl, A., Heidrich, S., & Sommerwerk, K. (2003). Groundwater pollution and remediation options for multi-source contaminated aquifers (Bitterfeld/Wolfen, Germany). Toxicology Letters, 140–141, 343–351.
Acknowledgments
Gwenaël Imfeld was supported by a European Union Marie Curie Early-Stage Training Fellowship (AXIOM, contract no. MEST-CT-2004-8332) fellowship. The Department of Groundwater Remediation and the SAFIRA Project of the UFZ are acknowledged for organizing field work. We wish to thank to M. Gehre, U. Günther, K. Ethner, and S. Täglich for their technical support in analytical and stable isotope measurements and F. Gillet for his support in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imfeld, G., Pieper, H., Shani, N. et al. Characterization of Groundwater Microbial Communities, Dechlorinating Bacteria, and In Situ Biodegradation of Chloroethenes Along a Vertical Gradient. Water Air Soil Pollut 221, 107–122 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0774-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0774-0