Abstract
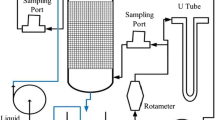
The biofilter system containing tire-derived rubber particle (TDRP) filter media was utilized to treat the odorous gas contaminant, hydrogen sulfide, in consideration of the economic advantage of reusing discarded tire materials and the high potential of TDRP media for biofilm attachment. The pilot-scale system having 0.38 m3 of bed volume operated with synthetic hydrogen sulfide gas on continuous basis from a range of 0.34 to 1.15 m3/min. This bioreactor system achieved over 94% removal efficiency at 20–90 ppm of inlet H2S concentration while operating in 20–67 s of empty bed retention time, indicating that overall effective operation was performed at mass loading rates of H2S ranging from 19.6 to 28.5 g H2S/(m3 h). It was apparent by the effectiveness of the system’s performance that this system had the capability to effectively remove hydrogen sulfide with high efficiency over a range of concentrations. A maximum elimination capacity was not found for the biofilter during this study, which tested loading rates between 0 and 30 g H2S/(m3 h).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbin, W. W., & Rodgers, M. B. (1994). The science of rubber compounding. In J. E. Mark, B. Erman, & F. R. Eirich (Eds.), Science and technology of rubber (pp. 419–469). San Diego: Academic.
Burgess, J. E., Parsons, A. A., & Stuetz, R. M. (2001). Developments in odour control and waste gas treatment biotechnology: A review. Biotechnology Advances, 19(35), 36–63.
Chung, Y.-C., Huang, C., & Tseng, C.-P. (1996). Operation optimization of Thiobacillus thioparus CH11 biofilter for hydrogen sulfide removal. Journal of Biotechnology, 52(1), 31–38.
Droste, R. L. (1997). Theory and practice of water and wastewater treatment. New York: Wiley.
Duan, H., Koe, L. C. C., et al. (2006). Biological treatment of H2S using pellet activated carbon as a carrier of microorganisms in a biofilter. Water Research, 40(14), 2629–2636.
Gabriel, D., Cox, H. H. J., & Deshusses, M. A. (2004). Conversion of full-scale wet scrubbers to biotrickling filters for H2S control at publicly owned treatment works. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 130(10), 1110.
Hansen, N. G., & Rindel, K. (2000). Bioscrubbing, an effective and economic solution to odour control at wastewater treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 41(6), 155.
Hirai, M., Kamamoto, M., et al. (2001). Comparison of the biological H2S removal characteristics among four inorganic packing materials. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 91(4), 396–402.
Jensen, A. B., & Webb, C. (1995). Treatment of H2S-containing gases: A review of microbiological alternatives. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 17, 2–10.
Koe, L. C. C., & Yang, F. (2000). A bioscrubber for hydrogen sulfide removal. Water Science and Technology, 41(6), 141.
Luo, J., & Lindsey, S. (2006). The use of pine bark and natural zeolite as biofilter media to remove animal rendering process odours. Bioresource Technology, 97(13), 1461–1469.
Moo-Young, H., Sellasie, K., et al. (2003). Physical and chemical properties of recycled tire shreds for use in construction. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 129(10), 921–929.
Morton, R., Lee, A., Tang, C. C., Horvath, R., & Stahl J. (2005) A two-stage biotrickling filter system for odors and volatile organic compounds removal. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation 73rd Annual Conference and Exposition, Washington, DC.
Nishimura, S., & Yoda, M. (1997). Removal of hydrogen sulfide from an anaerobic biogas using a bio-scrubber. Water Science and Technology, 36(6–7), 349.
Oh, D. I., Song, J., et al. (2009). Effects of adsorptive properties of biofilter packing materials on toluene removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(1), 144–150.
Pagans, E., Font, X., et al. (2007). Adsorption, absorption, and biological degradation of ammonia in different biofilter organic media. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 97(3), 515–525.
Park, J., Ellis T. G., Lally, M. (2006). Evaluation of tire derived rubber particles for biofiltration media. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation 74rd Annual Conference and Exposition, Dallas, TX.
Potivichayanon, S., Pokethitiyook, P., & Kruarachue, M. (2006). Hydrogen sulfide removal by a novel fixed-film bioscrubber system. Process Biochemistry, 41, 708.
Qiao, S., & Fu, L. et al. (2008). Removal characteristics of hydrogen sulfide in biofilters with fibrous peat and resin. In 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE.
Saliling, W. J. B., Westerman, P. W., et al. (2007). Wood chips and wheat straw as alternative biofilter media for denitrification reactors treating aquaculture and other wastewaters with high nitrate concentrations. Aquacultural Engineering, 37(3), 222–233.
Seda, J. H., Lee, J. C., et al. (2007). Beneficial use of waste tire rubber for swelling potential mitigation in expansive soils. Soil improvement (GSP 172). Denver: ASCE.
Shanchayan, B., Parker, W., et al. (2006). Dynamic analysis of a biofilter treating autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion gas. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 5(3), 263–272.
Shareefdeen, Z., Herner B., et al. (2003). Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) removal in synthetic media biofilters. Environmental progress, 22(3), 207–213.
Shareefdeen, Z., & Singh, A. (2005). Biotechnology for odor and air pollution control. New York: Springer.
Subletle, K. L., & Sylvester, N. D. (1987). Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide by Thiobacillus denitrificans: Desulfurization of natural gas. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 29, 249.
Wolstenholme, P., & Schafer, P. (2005) Odor control bioscrubbers. A 20 year history of successful applications. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation 73rd Annual Conference and Exposition, Washington, DC
Yang, C., Chen, H., et al. (2009). Modeling variations of medium porosity in rotating drum biofilter. Chemosphere, 74(2), 245–249.
Yang, C., Suidan, M. T., et al. (2003). Comparison of single-layer and multi-layer rotating drum biofilters for VOC removal. Environmental Progress, 22(2), 87–94.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to Envirotech Systems, Inc., for providing TDRP media, financing this research, and otherwise supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Evans, E.A. & Ellis, T.G. Development of a Biofilter with Tire-Derived Rubber Particle Media for Hydrogen Sulfide Odor Removal. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 145–153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0466-1