Abstract
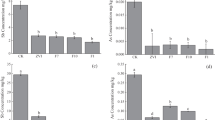
Stability and transport of As species in soils were investigated in three contaminated Central European regions in the Czech Republic; one of them represents naturally contaminated area, the others are results of a former mining activity. Total As content varied from 60 to <18,000 ppm depending on locality and sampling layer. Sequential extraction procedure (SEP) enabled to distinguish five main fractions of As in soils based on different chemical and binding properties. Non-specifically and weakly sorbed As, as well as As remained in solid rests of samples did not exceed 10% of total As; specifically bounded As varied from 5 to 15%. The substantial portion of As was bound to hydrated Fe oxides (HFO) in amorphous and poorly-crystalline forms (10–30% of the total As) and/or to a well-crystallized forms of the same phases (50–80%). As sorption on HFO surface, particularly on well-crystallized phases represented the most significant and stable As bond in soils. Model leaching experiments illustrated the increased mobility of As species at pH ≈ 7.0 in the soil–groundwater–surface water systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, X., Ma, L. Q., & Shiralipour, A. (2003). Effect of compost and phosphate amendments on arsenic mobility in soils and arsenic uptake by the hyperaccumulator, Pteris vittata L. Environmental Pollution, 126, 157–167.
Carbonell-Barrachina, A., Jugsujinda, A., DeLaune, R. D., Patrick, W. H., Burló, F., & Sirisukhodom, S., et al. (1999). The influence of redox chemistry and pH on chemically active forms of arsenic in sewage sludge-amended soil. Environment International, 25(5), 613–618.
Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (1989). Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chemical Reviews, 89, 713–764.
Davis, C. C., Knocke, W. R., & Edwards, M. (2001). Implications of aqueous silica sorption to iron hydroxide: Mobilization of iron colloids and interference with sorption of arsenate and humic Substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 2158–2162.
Doušová, B. (1989). Biogeochemical cycle of arsenic from the point of view of atmospheric processes. PhD Thesis, ÚGG CSAS Prague, Czech Republic (in Czech).
Doušová, B., Koloušek, D., Kovanda, F., Machovič, V., & Novotná, M. (2005). Removal of As(V) species from extremely contaminated mining water. Applied Clay Science, 28, 31–42.
Doušová, B., Machovič, V., Koloušek, D., Kovanda, F., & Dorničák, V. (2003). Sorption of As(V) species from aqueous systems. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 149, 251–267.
Fernández, P., Sommer, I., Cram, S., Rosas, I., & Gutiérrez, M. (2005). The influence of water-soluble As(III) and As(V) on dehydrogenase activity in soils affected by mine tailings. Science of the Total Environment, 348, 231–243.
Filippi, M. (2004). Oxidation of the arsenic-rich concentrate at the Přebuz abandoned mine (Erzgebirge Mts., CZ): Mineralogical evolution. Science of the Total Environment, 322(1–3), 271–282.
Filippi, M., Goliáš, V., & Pertold, Z. (2004). Arsenic in contaminated soils and anthropogenic deposits at the Mokrsko, Roudný and Kašperské Hory gold deposits, Bohemian Massif (CZ). Environmental Geology, 45, 716–730.
Goldberg, S. (2002). Competitive adsorption of arsenate and arsenite on oxides and clay minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 413–421.
Grafe, M., Eick, M. J., & Grossl, P. R. (2001). Adsorption of arsenate (V) and arsenite (III) on goethite in the presence and absence of dissolved organic carbon. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 1680–1687.
Gustaffson, J. P., & Jacks, G. (1995). Arsenic geochemistry in forested soil profiles as relevated by solid-phase studies. Applied Geochemistry, 10, 307–315.
Han, F. X., & Banin, A. (1995). Selective sequential dissolution techniques for trace metals in arid-zone soils: The carbonate dissolution step. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 26(3&4), 553–576.
Keegan, T. J., Farago, M. E., Thornton, I., Hong, B., Colvile, R. N., & Pesch, B., et al. (2006). Dispersion of As and selected heavy metals around a coal-burning power station in central Slovakia. Science of the Total Environment, 358, 61–71.
Keon, N. E., Swartz, C. H., Brabander, D. J., Harvey, C., & Hemond, H. F. (2001). Validation of an arsenic sequential extraction method for evaluating mobility in sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 2778–2784.
Ko, I., Kim, J. Y., & Kim, K. W. (2004). Arsenic speciation and sorption kinetics in the As-hematite-humic acid system. Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 234, 43–50.
Lumsdon, D. G., Meeussen, J. C. L., Paterson, E., Garden, L. M., & Anderson, P. (2001). Use of solid phase characterisation and chemical modelling for assessing the behaviour of arsenic in contaminated soils. Applied Geochemistry, 12, 571–581.
Manning, B. A., Fendorf, S. E., & Goldberg, S. (1998). Surface structures and stability of arsenic(III) on goethite: Spectroscopic evidence for inner-sphere complexes. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 2383–2388.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996). Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 121–131.
Matera, V., Le Hécho, I., Laboudigue, A., Thomas, P., Tellier, S., & Astruc, M. (2003). A methodological approach for the identification of arsenic bearing phases in polluted soils. Environmental Pollution, 126, 51–64.
Matschullat, J. (2000). Arsenic in the geosphere – A review. Science of the Total Environment, 249, 297–312.
Mihaljevič, M., Sisr, L., Ettler, V., Šebek, O., & Průša, J. (2004). Oxidation of as-bearing gold ore – A comparison of batch and column experiments. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 81(1–3), 59–70.
Mihaljevič, M., Poňavič, M., Ettler, V., & Šebek, O. (2003). A comparison of sequential extraction techniques for determining arsenic fractionation in synthetic mineral mixtures. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 377, 723–729.
Morávek, P., Janatka, P., Pertoldová, J., Straka, J., Ďurišová, J., & Pudilová, M. (1989). Mokrsko gold deposit – The largest gold deposit in the Bohemian Massif, Czechoslovakia. Economic Geology Monographs, 6, 252–259.
Randall, S. R., Sherman, D. M., & Ragnarsdottir, K. V. (2001). Sorption of As(V) on green rust (Fe4(II)Fe2(III)(OH)12SO4. 3H2O) and lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH): Surface complexes from EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 65 (7), 1015– 1023
Sherman, D. M., & Randall, S. (2003). Surface complexation of arsenic(V) to iron(III) (hydr)oxides: Structural mechanism from ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS Spectroscopy. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(22), 4223–4230.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Štyriaková, I., Štyriak, I., Kraus, I., Hradil, D., Grygar, T., & Bezdička, Biodestruction and deferritization of quartz sands by Bacillus species. Minerals Engineering, 16, 709–713.
Taggart, M. A., Carlisle, M., Pain, D. J., Williams, R., Osborn, D., & Joyson, A., et al. (2004). The distribution of arsenic in soils affected by the Aznalcóllar mine spill, SW Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 323(1–3), 137–152.
Thomaidis, N. S., Bakeas, E. B., & Siskos, P. A. (2003). Characterization of lead cadmium arsenic and nickel in PM2.5 particles in the Athens atmosphere, Greece. Chemosphere, 52, 956–966.
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Soil pH and soil acidity. In J. M. Bigham (Ed.) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3, chemical methods (pp. 475–489). Madison, WI, USA: SSSA - Book Series no. 5.
Voigt, D. E., & Brantley, S. L. (1996). Chemical fixation of arsenic in contaminated soils. Applied Geochemistry, 11, 633–643.
Warwick, P., Inam, E., & Evans, N. (2005). Arsenics interaction with humic acid. Environment & Chemistry, 2, 119–124.
Wenzel, W. W., Kirchbaumer, N., Prohaska, T., Stingeder, G., Lombi, E., & Adriano, D. C. (2001). Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 436, 309–323.
Williams, J. D., Stera, J. K., & Walker, T. W. (1967). Fractionation of solid inorganic phosphate by a modification of Chang and Jackson’s procedure. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc, 31, 736–739.
Yamamura, S., Ike, M., & Fujita, M. (2003). Dissimilatory arsenate reduction by a facultative anaerobe, Bacillus sp. Strain SF-1. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 96(5), 454–460.
Yunosuke, H., Hori, T., & Sugiyama, M. (2005). Release of trace oxyanions from littoral sediments and suspended particles included by pH increase in the epilimnion of lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 50(2), 636–645.
Zeng, T., Sarofim, A. F., & Senior, C. L. (2001). Vaporization of arsenic, selenium and antimony during coal combustion. Combustion and Flame, 126, 1714–1724.
Zhang, W., Singh, P., Paling, E., & Delides, S. (2004). Arsenic removal from contaminated water by natural iron ores. Minerals Engineering, 17, 517–524.
Acknowledgements
This work was part of the Research programme MSM 6046137302 (CR) and Institutional Research Plan no. AV0Z30130516 (Institute of Geology, AS CR, Prague).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doušová, B., Martaus, A., Filippi, M. et al. Stability of Arsenic Species in Soils Contaminated Naturally and in an Anthropogenic Manner. Water Air Soil Pollut 187, 233–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9511-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9511-0