Abstract
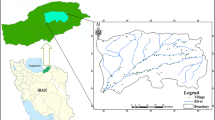
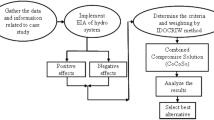
The state of a watershed is determined by its hydrological conditions, which themselves are dependent on the security of the individual components of the watershed such as economic, social, ecological and infrastructure. While the role of stakeholders in watershed management is vital and their opinions are very effective in management and the assessment of watershed hydrological security (WHS). Therefore, this research aims to evaluate WHS from economic and social perspectives based on stakeholder opinions surrounding the Gorganroud watershed in Iran. The multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) models including VlseKriterijumska Optimizcija I Kaompromisno Resenje (VIKOR), Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution (TOPSIS), Simple Additive Weighting (SAW), Complex Proportional Assessment (COPRAS), and Elimination and Choice in Translating to Reality (ELECTRE) were used to prioritize the sub-watersheds according to eight economic, social, and infrastructural variables. Shannon's entropy was used to compute the weight of these variables in the MCDM models. To validate the models, the percentage of variation (∆P) and intensity of variation (∆I) were used. The results showed that the application of indigenous knowledge in water management had the highest entropy with a weight of 0.327 (33%). The water-dependent livelihoods variable had the lowest entropy and weight but was still considered a key variable in WHS due to its consistently high scores among stakeholders. When ranking the sub-watersheds in terms of WHS, the sub-watersheds A9 and A3 were ranked first and last, respectively, for all five MCDM models, with the rankings of the other sub-watersheds differing between the models. A comparison of the evaluation indices showed that COPRAS (∆P = 38.75) and ELECTRE (∆I = 4.805) were the best-performing MCDM models for the WHS ranking of the Gorganroud watershed. The strategy proposed by the present study can facilitate the effective management of the Gorganroud watershed and ensure its sustainable development, and also provide the possibility of effective application of this strategy in another watersheds.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data Availability
The data will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aghajani Mir M, Taherei Ghazvinei P, Sulaiman NMN, Basri NEA, Saheri S, Mahmood NZ, Jahan A, Begum RA, Aghamohammadi N (2016) Application of TOPSIS and VIKOR improved versions in a multi criteria decision analysis to develop an optimized municipal solid waste management model. J Environ Manage 166:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.028
Akbari M, Meshram SG, Krishna RS, Pradhan B, Shadeed S, Khedher KM, Sepehri M, Ildoromi AR, Alimerzaei F, Darabi F (2021) Identification of the groundwater potential recharge zones using MCDM models: Full Consistency Method (FUCOM), Best Worst Method (BWM) and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Water Resour Manage 35:4727–4745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02924-1
Azari M, Saghafian B, Moradi HR, Faramarzi M (2017) Effectiveness of soil and water conservation practices under climate change in the Gorganroud basin. Iran Clean - Soil, Air, Water 45:1700288. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201700288
Bielinskas V, Burinskienė M, Palevičius V (2015) Assessment of neglected areas in Vilnius City using MCDM and COPRAS methods. Procedia Eng 122:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.10.004
Bin O, Shuyan F, Yu W, Liping W (2012) The comprehensive evaluation of rural drinking water security in Yunnan Province. Procedia Earth Planetary Sci 5:155–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2012.01.027
Carpenter S, Walker B, Anderies JM, Abel N (2001) From metaphor to measurement: Resilience of what to what? Ecosystems 4:765–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-001-0045-9
Chang CL, Hsu CH (2009) Multi-criteria analysis via the VIKOR method for prioritizing land-use restraint strategies in the Tseng-Wen reservoir watershed. J Environ Manage 90:3226–3230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.020
Chang CL, Lin YT (2014) Using the VIKOR method to evaluate the design of a water quality monitoring network in a watershed. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0195-2
Chen S-J, Hwang CL, Hwang FP (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making (methods and applications). Lect Notes Econ Math Syst 375:289–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46768-4_5
Dong J, Huo H, Liu D, Li R (2017) Evaluating the comprehensive performance of demand response for commercial customers by applying combination weighting techniques and fuzzy VIKOR approach. Sustain (Switzerland) 9:1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081332
Firdaus R, Nakagoshi N, Idris A (2014) Sustainability assessment of humid tropical watershed: A case of Batang Merao watershed, Indonesia. Procedia Environ Sci 20:722–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2014.03.086
Gebre SL, Cattrysse D, Van Orshoven J (2021) Multi-criteria decision-making methods to address water allocation problems: A systematic review. Water (switzerland) 13:125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020125
Heathcote IW (1998) Integrated watershed management: Principles and practice. In Other Information: PBD: 1998.
Hepelwa AS (2014) Dynamics of watershed ecosystem values and sustainability: An integrated assessment approach. Int J Ecosyst 4:43–52
Hernández-Delgado EA (2015) The emerging threats of climate change on tropical coastal ecosystem services, public health, local economies and livelihood sustainability of small islands: Cumulative impacts and synergies. Mar Pollut Bull 101:5–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.018
Ikram RMA, Meshram SG, Hasan MA, Cao X, Alvandi E, Meshram C, Islam S (2024) The application of multi-attribute decision making methods in integrated watershed management. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 38(1):297–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02557-3
Khoie MMM, Nasseri M, Banihashemi MA (2023) Determining the spatial contributions of land use changes on the streamflow and sediment transport regimes: a case study of the Gorganroud watershed in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:45029–45045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25478-8
Kumar B, Roy D, Kumar S, Kumar A (2024) Entropy-weighted-multi-criteria decision-making (E-MCDM) approach for erosion area prioritization: case study of a Himalayan River Basin. In: Agri-tech approaches for nutrients and irrigation water management. CRC Press, pp 153–187
Lawshe CH (1975) A quantitative approach to content validity. Pers Psychol 4:563–575. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.1975.tb01393.x
Lee CS (2012) Multi-objective game-theory models for conflict analysis in reservoir watershed management. Chemosphere 87:608–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.014
Li S, Liu H (2022) Spatio-temporal pattern evolution of coupling coordination between urbanization and ecological resilience in arid region: A case of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Arid Land Geogr 4:1281–1290. https://doi.org/10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2021.563
Li XS, Peng ZY, Li TT (2016) An evaluation index system of water security in China based on macroeconomic data from 2000 to 2012. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 1:012045. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/39/1/012045
Mahmoodi E, Azari M, Dastorani MT (2023) Comparison of different objective weighting methods in a multi-criteria model for watershed prioritization for flood risk assessment using morphometric analysis. J Flood Risk Manage 2:12894. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12894
Malekian A, Azarnivand A (2016) Application of integrated Shannon’s entropy and VIKOR techniques in prioritization of flood risk in the Shemshak watershed. Iran Water Resour Manage 1:409–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1169-6
Meshram SG, Singh VP, Kahya E, Alvandi E, Meshram C, Sharma SK (2020) The feasibility of multi-criteria decision making approach for prioritization of sensitive area at risk of water erosion. Water Resour Manage 34:4665–4685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02681-7
Meshram SG, Adhami M, Kisi O, Meshram C, Duc PA, Khedher KM (2021) Identification of critical watershed for soil conservation using game theory-based approaches. Water Resour Manage 35:3105–3120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02856-w
Meshram SG, Singh VP, Kahya E, Sepehri M, Meshram C, Hasan MA, Islam S, Duc PA (2022) Assessing erosion prone areas in a watershed using interval rough-analytical hierarchy process (IR-AHP) and fuzzy logic (FL). Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 36:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02134-6
Mosaffaie J, Salehpour Jam A, Tabatabaei MR, Kousari MR (2021) Trend assessment of the watershed health based on DPSIR framework. Land Use Policy 100:104911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104911
Mulliner E, Malys N, Maliene V (2016) Comparative analysis of MCDM methods for the assessment of sustainable housing affordability. Omega 59:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.05.013
Nasiri Khiavi A, Vafakhah M, Sadeghi SH (2023) Comparative applicability of MCDM-SWOT based techniques for developing integrated watershed management framework. Nat Resour Model 36:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12380
Nasiri Khiavi A, Vafakhah M, Sadeghi SH (2023) Flood-based critical sub-watershed mapping: comparative application of multi-criteria decision-making methods and hydrological modeling approach. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 37:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02417-0
Nguyen HT, Md Dawal SZ, Nukman Y, Aoyama H, Case K (2015) An integrated approach of fuzzy linguistic preference based AHP and fuzzy COPRAS for machine tool evaluation. PLoS ONE 10:133599. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133599
Nguyen NM, Bahramloo R, Sadeghian J, Sepehri M, Nazaripouya H, Nguyen Dinh V, Ghahramani A, Talebi A, Elkhrachy I, Pande CB, Meshram SG (2023) Ranking Sub-watersheds for flood hazard mapping: A multi-criteria decision-making approach. Water (switzerland) 15:2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112128
Nie RX, Wang JQ, Wang TL (2018) A hybrid outranking method for greenhouse gas emissions’ institution selection with picture 2-tuple linguistic information. Comput Appl Math 37:6676–6699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-018-0708-1
Norouzi Nazar MS, Asadolahi Z, Rabbani F, Abbaspour KC, Sakieh Y (2023) Modeling the integrated effects of landuse and climate change on the hydrologic response of Gorganroud watershed in Iran. Theoret Appl Climatol 151:1687–1707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04345-5
Olii MR, Olii AKZ, Olii A, Pakaya R, Kironoto BA (2024) Spatial modeling of soil erosion risk: a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) approach in the paguyaman watershed, gorontalo. Indones Arab J Geosci 17(7):226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-12032-0
Opricovic S (1998) Multicriteria optimization of civil engineering systems. Fac Civil Eng Belgrade 2:5–21
Pal S, Debanshi S (2021) Developing wetland landscape insecurity and hydrological security models and measuring their spatial linkages. Ecol Inform 66:101461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101461
Pham TM, Dinh HT, Pham TA, Nguyen TS, Duong NT (2024) Modeling of water scarcity for spatial analysis using water poverty index and fuzzy-MCDM technique. Model Earth Syst Environ 10(2):2079–2097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-023-01884-2
Raju KS, Kumar DN, Jalali A (2018) Prioritization of sub-catchments of a river basin using DEM and Fuzzy VIKOR. H2Open J 1:1–11. https://doi.org/10.2166/h2oj.2017.001
Rx N, Tian ZP, Wang JQ, Zhang HY, Wang TL (2018) Water security sustainability evaluation: Applying a multistage decision support framework in industrial region. J Clean Prod 196:1681–1704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.144
Sadeghi SH, Sharifi Moghadam E (2021) Integrated watershed management vis-a-vis water–energy–food nexus. Environ Footprints Eco-Design Prod Process 1:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0239-9_3
Sahraei R, Kanani-Sadat Y, Homayouni S, Safari A, Oubennaceur K, Chokmani K (2023) A novel hybrid GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making approach for flood susceptibility analysis in large ungauged watersheds. J Flood Risk Manag 16:12879. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12879
Salehi A, Izadikhah M (2014) A novel method to extend SAW for decision-making problems with interval data. Decision Sci Lett 3:225–236. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2013.11.001
Salvati L, Bajocco S (2011) Land sensitivity to desertification across Italy: Past, present, and future. Appl Geogr 31:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2010.04.006
Sampath VK, Radhakrishnan N (2024a) Assessment and prioritization of sub-watersheds vulnerable to soil erosion in an ungauged river basin using MOORA, COPRAS, MARCOS and MABAC Methods. J Indian Soc Remote Sensing 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-024-01942-x
Sampath VK, Radhakrishnan N (2024b) Prioritization of Sub-Watersheds Susceptible to Soil Erosion using Different Combinations of Objective Weighting and MCDM Techniques in an Ungauged River Basin. Water Resour Manage 38(9):3447–3469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03825-9
Sarkar P, Sarma US, Gayen SK (2023) Prioritization of sub-watersheds of Teesta River according to soil erosion susceptibility using multi-criteria decision-making in Sikkim and West Bengal. Arab J Geosci 16:398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11423-z
Scott CA, Hill AF, Wilson AM (2019) Pursuing water security in socio-hydrological systems. Water Secur 8:100037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasec.2019.100037
Sepehri M, Linh NTT, Pouya HN, Bahramloo R, Sadeghian J, Ghermezcheshme B, Talebi A, Peyrovan H, Thanh PN (2023) Developing a new multi-criteria decision-making for flood prioritization of sub-watersheds using concept of D numbers. Acta Geophys 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01119-z
Shih HS, Shyur HJ, Lee ES (2007) An extension of TOPSIS for group decision making. Math Comput Model 45:801–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2006.03.023
Shojaie AA, Babaie S, Sayah E, Mohammaditabar D (2018) Analysis and prioritization of green health suppliers using fuzzy ELECTRE method with a case study. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 19:39–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-017-0168-2
Skardi MJE, Afshar A, Solis SS (2013) Simulation-optimization model for non-point source pollution management in watersheds: Application of cooperative game theory. KSCE J Civ Eng 17:1232–1240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-013-0077-7
Taherdoost H, Madanchian M (2023) Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods and concepts. Encyclopedia 3:77–87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006
Tu Y, Chen K, Wang H, Li Z (2020) Regional water resources security evaluation based on a hybrid fuzzy BWM-TOPSIS method. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144987
Tu Y, Wang H, Zhou X, Shen W, Lev B (2021) Comprehensive evaluation of security, equity, and efficiency on regional water resources coordination using a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making method with different hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. J Clean Prod 310:127447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127447
Widianta MMD, Rizaldi T, Setyohadi DPS, Riskiawan HY (2018) Comparison of multi-criteria decision support methods (AHP, TOPSIS, SAW & PROMENTHEE) for employee placement. J Phys: Conf Ser 953:12116. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/953/1/012116
Yoon KP, Hwang CL (1995) Multiple attribute decision making: An introduction. Sage publications, USA
Yu X, Zhang S, Liao X, Qi X (2018) ELECTRE methods in prioritized MCDM environment. Inf Sci 424:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.09.061
Yu H, Gu X, Liu G, Fan X, Zhao Q, Zhang Q (2022) Construction of regional ecological security patterns based on multi-criteria decision making and circuit theory. Remote Sens 14:527. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030527
Zhang Y, Xu Z, Liao H (2019) Water security evaluation based on the TODIM method with probabilistic linguistic term sets. Soft Comput 23:6215–6230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3276-9
Zhou Y, Tao W, Song M (2022) Regional water resource security in China based on a new fuzzy method with combination weighting. Int J Fuzzy Syst 24:3584–3601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01298-9
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the stakeholders for their cooperation in the Gorganroud watershed.
Funding
This work is based upon research funded by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) under project No.4020845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by M Tavosi, M Vafakhah, SHR Sadeghi and SM Bateni. The first draft of the manuscript was written by M Tavosi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tavosi, M., Vafakhah, M., Sadeghi, S.H. et al. Sub-watershed Prioritization Based on Watershed Hydrological Security Using Different Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods. Water Resour Manage 39, 65–90 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03957-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-024-03957-y
Keywords
Profiles
- Mehdi Vafakhah View author profile