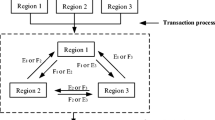
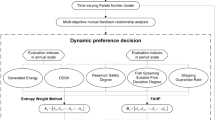
Abstract
Currently, water and land resources are treated as separate resources in allocation optimization for complex systems of water and land resources, which may have negative impacts on these water-land resource systems. In our study, an adaptive allocation model was established for a complex system of regional water and land resources using complex adaptive systems theory. The users of water and land resources were treated as adaptive agents, and the competition and synergy among various agents toward water and land resources were used as the driving forces for the evolution of the model. The model was accurately solved using a nested genetic algorithm to achieve the optimal joint allocation of regional water and land resources. A case study was conducted in the city of Kiamusze in Heilongjiang Province, and the results indicated that the evolution of the model was consistent with the actual behaviors of adaptive agents. Moreover, after the implementation of the optimized allocation results, the economic benefits in the study area were expected to increase by 3.34 %, and the comprehensive user satisfaction index regarding water increased from 0.61 to 0.73; moreover, the ecological footprint of the ecological sector increased by 5.6 %. Our results provide important guidance for achieving the sustainable use of regional water and land resources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balling RJ, Taber JT, Kirsten D, Scott W (2000) City planning with a multiobjective genetic algorithm and a pareto set scanner. Evol Des Manuf 125:237–247
Barbier EB (1989) Cash crops, food crops, and sustainability: the case of Indonesia. World Dev 17(6):879–895
Barbier EB, Burgess JC (2015) Sustainable development: an economic perspective. International Encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences (2nd Edition). 823–827
Becu N, Perez P, Walker A, Barreteau O, Le Page C (2003) Agent based simulation of a small catchment water management in northern Thailand description of the CATCHSCAPE model. Ecol Model 170(2–3):319–331
Chowdary VM, Chakraborthy D, Jeyaram A, Murthy YVNK, Sharma JR, Dadhwal VK (2013) Multi-criteria decision making approach for watershed prioritization using analytic hierarchy process technique and GIS. Water Resour Manag 27(10):3555–3571
Cobb CW, Douglas PH (1928) A theory of production. Am Econ Rev 18(Supplement):139–165
Dai CS, Long XZ, Wang B (2012) Study on utilization and protection measures of water and land resources in three river plain. China Press of Agric Sci Technol. (In Chinese)
DeRosa JK, McCaughin LK (2007) Combined systems engineering and management in the evolution of complex adaptive systems. Syst Conf 1:1–8
Folke C, Carpenter S, Elmqvist T, Gunderson L, Holling CS, Walker B (2002) Resilience and sustainable development: building adaptive capacity in a world of transformations. Ambio 31(5):437–440
Fu Q, Wang K, Ren SD (2012) Real coded multi-objective nested accelerating genetic algorithm based on complex system evolutionary optimization. Syst Eng Theory Pract 32:2718–2723 (In Chinese)
Fu Q, Gong FL, Jiang QX, Cheng K, Dong H, Ma XS (2013) Risk assessment of the city water resources system based on pansystems observation-control model of periphery. Nat Hazards 71(3):1899–1912
Geldof GD (1995) Adaptive water management: integrated water management on the edge of chaos. Water Sci Technol 32(1):7–13
Grayson RB, Doolan JM, Blake T (1994) Application of AEAM (Adaptive Environmental Assessment and Management) to water quality in the latrobe river catchment. J Environ Manag 41:245–258
Guo DH, Santos EE, Singhal A, Santos E, Zhao QH (2007) Adaptivity modeling for complex adaptive systems with application to biology. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 10:272–277
Hare M, Medugno D, Heeb J, Pahl-Wostl C (2002) An applied methodology for participatory model building of agent-based models for urban water management. SCS-European Publishing House, Germany, pp 61–66
Holland JH (1995) Hidden order: how adaptation builds complexity. The Perseus Books Group, Canada
Holland JH (1998) Emergence: from chaos to order. The Perseus Books Group, America
Huang SZ, Huang Q, Chang JX, Chen YT, Xing L, Xie YY (2015) Copulas-based drought evolution characteristics and risk evaluation in a typical arid and semi-arid region. Water Resour Manag 29(5):1489–1503
Jiang QX (2011) Land and water resources bearing capacity evaluation of three river plain and its dynamic simulation research of sustainable utilization. Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin (In Chinese)
Jin L, Huang G, Fan YR, Nie XH, Cheng GH (2012) A hybrid dynamic dual interval programming for irrigation water allocation under uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 26(5):1183–1200
Knuppe K, Pahl-Wostl C (2011) A framework for the analysis of governance structures applying to groundwater resources and the requirements for the sustainable management of associated ecosystem services. Water Resour Manag 25(13):3387–3411
Li WQ, Xie JC, Li JX (2012) Water resources allocation based on the grey theory and the improved electromagnetism-like algorithm. J Hydraul Eng 43(1447–1456):1463 (In Chinese)
Li FW, Zhao Y, Feng P, Zhang W, Qiao JL (2015) Risk assessment of groundwater and its application. Part I: risk grading based on the functional zoning of groundwater. Water Resour Manag 29(8):2697–2714
Liechti TC, Matos JP, Boillat JL, Schleiss AJ (2015) Influence of hydropower development on flow regime in the Zambezi river basin for different scenarios of environmental flows. Water Resour Manag 29:731–747
Liu DD, Wang GX, Chen XH, Liu BJ, Wang ZL (2011) Optimal water resources deployment based on chaos harmony search algorithm. Syst Eng Theory Pract 31:1378–1386 (In Chinese)
Liu J, Wang SY, Li DM (2014) The analysis of the impact of land-use changes on flood exposure of Wuhan in Yangtze River Basin, China. Water Resour Manag 28(9):2507–2522
Moiwo JP, Tao FL (2014) Evidence of land-use controlled water storage depletion in Hai River Basin, North China. Water Resour Manag 28:4733–4746
Pahl-Wostl C (2007) The implications of complexity for integrated resources management. Environ Model Softw 22(5):561–569
Pathak SD, Dills DM, Biswas G (2007) On the evolutionary dynamics of supply network topologies. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 54(4):662–672
Rammel C, Stagl S, Wilfing H (2007) Managing complex adaptive systems-a co-evolutionary perspective on natural resource management. Ecol Econ 63(1):9–21
Rasmussen LV, Rasmussen K, Reenberg A, Proud S (2012) A system dynamics approach to land use changes in agro-pastoral systems on the desert margins of sahel. Agric Syst 107:56–64
Shannon CE (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. Univ of Illinois Press
Stern DI, Common MS, Barbier EB (1996) Economic growth and environmental degradation: the environmental Kuznets curve and sustainable development. World Dev 24(7):1151–1160
Sun LN, Lu WX, Yang QC, Martín JD, Li D (2013) Ecological compensation estimation of soil and water conservation based on cost-benefit analysis. Water Resour Manag 27(8):2709–2727
Tamene L, Le QB, Vlek PLG (2014) A landscape planning and management tool for land and water resources management: an example application in northern Ethiopia. Water Resour Manag 28(2):407–424
Wackernagel M, Rees WE (1996) Our ecological footprint-reducing human impact on earth. New Society Publishera, Philadephia
Wang SY, Zhou CS (2012) Analysis of the correlation between disaster reduction engineering and output of agricultural production. J Harbin Inst Technol 44:68–73 (in Chinese)
Wang HM, Tong JP, Ma XP, Ni JJ, Niu WJ (2005) Complex Adaptive System(CAS)-based allocation and management of river basin water resources. Syst Eng Theory Pract 12:118–124 (In Chinese)
Wang HM, Tong JP, Lin C, Liu Y, Zhang XX (2007) CAS-based modeling and simulation of water rights trading. Syst Eng Theory Pract 11:164–176 (In Chinese)
Wang L, Xie JC, Zhang JL, Li JX (2011) Application of dynamic water allocation planning based on comprehensive integrated service platform. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Ed) 39(S1):170–175 (In Chinese)
Wang Q, Creaco E, Franchini M, Savić D, Kapelan Z (2015) Comparing low and high-level hybrid algorithms on the two-objective optimal design of water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 29(1):1–16
Zhao JS, Wang ZJ, Wong WB (2004) Study on the holistic model for water resources system. Sci China Ser E Technol Sci 34(S1):60–73 (In Chinese)
Zheng JK, Yu XX, Xia B, Jia GD, Pang Z, Song SM (2010) Land use pattern optimization based on eco-service value in the upper Chaobai River Basin. Trans CSAE 26:337–344 (In Chinese)
Zhou X, Yang ST, Liu XY, Liu CM, Zhao CS, Zhao HG, Zhou QW, Wang ZW (2015) Comprehensive analysis of changes to catchment slope properties in the high-sediment region of the Loess Plateau, 1978–2010. J Geogr Sci 25(4):437–450
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the following: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 51179032, 51209038, and 51279031), the Ministry of Water Resources Special Funds for Scientific Research on Public Causes (No: 201301096), the Province Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang (No: E201241), the New Century Talent Supporting Project of the Ministry of Education, the Yangtze River Scholars Support Program of Colleges and Universities in Heilongjiang Province, the Cultivation Plan of Excellent Talents in New Century of Colleges in Heilongjiang Province (No: 1155-NCET-004), the Heilongjiang Province Water Conservancy Science and Technology project (No: 201318), and the Excellent Youth Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (JC201402).
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
1 Optimized joint allocation of regional water and land resources was achieved based on the theory of a complex adaptive system, and the application scope of the complex adaptive system theory was expanded.
2 The amount of information carried by the adaptive agent was measured using information entropy in a uniform manner.
3 The competition and synergy toward resources of agents of all levels in the complex system of water and land resources were used as the driving force of the model evolution.
4 An accurate solution of the multi-dimensional model was derived using a nested genetic algorithm.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, K., Fu, Q., Chen, X. et al. Adaptive Allocation Modeling for a Complex System of Regional Water and Land Resources Based on Information Entropy and its Application. Water Resour Manage 29, 4977–4993 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1099-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1099-3