Abstract
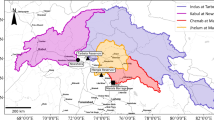
The applicability of fuzzy genetic (FG) approach in modeling reference evapotranspiration (ET0) is investigated in this study. Daily solar radiation, air temperature, relative humidity and wind speed data of two stations, Isparta and Antalya, in Mediterranean region of Turkey, are used as inputs to the FG models to estimate ET0 obtained using the FAO-56 Penman–Monteith equation. The FG estimates are compared with those of the artificial neural networks (ANN). Root mean-squared error, mean absolute error and determination coefficient statistics were used as comparison criteria for the evaluation of the models’ accuracies. It was found that the FG models generally performed better than the ANN models in modeling ET0 of Mediterranean region of Turkey.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abghari H, Ahmadi H, Besharat S, Rezaverdinejad V (2012) Prediction of daily pan evaporation using wavelet neural networks. Water Resour Manage 26:3639–3652
Ahmed JA, Sarma AK (2005) Genetic algorithm for optimal operating policy of a multipurpose reservoir. Water Resour Manage 19:145–161
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration guidelines for computing crop water requirements, FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper No. 56, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Brutsaert WH (1982) Evaporation into the atmosphere. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht
Cobaner M (2011) Evapotranspiration estimation by two different neuro-fuzzy inference systems. J Hydrol 398:292–302
Demirtas C, Buyukcangaz H, Yazgan S, Candogan BN (2007) Evaluation of evapotranspiration estimation methods for sweet cherry trees (Prunus avium) in Sub-humid Climate. Pak J Biol Sci 10(3):462–469
Dinpashoh Y, Jhajharia D, Fakheri-Fard A, Singh VP, Kahya E (2011) Trends in reference evapotranspiration over Iran. J Hydrol 399:422–433
Gavilan P, Estevaz J, Berengena J (2008) Comparison of standardized reference evapotranspiration equations in Southern Spain. J Irrig Drain Eng 134(1):1–12
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search: optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Haykin S (1998) Neural networks - a comprehensive foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 26–32
Hecht-Nielsen R (1991) Neurocomputing. Addison-Wesley Publ Co., New York
Jain SK, Nayak PC, Sudheer KP (2008) Models for estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural networks, and their physical interpretation. Hydrol Process 22:2225–2234
Jensen ME, Burman RD, Allen RG (1990) Evapotranspiration and irrigation water requirements. ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practices No. 70., ASCE, New York, NY, 360 pp
Jhajharia D, Ali MI, Deb Barma S, Durbude DG, Kumar R (2009) Assessing reference evapotranspiration by temperature-based methods for humid regions of Assam. J Indian Water Resour Soc 29(2):1–8
Jhajharia D, Dinpashoh Y, Kahya E, Singh VP, Fakheri-Fard A (2012) Trends in reference evapotranspiration in the humid region of northeast India. Hydrol Process 26:421–435
Keskin ME, Terzi O, Taylan D (2004) Fuzzy logic model approaches to daily pan evaporation estimation in western Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 49(6):1001–1010
Khoob AR (2008a) Comparative study of Hargreaves’s and artificial neural network’s methodologies in estimating reference evapotranspiration in a semiarid environment. Irrig Sci 26(3):253–259
Khoob AR (2008b) Artificial neural network estimation of reference evapotranspiration from pan evaporation in a semi-arid environment. Irrig Sci 27(1):35–39
Kim S, Kim HS (2008) Neural networks and genetic algorithm approach for nonlinear evaporation and evapotranspiration modelling. J Hydrol 351:299–317
Kim S, Shiri J, Kisi O (2012) Pan evaporation modeling using neural computing approach for different climatic zones. Water Resour Manage 26(11):3231–3249
Kim S, Shiri J, Kisi O, Singh VP (2013) Estimating daily pan evaporation using different data-driven methods and lag-time patterns. Water Resour Manage 27(7):2267–2286
Kisi O, Uncuoglu E (2005) Comparison of three backpropagation training algorithms for two case studies. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 12:443–450
Kisi O (2006a) Evapotranspiration estimation using feed-forward neural networks. Nord Hydrol 37(3):247–260
Kisi O (2006b) Generalized regression neural networks for evapotranspiration modelling. Hydrol Sci J 51(6):1092–1105
Kisi O (2007a) Evapotranspiration modelling from climatic data using a neural computing technique. Hydrol Process 21:1925–1934
Kisi O (2007b) Streamflow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms. ASCE J Hydrol Eng 12(5):532–539
Kisi O (2008) The potential of different ANN techniques in evapotranspiration modelling. Hydrol Process 22:1449–2460
Kisi O, Cimen M (2009) Evapotranspiration modelling using support vector machines. Hydrol Sci J 54(5):918–928
Kisi O, Ozturk O (2007) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy computing technique for evapotranspiration estimation. J Irrig Drain Eng 133(4):368–379
Kisi O, Yildirim G (2005a) Discussion of ‘estimating actual evapotranspiration from limited climatic data using neural computing technique’ by K.P. Sudheer; A.K. Gosain; and K.S. Ramasastri. J Irrig Drain Eng 131(2):219–220
Kisi O, Yildirim G (2005b) Discussion of ‘forecasting of reference evapotranspiration by artificial neural networks’ by S. Trajkovic; B. Todorovic; and M. Stankovic. J Irrig Drain Eng 131(4):390–391
Kiszka JB, Kochanskia ME, Sliwinska DS (1985a) The influence of some fuzzy implication operators on the accuracy of fuzzy model, part I. Fuzzy Set and Syst 15:111–128
Kiszka JB, Kochanskia ME, Sliwinska DS (1985b) The influence of some fuzzy implication operators on the accuracy of fuzzy model, part II. Fuzzy Set and Syst 15:223–240
Kosko B (1993) Fuzzy thinking: the new science of fuzzy logic. Hyperion, New York
Kumar M, Bandyopadhyay A, Rahguwanshi NS, Singh R (2008) Comparative study of conventional and artificial neural network-based ETo estimation models. Irrig Sci 26(6):531–545
Kumar M, Raghuwanshi NS, Singh R (2009) Development and validation of GANN model for evapotranspiration estimation. J Hydrol Eng 14(2):131–140
Kumar M, Raghuwanshi NS, Singh R (2011) Artificial neural networks approach in evapotranspiration modeling: a review. Irrig Sci 29:11–25
Landeras G, Ortiz-Barredo A, Lopez JJ (2009) Forecasting weekly evapotranspiration with ARIMA and artificial neural network models. J Irrig Drain Eng 135(3):323–334
Marti P, Manzano J, Royuela A (2011a) Assessment of a 4-input artificial neural network for ETo estimation through data set scanning procedures. Irrig Sci 29:181–195
Marti P, Gonzalez-Altozano P, Gasque M (2011b) Reference evapotranspiration estimation without local climatic data. Irrig Sci 29:479–495
McVicar TR, Roderick ML, Donohue RJ, Li LT, Van Niel TG, Thomas A, Grieser J, Jhajharia D, Himri Y, Mahowald NM, Mescherskaya AV, Kruger AC, Rehman S, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Global review and synthesis of trends in observed terrestrial near-surface wind speeds: implications for evaporation. J Hydrol 416–417:182–205
Naoum S, Tsanis IK (2003) Hydroinformatics in evapotranspiration estimation. Environ Model Softw 18:261–271
Perugu M, Singam AJ, Kamasani CSR (2013) Multiple linear correlation analysis of daily reference evapotranspiration. Water Resour Manag 27:1489–1500
Preis A, Ostfeld A (2008) Multiobjective contaminant sensor network design for water distribution systems. J Water Resour Plann Manage 134(4):366–377
Russel SO, Campbell PF (1996) Reservoir operating rules with fuzzy programming. J Water Resour Plann Manage ASCE 122(3):165–170
Sanikhani H, Kisi O, Nikpour MN, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Estimation of daily pan evaporation using two different adaptive neuro-fuzzy computing techniques. Water Resour Manag 26:4347–4365
Scheffé H (1959) The analysis of variance. Wiley, New York
Şen Z (1998) Fuzzy algorithm for estimation of solar irridation from sunshine duration, Sol. Energy 63(1):39–49
Smith M, Allen R, Pereira L (1997) Revised FAO methodology for crop water requirements. Land and Water Development Division, FAO, Rome
Sudheer KP, Gosain AK, Ramasastri KS (2003) Estimating actual evapotranspiration from limited climatic data using neural computing technique. J Irrig Drain Eng 129(3):214–218
Trajkovic S (2005) Temperature-based approaches for estimating reference evapotranspiration. J Irrig Drain Eng 131(4):316–323
Trajkovic S, Todorovic B, Stankovic M (2003) Forecasting reference evapotranspiration by artificial neural networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 129(6):454–457
Wang QJ (1991) The genetic algorithm and its application to calibrating conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour Res 27(9):2467–2471
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Information and Control 8(3):38–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kisi, O., Cengiz, T.M. Fuzzy Genetic Approach for Estimating Reference Evapotranspiration of Turkey: Mediterranean Region. Water Resour Manage 27, 3541–3553 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0363-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0363-7